FDA’s First Potential TIL Therapy Review Delayed
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
FDA’s First Potential TIL Therapy Review Delayed: How to Understand FDA’s “Resource Constraints”?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
FDA’s First Potential TIL Therapy Review Delayed: How to Understand FDA’s “Resource Constraints”?
On September 14th, Iovance Biotherapeutics announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will need more time to complete the priority review of the biologics license application (BLA) for lifileucel, a tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy, due to resource constraints. This BLA seeks to expedite approval for the treatment of advanced melanoma patients.
The FDA has extended the target action date, as per the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA), to February 24, 2024, but has agreed to collaborate with Iovance to expedite the remaining review work in pursuit of an earlier approval date.
The entire BLA process remains in the priority review stage, and recent updates have been positive. Iovance stated that the FDA has reaffirmed that there are no significant review issues and no plans for an advisory committee meeting. Furthermore, all pre-approval inspections of clinical research institutions, internal, and external manufacturing and testing facilities have been successfully completed. The FDA has also been involved in the TILVANCE-301 pivotal trial for advanced melanoma and has not expressed any concerns about the trial’s progress.
On this topic, Endpoints News interviewed Dr. Du Xin, former FDA senior review officer and CEO of Egrin Pharma. In his view, it’s crucial to accurately understand the FDA’s “resource constraints.”
Firstly, the FDA has postponed the scheduled PDUFA action date from November 25 to February 24, 2024, which is exactly three months within the FDA’s normal time frame for delaying approvals. This demonstrates that the FDA has not revoked the priority review status of this BLA. If the priority review were canceled, the review time would extend from six months to ten months, specifically to March 24, 2023.
Secondly, the FDA communicated this decision to the applicant during a late-stage review meeting. Late-stage review meetings are a critical part of the BLA review process and typically mark the moment when the FDA makes its final decisions.
Lastly, the FDA cited “insufficient resources” as the reason for the delay, specifically for reviewing the applicant’s responses to information required for a late-stage review meeting scheduled for September 11. This means that the content of this response exceeded the FDA’s capacity to complete the review within the original resources and timeframe.
Instances of the FDA using “resource constraints” as a reason for delaying the review endpoint are not uncommon, especially in late-stage reviews when the applicant provides new or excessive information. This reason is both reasonable and acceptable to the applicants. Behind the FDA’s use of “resource constraints,” there could be two reasons: either the FDA genuinely lacks the manpower to complete the review within the original timeline, or the FDA believes that the BLA from the applicant has significant issues or deficiencies that require more time to address and resolve.

Based on Iovance’s news, where the FDA has indicated no significant issues during the review, Dr. Du Xin believes that this delay in the review endpoint may be attributed to the responses provided by the applicant in the late-stage review.
Despite holding both priority review and regenerative medicine advanced therapy (RMAT) designations, along with successful pre-approval inspections, Iovance’s review endpoint has been delayed by three months. While it may not have a significant impact on the final approval, it does come with some losses. This incident serves as a valuable lesson for those preparing and submitting BLAs: familiarity with the review process, key milestones, and the volume and quality of supplementary information is crucial to ensure a smooth BLA submission and timely completion.
Iovance’s interim President and CEO, Frederick Vogt, remains confident in the approval of lifileucel. As a personalized therapy, lifileucel is intended for advanced melanoma patients who have previously received anti-PD-1/L1 therapy and targeted therapy or have experienced disease progression thereafter. Currently, there is no FDA-approved therapy for this treatment scenario.
This means that if lifileucel is approved, it will be the first and only TIL therapy for advanced melanoma patients, as well as the first one-time cell therapy for solid tumor cancers.
Iovance had initially planned to submit the BLA for lifileucel in 2020. However, in a meeting held in October 2019, Iovance failed to reach an agreement with the FDA regarding the efficacy analysis required for lifileucel’s treatment of metastatic melanoma. As a result, the marketing application for Lifileucel was postponed from the end of 2020 to 2021.
In May 2021, the FDA requested additional data on the efficacy analysis of lifileucel to ensure that each batch of TIL products meets the standards. This further delayed the BLA submission for lifileucel to 2022, and the then-CEO Maria Fardis also resigned.
In May 2023, the FDA accepted the BLA for lifileucel under priority review and had previously granted the RMAT designation for the treatment of advanced melanoma with lifileucel.
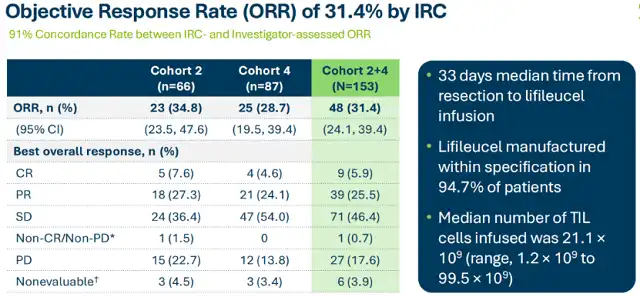
The lifileucel BLA received support from the positive data of the C-144-01 clinical trial. This trial targeted advanced melanoma patients who had previously received anti-PD-1/L1 therapy and targeted therapy or experienced progression. In cohort 2, the objective response rate (ORR) was 34.8%, with a median duration of response (mDOR) yet to be reached; in cohort 4, ORR was 28.7%, with an mDOR of 10.4 months; the combined ORR for cohorts 2 and 4 was 31.4%, with mDOR yet to be reached.
If lifileucel receives accelerated approval, the randomized phase III TILVANCE-301 trial for first-line advanced melanoma could serve as confirmatory research to support full approval. It is expected that the TILVANCE-301 trial will proceed smoothly upon approval.
In addition to lifileucel, Iovance’s development of the second-generation TIL therapy LN-145 has also made significant progress recently. On July 10th, Iovance revealed that it had received positive regulatory feedback during a Type B phase III pre-clinical meeting, indicating that the design of the IOV-LUN-202 trial might be accepted for accelerating the approval of LN-145 TIL therapy as a PD-1 antibody for second-line treatment of advanced (unresectable or metastatic) non-small cell lung cancer.
On July 13th, Iovance completed a $172.5 million fundraising to support future commercialization efforts and advance clinical development and pipeline.
The antibody industry has experienced rapid and significant development over the past few decades, becoming a rapidly growing and highly regarded field in the biopharmaceutical sector. Since the approval of the first monoclonal antibody drug (Muromonab-CD3) in the 1980s, many antibody drugs have been approved for the treatment of various diseases, including cancer, immunological disorders, and infectious diseases. There are already dozens of successful antibody drugs on the market, with more candidates in clinical development and research, indicating that more new drugs are expected to be launched in the future.
Nowaday, in addition to traditional monoclonal antibodies, a variety of new antibody technologies are continuously being developed, including bispecific antibodies, polyclonal antibodies, humanized antibodies, recombinant antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, and more. These new technologies provide antibody drugs with higher specificity, affinity, stability, and manufacturability, expanding their applications in the field of medicine.
The world first TIL cell therapy targeting advanced melanoma is coming soon
Potentially the first TIL therapy: The disease control rate of 79.3%!
Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes ( TILs ) in tumor immunotherapy
FDA’s First Potential TIL Therapy Review Delayed: How to Understand FDA’s “Resource Constraints”?
(source:internetdPqvTZ6-Ml27sLV2ULblrA, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



