Anti-PD-1 response and drug resistance in advanced renal cell carcinoma
- Oregon Reverses Course: From Decriminalization to Recriminalization of Drug Possession
- Why Lecanemab’s Adoption Faces an Uphill Battle in US?
- Yogurt and High LDL Cholesterol: Can You Still Enjoy It?
- WHO Releases Global Influenza Vaccine Market Study in 2024
- HIV Infections Linked to Unlicensed Spa’s Vampire Facial Treatments
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
Cancer Cell: Determinants of anti-PD-1 response and drug resistance in advanced renal cell carcinoma
- Was COVID virus leaked from the Chinese WIV lab?
- HIV Cure Research: New Study Links Viral DNA Levels to Spontaneous Control
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Cancer Cell: Determinants of anti-PD-1 response and drug resistance in advanced renal cell carcinoma
Renal clear cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most common type of kidney cancer, accounting for 70%-80% of kidney cancers, and the incidence is increasing worldwide.
ccRCC is one of the most severe types of solid tumors with immune infiltration. Compared with other cancers, high immune infiltration is associated with poor prognosis after nephrectomy.
In patients who responded to Atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody, T drug) and Nivolumab (anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, O drug) treatment, the proportion of lymphocytes was significantly higher.
However, cross-validation of these features as predictive biomarkers has produced inconsistent results.
Recently, a research team from the Francis Crick Institute in the United Kingdom and the Cancer Institute of University College London jointly published a research paper on Cancer Cell entitled: Determinants of anti-PD-1 response and resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma .
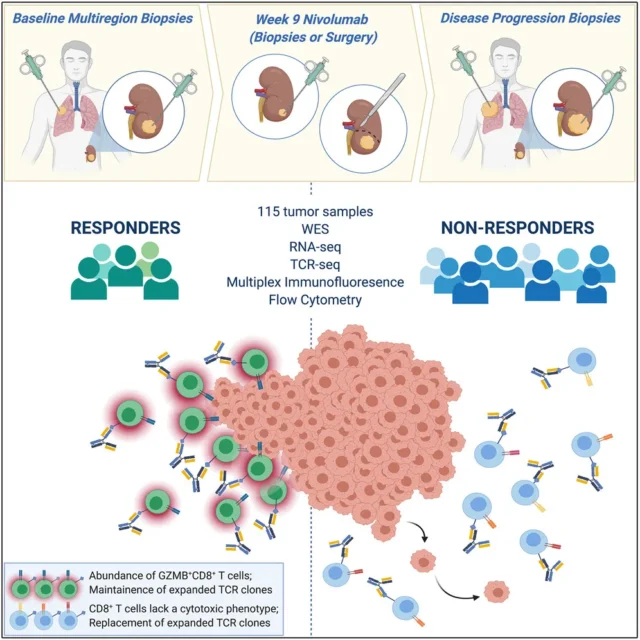
ADAPTeR (NCT02446860) is a phase II, single-arm, open-label study of Nivolumab in the treatment of patients with metastatic ccRCC. The patient’s primary and/or metastatic sites were multi-regional at baseline, at the 9th week, at the time of surgery, and when the disease progressed. Tumor sampling. The main purpose of ADAPTeR is to evaluate the molecular and tumor immune microenvironment (TME) characteristics throughout the treatment process .
Through the ADAPTeR cohort, the research team found that the number of amplified TCR clones in Nivolumab responders before treatment increased significantly. After treatment, maintaining a highly similar TCR cluster can predict the response. Nivolumab-bound CD8+ T cells were amplified and expressed GZMK/B. It shows that Nivolumab promotes the maintenance and replacement of previously expanded T cell clones, but only maintenance is related to the response, so maintaining and enhancing the pre-existing response is a key factor in the anti-PD-1 mode of action .
First, the research team performed whole exome and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) . They found that there are 10 human endogenous retrovirus (HERV) genes and 12 long terminal repeat (LTR) elements that distinguish responders from non-responders. Importantly, almost all of these genes are mainly expressed in non-responders before treatment, indicating that HERV and LTR elements that are highly specific to ccRCC are overexpressed before treatment in non-responders, and are related to anti-tumor immune responses and anti-PD- 1 Reaction defect is related.

Further analysis showed that compared with non-responders, tumors from responders had significantly higher levels of T cells before and after treatment, and the expression of CD3E, CD8A, GZMB, and TCF7 were also higher. “Immune activation” and “TCR signaling” pathways are enriched in responders, but not in non-responders.
At any point in time, the research team observed no difference in the number of T cells or the total expression of PD-1 among the responders. The GZMB expression levels of responders and non-responders before treatment were lower. However, after treatment (9th week) , both overall and CD8+ T cell-specific GZMB expression increased significantly.

Whether tumor-specific T cells activated by immune checkpoint inhibitors are present in the tumor or whether they are replaced by new T cell clones recruited by TME is still under debate. The research team sequenced the β-chain TCR sequences of 14 patients before and after treatment, including 64 tumors and 29 peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples. In general, compared with PBMC, the TCR in tumor samples is more clonal. The baseline intratumoral TCR clonality of responders was higher than that of non-responders, but the difference was not significant after treatment. The maintenance of previously expanded TCR clones supports continuous antigen-driven stimulation of pre-existing T cells in responders, and Nivolumab binds to pre-expanded CD8 + T cells and induces a cytotoxic phenotype in responders.

In summary, the study revealed the characteristics of ccRCC’s anti-PD-1 response and drug resistance, and identified tumor-specific T cells with cytotoxic characteristics, which brought hope to the development of adoptive cell therapy for this cancer. At the same time, many The omics analysis process provides an important reference for ccRCC’s future research on immune tumor biomarkers.
Paper link:
https://www.cell.com/cancer-cell/fulltext/S1535-6108(21)00543-2
Cancer Cell: Determinants of anti-PD-1 response and drug resistance in advanced renal cell carcinoma
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.