What is the mechanism of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune response?
- WHO Releases Global Influenza Vaccine Market Study in 2024
- HIV Infections Linked to Unlicensed Spa’s Vampire Facial Treatments
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
What is the mechanism of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune response?
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
What is the mechanism of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune response?
In December 2020, the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine ( BNT162b2 ) developed by Pfizer /BioNTech received emergency use authorization from the US FDA , becoming the first approved mRNA vaccine in history.
In Phase III clinical trials, the mRNA vaccine showed up to 95% protection against the novel coronavirus pneumonia ( COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection . However, despite the widespread use of BNT162b2, the mechanism by which it stimulates protective immunity remains largely unknown.
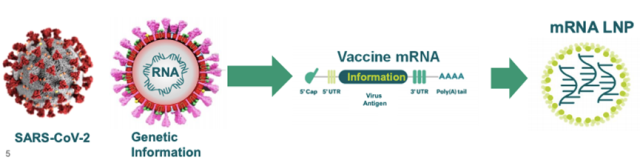
On March 14, 2022, the team of Professor Bali Pulendran , Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Stanford University School of Medicine, USA, published a research paper titled: Mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity to the Pfizer-BioNTechBNT162b2 vaccine online in the journal Nature Immunology .
The research team analyzed the innate and adaptive immune responses after vaccination with BNT162b2 in mice and found that the immunization stimulated potent antibody and antigen-specific T cell responses and significantly enhanced the innate immune response after secondary immunization , mRNA Vaccine-mediated protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection is mainly mediated by humoral immunity, whereas cellular immunity is effective in clearing the infection. These findings provide new insights into the immune responses induced by mRNA vaccines in vivo, which can be used to guide and improve future vaccine designs.

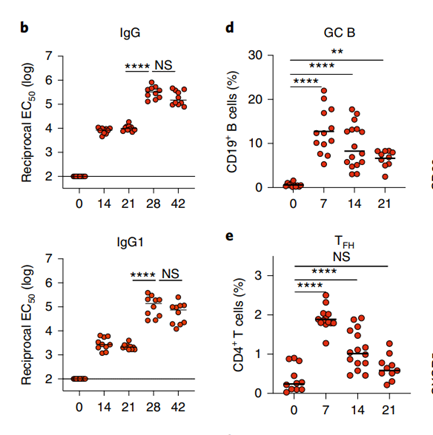
BNT162b2 immune stimulates strong germinal center response
To evaluate the immune response to BNT162b2, the researchers immunized mice with the BNT162b2 vaccine intramuscularly. Anti-spike-binding IgG responses were significantly increased, while secondary immunizations increased responses more than tenfold.
The researchers examined the responses of germinal center (GC)B cells and TFH cells, as well as plasma cells. BNT162b2 immunization induceda significant increase in the number(GC)Collectively, these data demonstrate potent stimulation of humoral immune responses by BNT162b2.
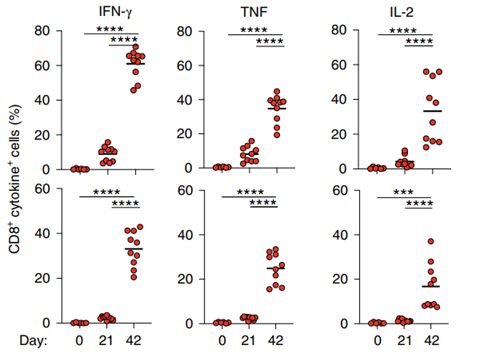
BNT162b2 vaccine induces T cell responses
The researchers initiated an immune boosting strategy, measuring antigen-specific T cell responses in the spleen and lung .
Antigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses detected in both tissues in a single immunization. After the second immunization, the frequency of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells increased significantly.
Specific CD8+ T cells secreting IFN-γ, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-2 were strongly induced after stimulation with overlapping peptide pools in vitro.
Next, the researchers analyzed serum cytokine responses. BNT162b2 immunization induced the release of many cytokines, including MCP1, MIP1b, IL-6 and CXCL10, as well as interferon-γ. These data demonstrate that the BNT162b2 vaccine induces a strong T cell response.
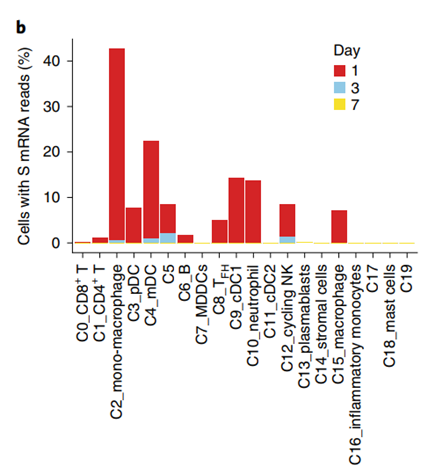
Uptake of mRNA by lymph node dendritic cells and macrophages
Many properties of LNP-mRNA vaccines, including LNP size, pKa of ionizable lipids, and lipid gradients, affect the tissue and cell specificity of mRNA vaccines .
Using single-cell RNA-sequencing data, the scientists studied cells in the draining lymph node (dLN) that contained spike mRNA.
It was observed that the expression level of spike mRNA was high on day 1 and dropped sharply by day 3. Reads were mainly restricted to monocytes/macrophages and mDCs. Cell quantification with at least one read per cell revealed that, at day 1, 40% of monocytes/macrophages and 20% of mDCs contained spike mRNA. The frequency of these cells increased after seeding.
Finally, the researchers analyzed gene expression profiles associated with spike mRNA signaling in macrophages and mDCs. In both cell clusters, spike mRNA signaling was closely associated with interferon-related and innate immune response-related BTMs, including type I interferon responses.
BNT162b2 stimulates CD8+ T cell responses via the MDA5-IFN-α axis
TLRs are the most studied sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns. TLR3 and TLR7 recognize double-stranded and single-stranded RNA, respectively. Therefore, the researchers first tested whether the loss of these receptors results in a diminished immune response to BNT162b2.
However, immunization of TLR3-deficient or TLR7-deficient mice did not result in a reduction in antibody or T-cell responses, suggesting that they are not the primary sensors of BNT162b2 in vivo.
The RIG-I-like receptor family of proteins senses cytoplasmic RNA and is a second family sensor of BNT162b2.
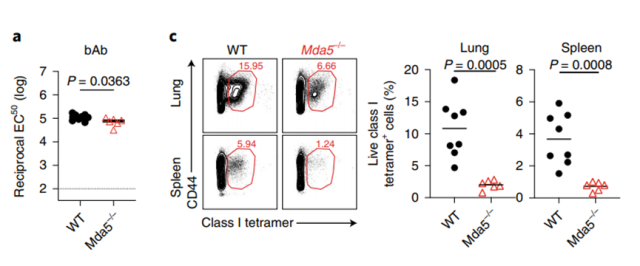
To assess whether RIG-I-like receptors are involved in mRNA recognition, the researchers immunized MDA5-deficient mice.
Antibody responses did not decrease. Interestingly, the frequency of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells and the number of class I tetramer-specific CD8+ T cells and IFN-γ-producing CD8+ T cells were significantly reduced in MDA5-deficient mice after primary and secondary immunizations Prove it.
This suggests that MDA5 induction by BNT162b2 is critical for the induction of specific CD8+ T cell responses. In addition, the frequency of IFN-γ-secreting spike-specific T cells was significantly but incompletely downregulated.
Collectively, these data suggest that MDA5-sensing BNT162b2 induces the expression of IFN-α and that IFNAR1 stimulates the expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells, thereby promoting the massive expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells.
In conclusion, the researchers analyzed innate and adaptive immune responses to BNT162b2 in mice and found that immunization stimulated potent antibody and antigen-specific T cell responses and significantly enhanced innate immune responses following secondary immunization.
Analysis of knockout mice showed that induction of antibody and T-cell responses to BNT162b2 was independent of Toll-like receptor signaling, inflammasome activation, or necrosis or pyroptosis cell death pathway.
In contrast, BNT162b2-induced CD8+ T cell responses were dependent on type I interferon-dependent MDA5 signaling. These results provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms by which the BNT162b2 vaccine stimulates immune responses .
Reference :
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-022-01163-9
What is the mechanism of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune response?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.