How does the cyano (-CN) structure improve the activity of drug molecules?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
How does the cyano (-CN) structure improve the activity of drug molecules?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
How does the cyano (-CN) structure improve the activity of drug molecules?
Cyano groups are very common in drug discovery. At present, more than 50 different cyano-containing small molecule drugs have been developed.
In classic medicinal chemistry, cyano groups are generally considered to be the biological electrons of carbonyl, hydroxyl, carboxyl and halogen atoms. Isometric body.
However, there is a lack of in-depth understanding of the structure and energy properties of cyano groups in protein receptor-ligand interactions.
The Huang Niu research group of the Beijing Institute of Life Sciences investigated the Protein Data Bank and ChEMBL database in 2018, reviewed the protein receptor-interaction with nitrogen-containing compound ligands, and discussed the cyano group’s ability to improve the affinity of the compound with the target. Various roles.
▉ Content foreword

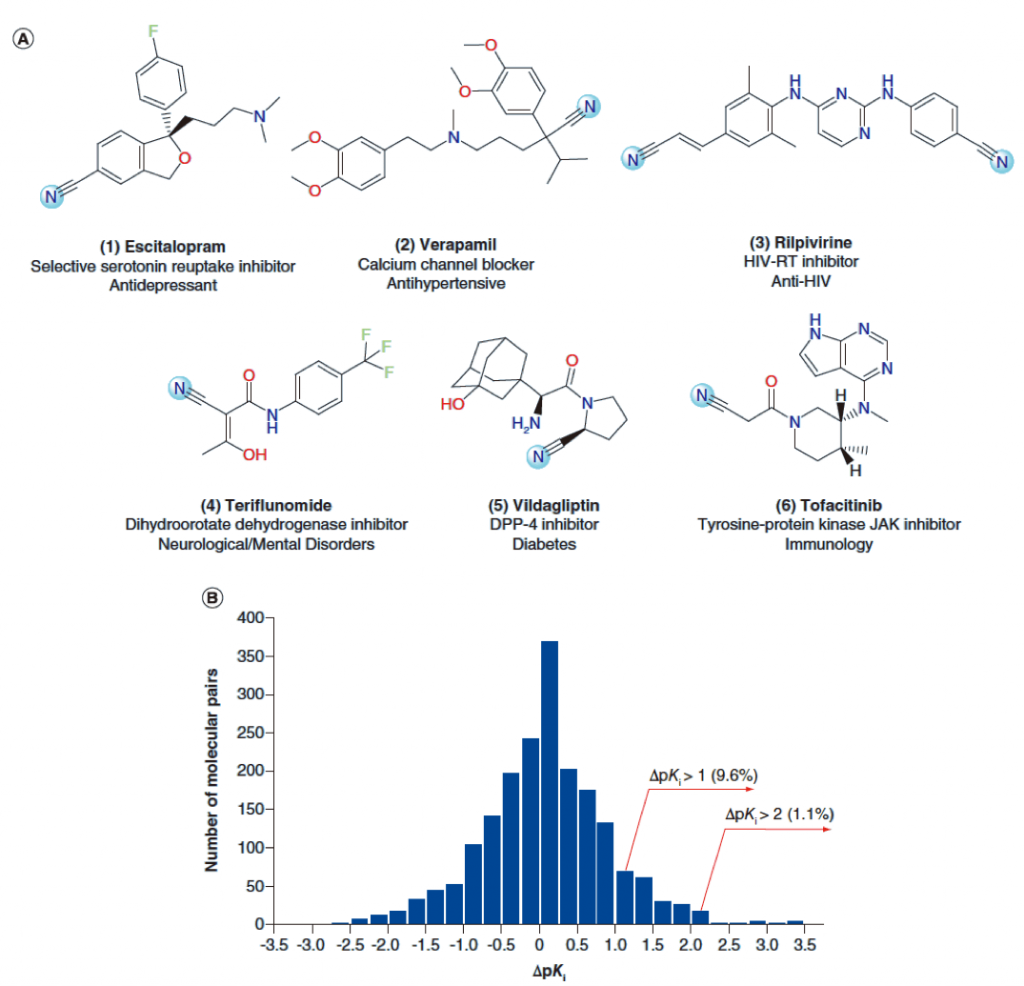
Approximately 2.4% of the 2,327 marketed small molecule drugs included in the DrugBank database contain cyano functional groups. The best-selling drugs containing cyano include escitalopram, verapamil, and ripavirin (Figure A below).
The author analyzed the ChEMBL database 1961 on the compound by MMP (matched molecular pair) method, and evaluated the effect of cyano substitution on the biological activity of the compound (Figure B below).
In most cases, cyano substitution has little effect on activity adjustment; 9.6% of the activity can be increased by 10 times (deltpK i >1); only 1.1% of the activity can be increased by more than 100 times.
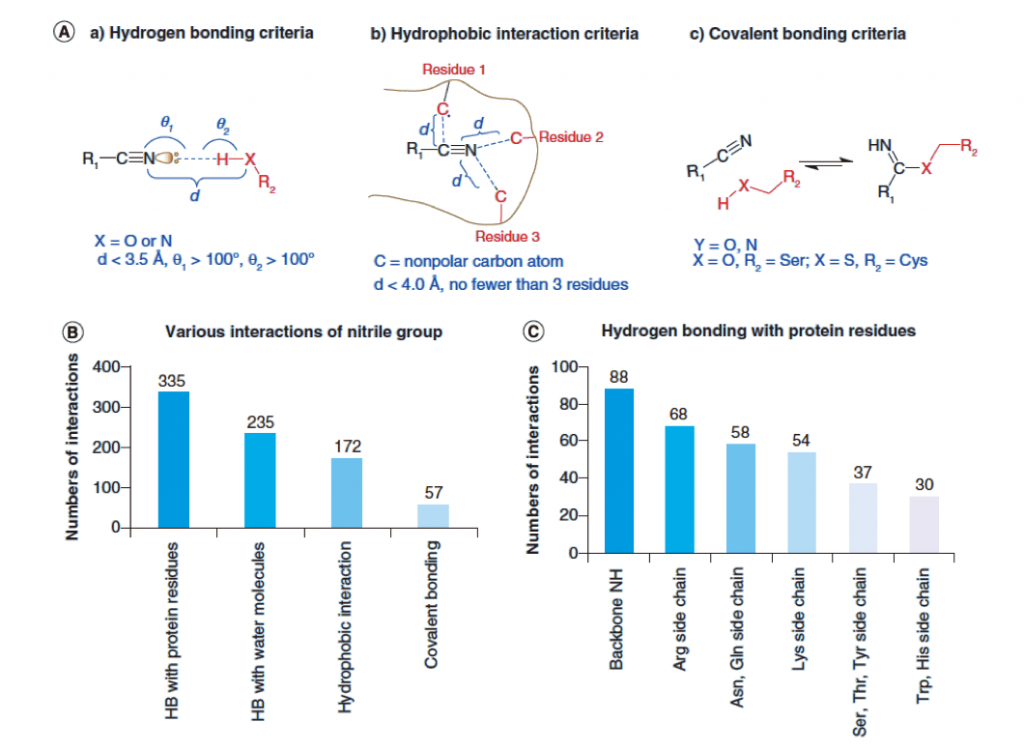
The author further analyzed the PDB (2018/5) database and retrieved a total of 949 cyano-containing eutectic compounds, including 751 cyano-containing small molecule compounds. Summarize the three main types of interactions in which cyano groups participate in the above figure (below):
1. The cyano N atom contains a lone pair of electrons, which can act as a hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) to form hydrogen bonds, and form hydrogen bonds with the backbone NH and the side chains of Arg, Asn, Gln, and Lys more frequently;
2. Polar C atoms form hydrophobic interaction;
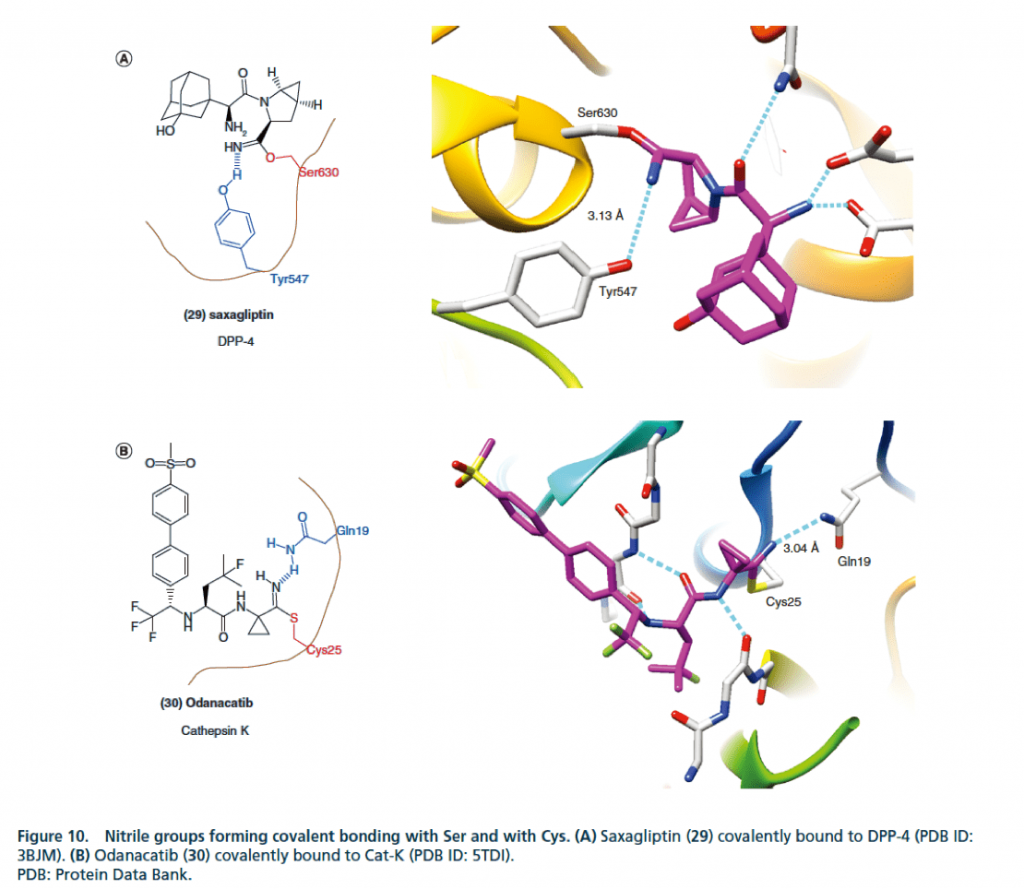
3. Form covalent bonds with Ser and Cys.
▉ Illustration of an example of hydrogen bond formation with backbone NH after cyano substitution to enhance activity
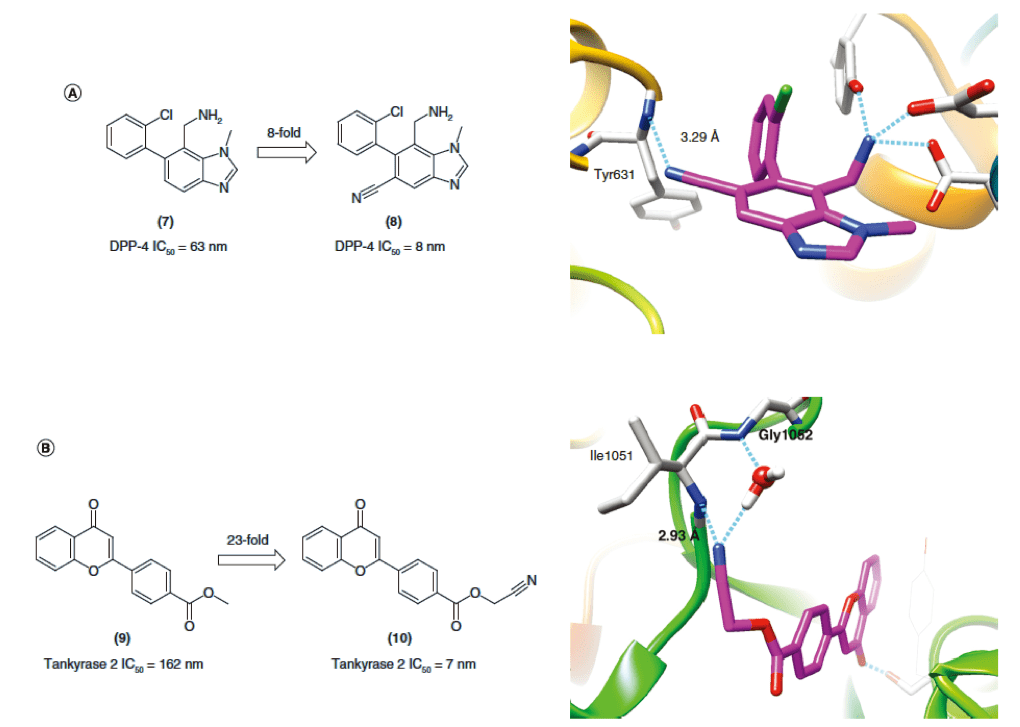
The cyano group interacts with the NHs group.
(A) On the left, the cyano group in the DPP-4 inhibitor replaces the H group to enhance the binding affinity; on the right, the eutectic structure of 8 is combined with DPP-4.
(B) In the left picture, in tankyrase inhibitors, the binding affinity of the cyano group is increased after the H group is substituted; the right picture is the co-crystal structure of 10 bound totankyrase 2.
The cyan dotted line indicates the hydrogen bond. The text in the figure below does not introduce too much. It can be seen that the English introduction below the picture is similar in general to this one (enhanced activity).
▉ Illustration of an example of hydrogen bond formation with Arg side chain after cyano substitution to enhance activity
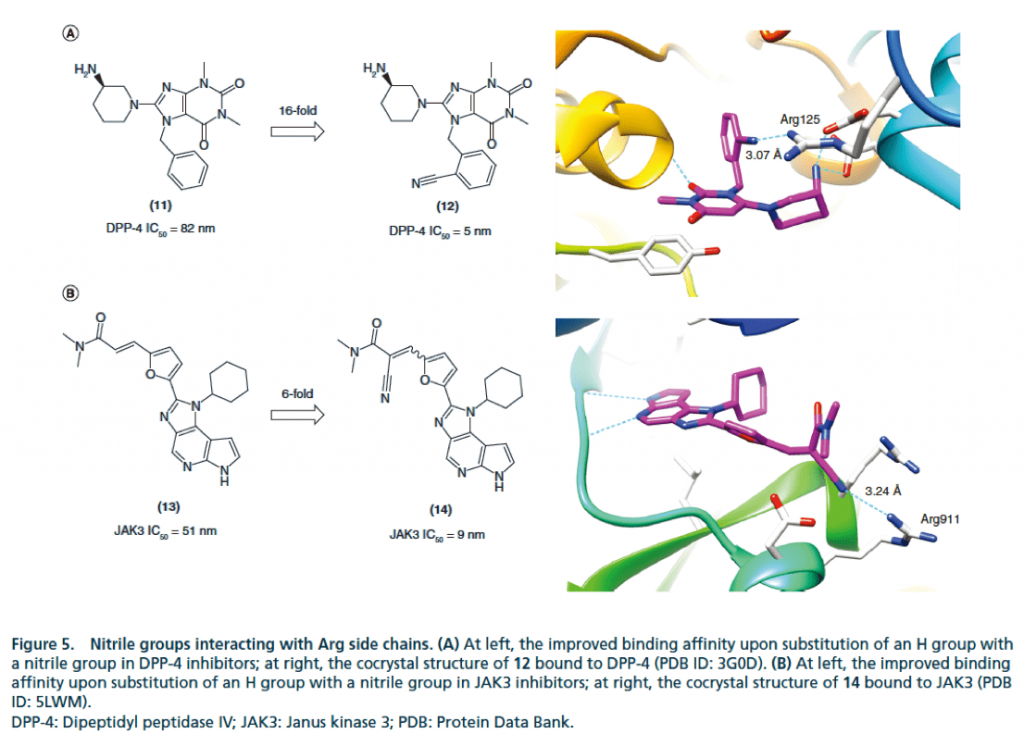
▉ Example illustration of hydrogen bond formation with Asn side chain after cyano substitution to enhance activity
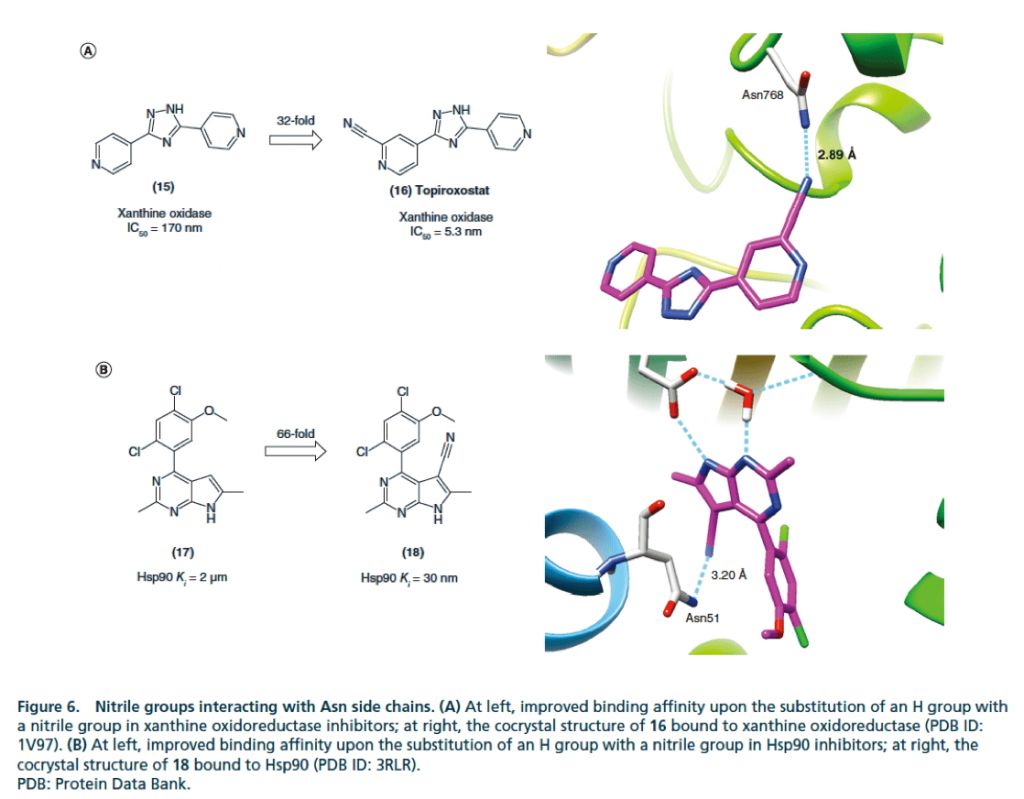
▉ Illustration of an example of hydrogen bond formation with Lys side chain after cyano substitution to enhance activity
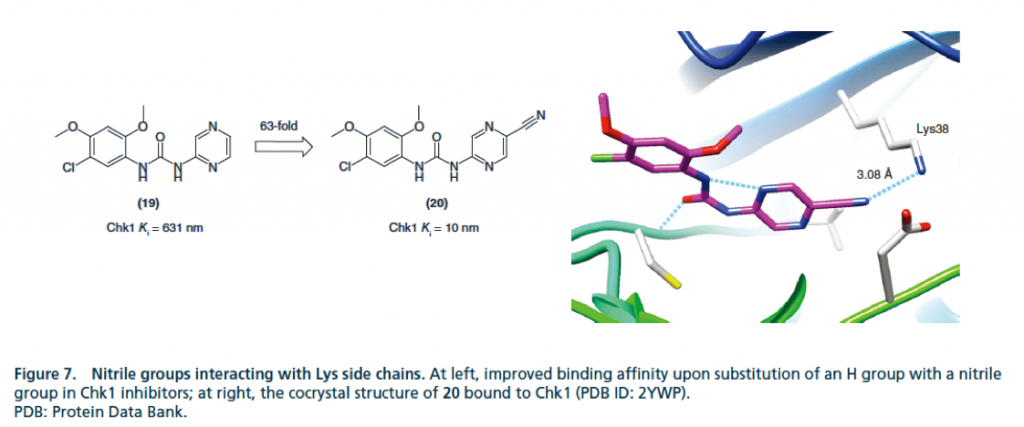
▉ Example diagram of cyano group forming hydrogen bond to enhance activity by bridging water and protein
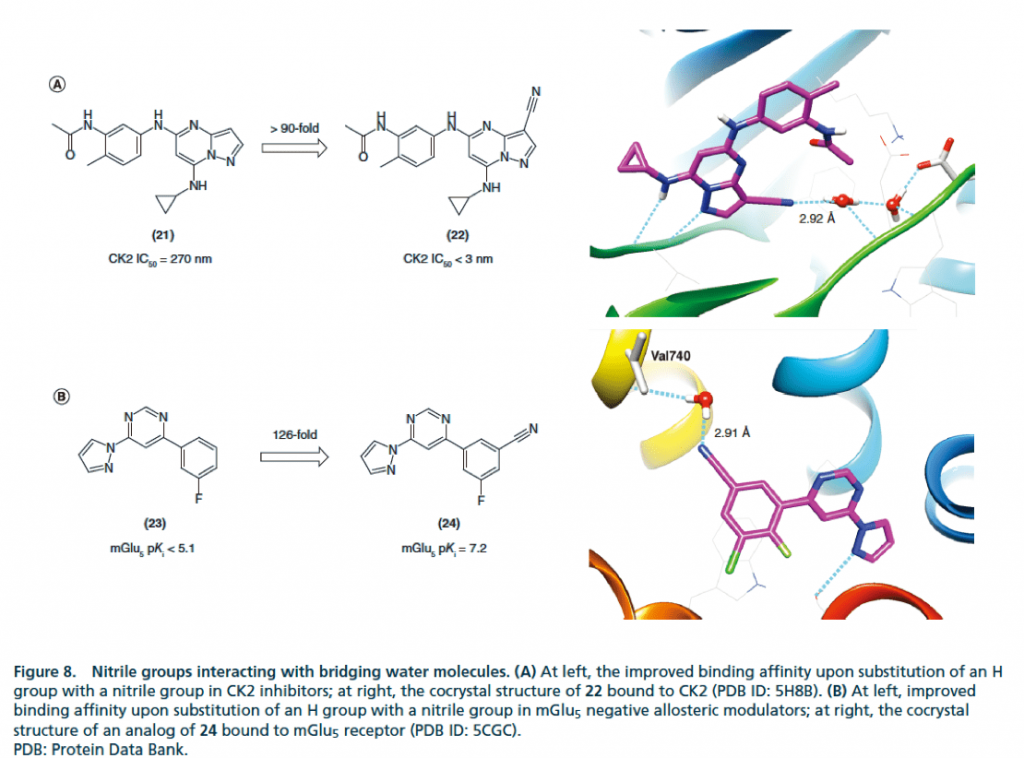
▉ Example illustration of cyano group occupying hydrophobic cavity to enhance activity
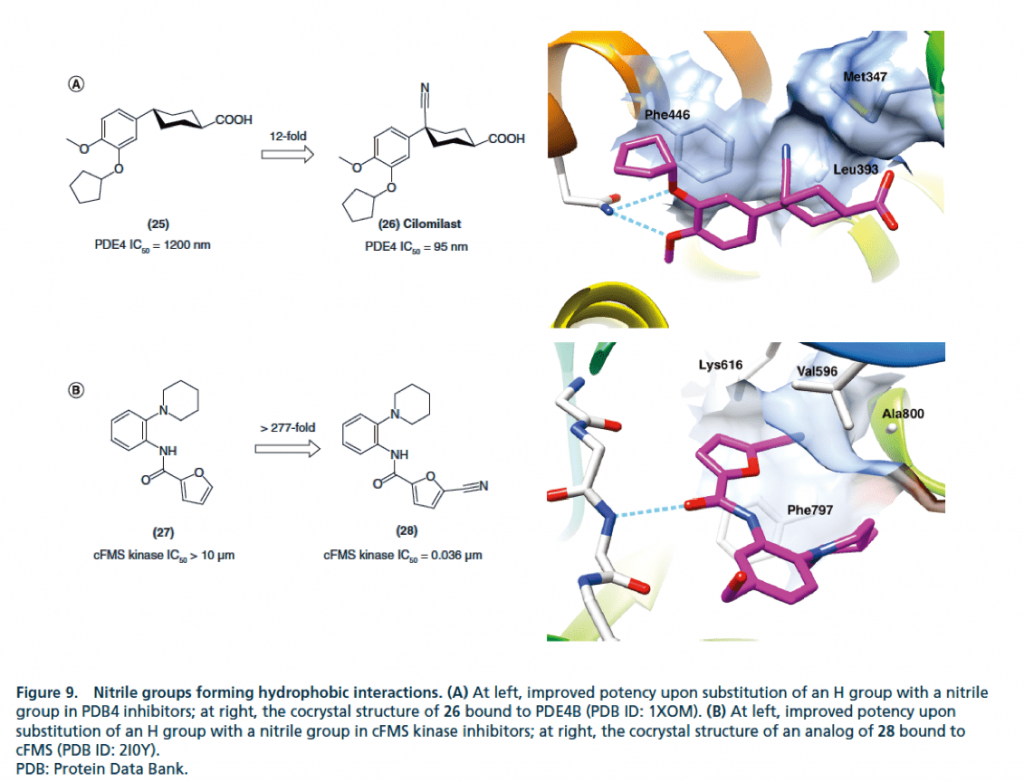
▉ Illustration of an example of cyano group forming a covalent bond to enhance activity
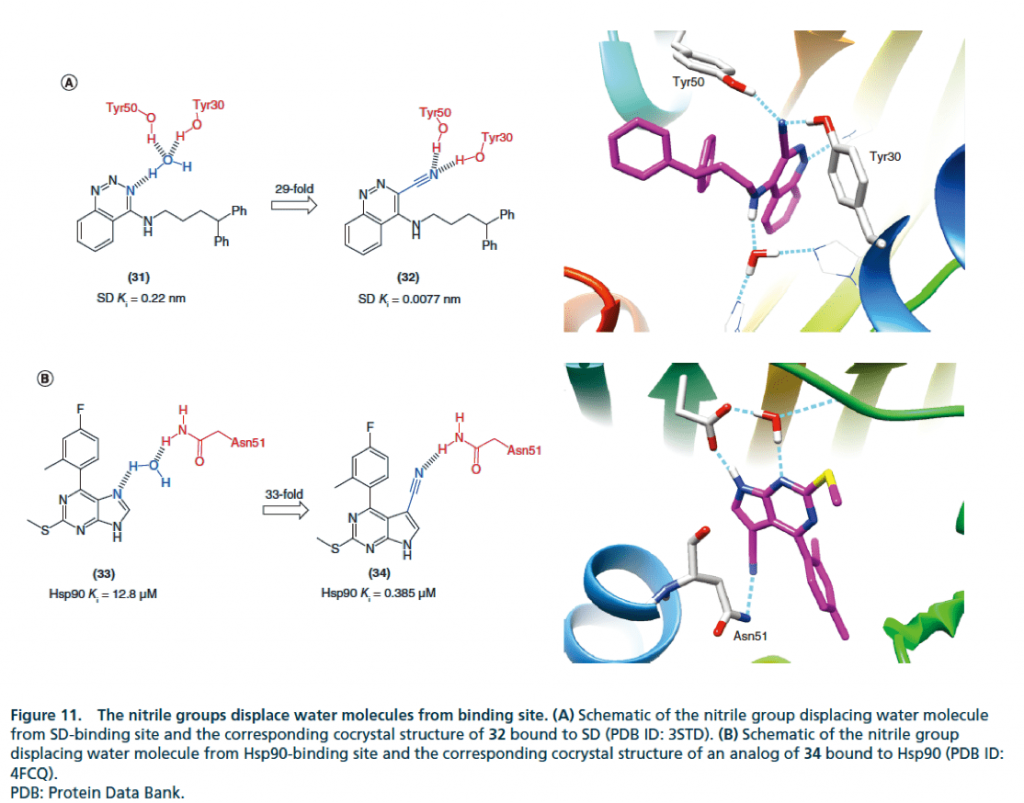
▉ Cyano group replaces bound water directly to form hydrogen bond with protein to enhance activity example diagram
Summary
The ubiquitous H atoms and aromatic N atoms in lead compounds are usually substituted by cyano or C-CN groups.
Compared with the magic methyl effect and the necessary nitrogen atom effect (this simply means: simple structural modifications may significantly affect binding affinity), the potential of cyano groups to enhance binding affinity through direct interaction or water displacement is underestimated .
This review is helpful for us to deeply understand the way the cyano group interacts with the receptor protein.
At the same time, it can be combined with reliable calculation methods to promote the development of excellent drug molecules based on the cyano structure in the future.
How does the cyano (-CN) structure improve the activity of drug molecules?
(source:internet)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



