How to treat Parkinson’s disease in Japan?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
How to treat Parkinson’s disease in Japan?
How to treat Parkinson’s disease in Japan? JMT丨Parkinson’s disease: What is the treatment of Japan, the world’s third-largest senile disease “killer”?
Parkinson’s disease is the world’s third-largest elderly disease”
The demographic situation of many countries is undergoing sudden changes. Fewer births, aging, and diminishing labor have become irreversible trends. The demographic structure is the foundation of national conditions, and the demographic structure determines the various social conditions.
There are more and more elderly people, and the incidence of senile diseases is increasing. What about the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, the world’s third-largest senile disease “killer” in Japan?
1 Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease is a common neurodegenerative disease. The average age of onset is about 60 years old, with an incidence rate of 1-2%. It has become the world’s third-largest “killer” of senile disease. In the late stage, patients often experience negative emotions such as depression and irritability due to reasons such as inability to take care of themselves, sleep disorders, and reduced quality of life.

Pathogenesis, causes and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease
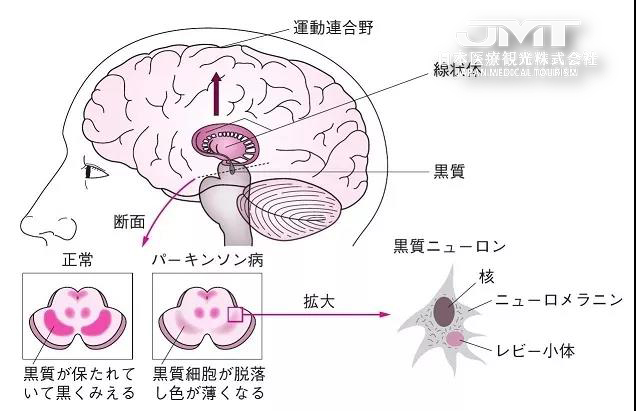
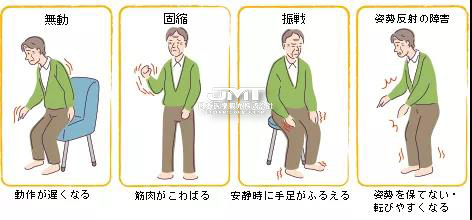
The most important pathological change of Parkinson’s disease is a significant decrease in dopamine secreted by substantia nigra cells of the midbrain. The main manifestations are increased muscle tone, slow movement, resting tremor, and cognitive impairment. At present, the cause of the disease is not clear, and it may be related to factors such as genes, chemical substances, and brain injury.
2 Japan-DBS therapy (brain pacemaker)
DBS therapy is a deep brain stimulation (DBS) therapy currently implemented by neurologists at the Scottsdale Mayo Clinic Medical Center in the United States to treat a hereditary dystonia, which can significantly improve the condition. DBS therapy mainly involves implanting electrodes into the patient’s brain, using a pulse generator to stimulate certain nerve nuclei in the deep part of the brain, correcting abnormal brain electrical circuits, and reducing these neurological symptoms. Unlike some treatments (cautery or radiotherapy) that permanently damage the brain that is irreversible and irreversible, DBS does not damage the brain structure and can allow for further treatment in the future.
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease, because the number of brain substantia nigra cells is attenuated, neurotransmitter disorders, and nerve signal conduction abnormalities, leading to various symptoms of Parkinson’s.
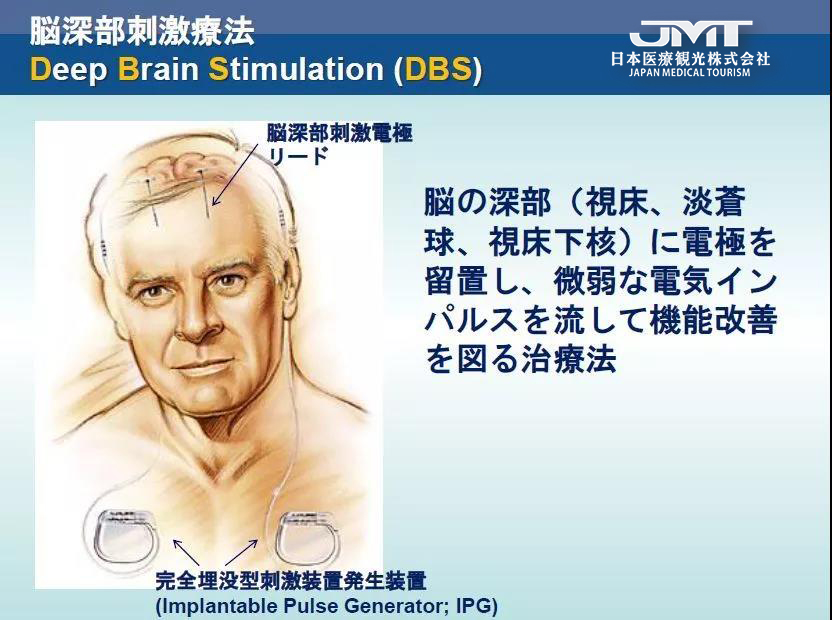
Brain pacemaker is the common name for deep brain stimulation (DBS). It uses electrodes implanted in the brain to deliver weak electrical impulses to stimulate the nerve nuclei that control movement in the brain and inhibit abnormal brain nerves that cause Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Signal, thereby eliminating the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, so that the patient can restore the original mobility and self-care ability.
DBS therapy improves dystonia
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contraction, which forces some abnormalities of the body, sometimes painful movement or posture. Dystonia can affect any part of the body, including limbs, trunk, neck, eyelids, face and even vocal cords.
During the implementation of DBS, doctors can use EEG scans to find targeted nerve nuclei by recording the characteristics of different depths and trajectories of the brain, and observe the patient’s response to stimulation. This EEG scan allows the surgeon to pinpoint the correct area to place the electrode, thereby minimizing side effects. Researchers said that this technique greatly shortens the time of surgery and increases the accuracy of treatment.
During the treatment, the patient is always awake, and after receiving a small dose of sedatives, they can describe the side effects caused by the stimulation. The center also uses a unique acupuncture therapy to relieve the anxiety and pain of patients during the treatment, in order to reduce the patient’s dose of sedatives and anesthetics. DBS treatment usually takes 3 to 4 hours, and patients are usually hospitalized for 1 to 2 days. The pulse generator can be placed under the clavicle of the patient, and the programmed program can make the pulse last until one week after the operation.
DBS includes brain stimulation electrodes, subcutaneous wires, pulse generators, and magnet switches. The brain stimulation electrode has a diameter of 1.27 mm and has 4 stimulation contacts, each with an interval of 0.5mm or 1.5mm for stimulation. Stimulating electrodes are inserted into specific nuclei in the brain through stereotactic technology and microelectrode recording technology, and continuous high-frequency pulse electrical stimulation is used to inhibit abnormal brain nucleus discharges to achieve therapeutic effects, but the specific mechanism is not very clear.
The pulse generator is an instrument that generates high-frequency pulses. It is the core part of the system. The pulse generator is embedded under the skin of the chest during the operation, and the pulse stimulation is transmitted to one or both sides of the stimulation electrode through the subcutaneous wire. Both the stimulation electrodes and the subcutaneous wires are permanent, but the pulse generator battery has a certain capacity, which can generally be used for 6-8 years. If the battery is exhausted, the pulse generator needs to be replaced. The magnet switch is a simple switch that can turn the pulse generator on or off.
The use of DBS treatment not only has a significant improvement in the lives of patients with dystonia, but is also effective for advanced Parkinson’s disease and severe essential tremor.
What kind of patient is suitable for brain pacemaker surgery?
Before brain pacemaker surgery, what items should patients test?
Levodopa impact test
The responsiveness of movement fluctuations and dyskinesias to dopamine indicates the effect of DBS surgery. To evaluate the responsiveness of dyskinesia and compound dopamine, UPDRS-3 score is often used. The opening time is not important. What is important is that the improvement of dyskinesia is more important. The levodopa shock test is an important predictor for judging DBS therapy.
The maximum improvement rate of levodopa is directly related to the surgical effect
The specific method is that subjects need to stop dopamine receptor agonists for 72 hours, compound levodopa preparations and other anti-PD drugs for 12 hours. The test drug is a standard compound levodopa tablet, and the dose is 1.5 times the equivalent dose of levodopa based on the anti-PD drug taken for the first time each morning. In the fasting state, the UPDRS score is taken as the baseline first, and then taken? Butyroline (domperidone tablets) 10mg, take compound levodopa standard tablets 30 minutes later, and then evaluate it every 30 minutes with UPDRS-3 score until 4 hours after taking the drug.
Calculate the maximum improvement rate of UPDRS. The calculation method is the baseline score before taking the drug-the lowest score after taking the drug / the baseline score before taking the drug * 100%. If the improvement is more than 30%, it indicates that the DBS operation is effective, such as no change in symptoms other than tremor, and dyskinesia persists. The effect of DBS surgery is poor.
Cognitive test
Severe cognitive impairment (dementia) is a contraindication to DBS surgery. About 40% of advanced PD patients suffer from dementia. Therefore, surgery is not recommended for patients with dementia before surgery. Evaluation programs include MMSE, MoCA, ADAS-Cog, Webster’s Adult Intelligence Scale, etc.
Mental test
Severe and refractory mental disorders are contraindications to DBS therapy. Hamilton Depression Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Scale are used to assess mood disorders, neuropsychiatric scales, and concise psychiatric scales are used to assess mental disorders.
Other factors
It is best for patients not to be more than 75 years old and the course of the disease is more than 5 years (this is helpful for the identification of MSA with multisystem atrophy of brain and PSA with progressive supranuclear palsy), but if the tremor is the main case, the drug treatment effect is poor. DBS operation should be done as soon as possible (over 3 years).
Medication
Cases in which levodopa has been effective, the adjustment of the drug regimen for movement fluctuations and dyskinesias has no better effect, and the quality of life is clearly reduced.
Reasonable expectation
It should be known before surgery that surgery cannot change the progression of Parkinson’s disease, but can only improve the quality of life for a period of time during the course of the disease, and relieve muscle tone and tremor, but the relief of non-dyskinesia symptoms is not clear, not all patients All can reduce or stop the drug, and the operation is generally safe and effective, improving the quality of life, but there are also surgical risks.
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



