Immunology: IL-36 | Inflammation and Tumor
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Immunology: IL-36 | Inflammation and Tumor
Immunology: IL-36 | Inflammation and Tumor. IL-36 was discovered in 1999 and belongs to the IL-1 cytokine family. IL-36 can become an active functional form after N-terminal cleavage, which plays an important role in inflammation and tumor immunity.
IL-36 molecule and signal pathway
Four subtypes are currently found: IL-36α (IL-1F6), IL-36β (IL-1F8), IL-36γ (IL-1F9), IL-36Rα (IL-1F5); the first three are IL- 36 receptor agonist, promote inflammation; IL-36Rα is a receptor antagonist, antagonize inflammation. IL-36 receptor is a heterodimer (IL-1R6, IL-1RAcP).
IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ are spliced into active form, bind to IL-36 receptor, transmit signals through MyD88-MAPK/IKK-AP1/NF-κB, and finally release cytokines (IL-36, etc.) , Chemokines, promote inflammation.
The active form of IL-36Rα cannot bind to IL-36 receptors, has no signal transduction, and has the effect of antagonizing inflammation.
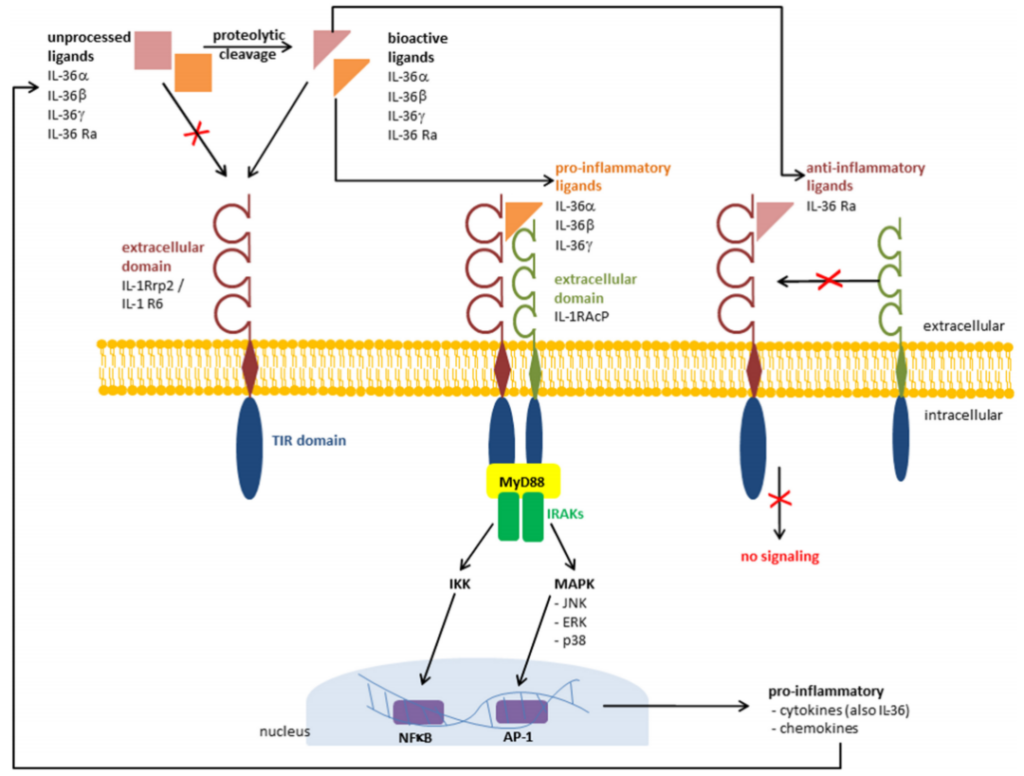
IL-36 signaling pathway
IL-36 targets cells and functions
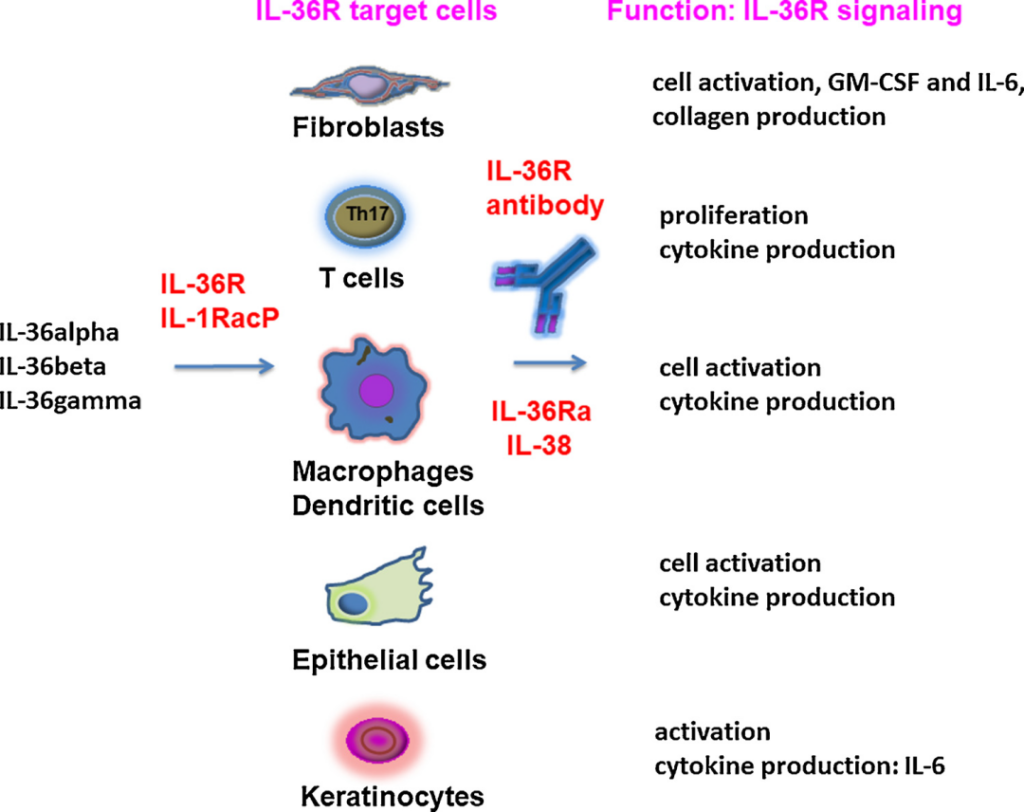
IL-36 acts on target cells and functions (Reference 3)
Fibroblasts: activate, secrete GM-CSF, IL-6, and produce collagen
T cells: IL-36R is mainly expressed in CD4+ T cells, promotes differentiation into Th1 and Th17, and promotes their proliferation, and inflammatory cytokine production
IL-36 promotes the activation of macrophages, DC cells, epithelial cells, and keratinocytes, and secretes inflammatory factors IL-6, IL-1β, IL-12, IL-23, TNF-α, etc.
IL-36 and disease
1. Inflammatory diseases
Skin inflammation
Tissue resident immune cells, keratinocytes, etc. express IL-36R, which can be activated by IL-36 and express a series of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, IL-17A, TNF, CXCL1, CXCL8, CCL3, CCL5, CCL20, etc.). IL-36 has been reported to be involved in skin inflammation such as hidradenitis suppurativa, folliculitis and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis, Staphylococcus aureus-mediated dermatitis, psoriasis and other skin inflammations.
Eye inflammation
A clinical study showed that the levels of IL-36, 37, 38 and other cytokines in chronic primary angle-closure glaucoma were significantly increased.
In addition, IL-36 is involved in inflammatory pain and neurological diseases, kidney inflammation, liver inflammation, rheumatic diseases, etc.
2. Anti-infection
IL-36 participates in resistance to conjugate bacillus infection, Legionella pneumophila infection, Candida albicans, antiviral infection, etc.
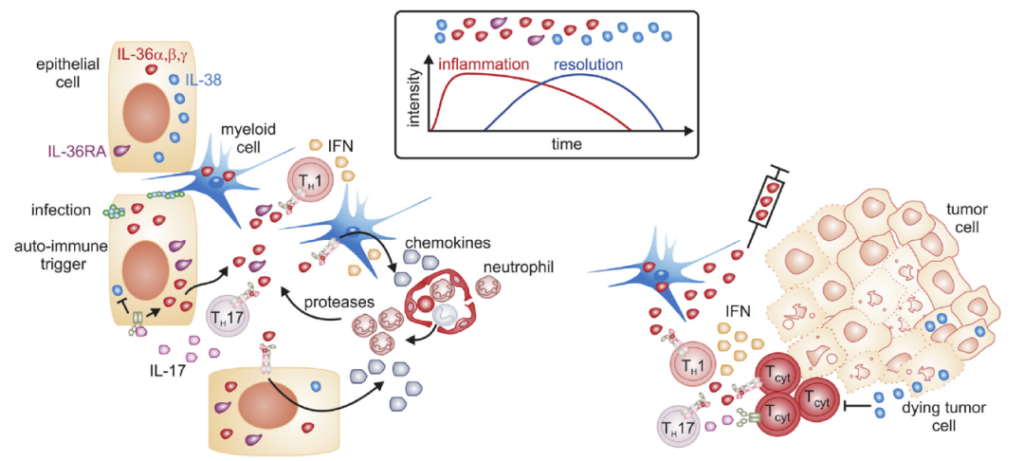
IL-36 is involved in inflammation and tumors (Reference 4)
3. Anti-tumor
IL-36 plays a multi-directional role in inflammation and can activate various immune cells (such as T cells). However, IL-36 alone cannot stimulate effector CD8 T cells, and requires the synergistic effect of IL-2 and IL-12.
In vivo studies have shown that dual costimulation therapy reduces B16 melanoma tumor growth and induces IL-36R expression. A recent study used IL-36 gene therapy to treat experimental fibrosarcoma. IL-36 treatment resulted in a significant reduction in tumor growth, indicating an anti-tumor effect.
In colon cancer, high expression of IL-36α and IL-36β or IL-36α plus low level of IL-36γ shows longer survival time. Patients with metastatic tumors with high IL-36α levels or low IL-36γ showed improved survival rates. These results indicate that IL-36α and IL-36γ are potential biomarkers for the prognosis of colorectal cancer. IL-36α and IL-36γ seem to play different roles in controlling tumor growth and expansion.
IL-36 drug development
IL-36mRNA injection to treat tumors has shown anti-tumor activity (reference 5).
BI655130 (boehringer ingelheim)
IL-36R humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody blocks the signal transduction mediated by human IL-36 ligand. Therefore, the antibody can be used to treat autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases in patients. Pustular Psoriasis (Pustular Psoriasis, GPP). Clinical trials (NCT02978690) (Reference 6) and inflammatory bowel disease (NCT03100864) obtained positive clinical results. Clinical trials for atopic dermatitis (NCT04086121) and palmoplantar pustulosis are also underway.
Expert commetns:
IL-36 has a wide range of effects. However, anti-tumor activity requires the synergistic effect of IL-2 and IL-12, so there are some problems with the preparation of drugs alone. By blocking the binding of IL-36 and IL-36R, antagonizing inflammation, began to enter clinical research.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



