What’s the detection methods of lentivirus titer?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
What’s the detection methods of lentivirus titer?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
What’s the detection methods of lentivirus titer?
CAR-T technology has shown broad development prospects in cancer treatment, and this method is triggering a revolutionary change in cancer immunotherapy.
The so-called CAR-T refers to the use of genetically modified primary T cells to express the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) gene. By using plasmid transfection, mRNA, lentivirus or retrovirus can transduce CAR into T cells stably Expressed to construct CAR-T cells, which are injected into the human body to target and kill tumor cells [1].
So far, there have been five autologous CAR-Ts targeting hematological malignancies in the world. They all use lentivirus or retroviral transduction methods to transduce target genes into T cells for stable expression. The transduction efficiency of T cells is a key step of CAR-T technology.
Lentiviruses belong to the retroviral family and are RNA viruses, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV).
Today, LV technology has become one of the most effective tools for delivering foreign genes to various types of cells in vivo and in vitro [2-5].
The advantage of lentiviral transduction genes is that they can not only infect a variety of dividing and non-dividing cells, but also can efficiently integrate the target gene into the host genome and express it stably for a long time [6].
Among them, the high-efficiency transduction of human primary T cells is still challenging, and the methods to achieve effective gene transduction are usually expensive and time-consuming [8].
In order to establish an efficient and stable method for preparing high-titer viral vectors and efficient transduction methods for T cells, this article mainly introduces various methods for the determination of lentiviral titer.
Commonly used detection methods include immunostaining, flow cytometry, fluorescent quantitative PCR, p24 protease-linked immunoassay (ELISA), etc.
1. Fluorescence staining method and flow cytometry
Experimental principle:
Use the virus to carry out the antigen-antibody binding reaction for color development or the lentiviral vector to carry other Marker Gene, such as RFP\BFP, you can use a fluorescence microscope to observe the fluorescence expression under the corresponding excitation light wavelength. There are two kinds of direct method and indirect method.
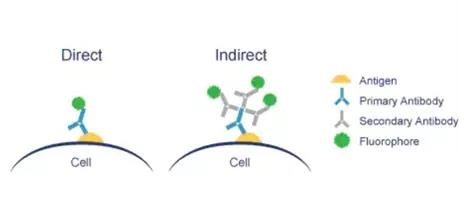
Take the self-fluorescent lentivirus as an example to introduce the experimental process:
Description:
*If you need to add a primary antibody or a secondary antibody to the experiment, add it after the virus infection experiment, and then perform the test;
*The health of the target cell line is essential to obtain accurate titer;
*Regularly check the cells for mycoplasma;
*Do not overgrow or undergrow cells;
* Thaw a new vial cell after 20 to 30 generations;
*Do not add penicillin/streptomycin to the medium;
*The titer will be different between different cell lines;
*It is not recommended to perform multiple freeze-thaw cycles on the lentiviral supernatant;
*If the infection efficiency is greater than 40%, it is likely that the result is underestimated.
Calculation formula:
Method 1: TU/mL = (number of transduced cells x fluorescence percentage x dilution factor)/(transduction volume (mL))
Example of Method 1:
There are 25% fluorescent cells in 100 wells and 150,000 cells were initially transduced, then (150,000 x 0.25 x 100)/(1.5 mL) = 2.5x106TU/mL;
Method 2: TU/mL = (number of transduced cells x fluorescence percentage)/(virus volume, in mL)
Example of method 2:
If 15 µL of virus is added to 150,000 cells, resulting in 25% of fluorescent cells, there is (150,000 x 0.25)/(0.015 mL) = 2.5x106TU/mL
Examples of experimental results:
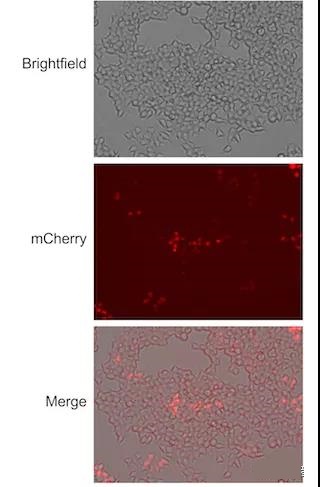
Figure 1: Lenti-X 293T cells were transduced with a series of dilutions of 64108 pHAGE-TO-dCas9-3XmCherry. 72 hours after transduction, fluorescence microscopy was used to detect the mCherry expression of the cells.
2. Real-time quantitative PCR method for determination of recombinant lentivirus titer
Experimental principle:
The so-called Real-TimePCR technology refers to the method of adding fluorescent groups to the PCR reaction system, using the accumulation of fluorescent signals to monitor the entire PCR process in real time, and finally quantitatively analyzing the unknown template through the standard curve.
In this method, quantitative primers are designed in the long terminal repeat region (LTR) of the vector, and real-time quantitative PCR is used to determine the copy number of LTR in the recombinant lentivirus to determine the number of virus particles and the number of virus particles that are effectively infected.
The change in fluorescence signal is used to detect the change in the amount of the amplified product in each cycle of the PCR amplification reaction in real time, and the starting template is quantitatively analyzed through the analysis of the Ct value and the standard curve.
The real-time PCR technology, that is, real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR, avoids the deviation caused by traditional PCR to monitor and quantify the final product, and improves the repeatability of the experiment.
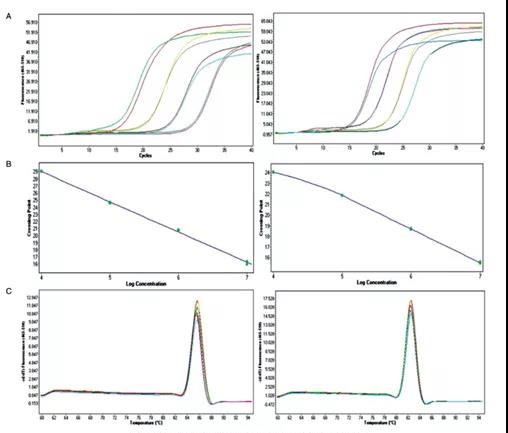
Experimental process (take literature 12 as an example):
Take the virus concentrate and dilute it step by step by 10 times. Take 0.1, 0.01, 0.001μL of the virus concentrate to infect 1.5×106 293T cells.
After 2 days of infection, use real-time quantitative PCR to detect LTR in the DNA of cells infected with different amounts of virus. The number of integrated copies.
Experimental results:
3. p24 protein ELISA method [13]
This method detects the physical unit of the virus. The p24 protein is the most abundant marker protein in the lentivirus shell.
Generally speaking, the p24 protein ELISA test can detect all p24 proteins, so as to realize the quantification of virus titer. The ELISA method is sensitive and can detect 1 ng/mL HIV p24 protein.
Finally, the data is read by a spectrophotometer.
However, it is not possible to distinguish between virus particles with infectious ability and non-infectious virus particles, and cannot reflect the true infectious viability of the virus, so the application of this method is also limited.
It is understood that there is a lentivirus titer test kit (lentivirus-related p24 protein ELISA test): this problem can be minimized, and the principle is to free the lentivirus from the solution before running the ELISA part of the assay. p24 separation.
As for the specific results, the editor has not found any report about the comparison of this new method with other methods.
What’s the detection methods of lentivirus titer?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



