Netformin can improve treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
The magical effect of Netformin! It can promote the release of extracellular vesicles of mesenchymal stem cells and optimize the therapeutic effect of intervertebral disc degeneration.
Netformin can improve treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Metformin treatment can not only affect the quantity of MSC-EVs released, but also affect the quality. This study reveals the potential of metformin in the treatment of stem cell vesicles, and also provides new ideas for the regeneration and repair of intervertebral discs.
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is a widespread musculoskeletal disease and the main cause of low back pain. It is generally believed that aging, trauma and genetic factors are the main causes of inflammation and degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Although surgery can relieve pain to a great extent, the accompanying side effects cannot be ignored. The degeneration of the intervertebral disc after surgery is irreversible and will be further aggravated.
Most of the biological treatments of intervertebral disc degeneration focus on the regeneration of residual cells in the intervertebral disc and the repair of damaged cells. The self-repairing ability of cells in the intervertebral disc area is weak, and more and more stem cell-related treatments have been reported.
1. Related basic knowledge
Intervertebral disc degeneration and MSCs
Intervertebral disc degeneration is the main cause of low back pain. It is generally believed that aging, trauma and genetic factors are the main causes of inflammation and degeneration of the intervertebral disc. The intervertebral disc is composed of inner nucleus pulposus (NP), outer fibrous annulus (AF) and endplates at both ends. NP cells produce extracellular matrix to maintain structural and functional stability. The regeneration of NP cells or the restoration of cell viability is a key challenge for the regeneration of intervertebral discs.
The therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are mainly attributed to their immunoregulatory function under the regulation of the inflammatory environment, and can be used to treat a wide range of degenerative and inflammatory diseases.
Mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles
Extracellular vesicles are considered to be excellent drug delivery vehicles. At the same time, it mediates communication and interaction between cells. Studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) have similar biological functions to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and play an important role in tissue repair and regeneration. Exosomes are cheaper, more stable, and relatively easy to store and transport. MSC-Evs is considered to be an ideal substitute for MSCs in the treatment of certain diseases.
2. MSC-EVs promote the repair of intervertebral disc degeneration
Professor Yang Cao’s team from the Department of Orthopedics, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology found that metformin can promote the release of mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) and increase the level of proteins that regulate cell proliferation in the vesicles.
Optimize the application effect of extracellular vesicles in the regeneration and repair of intervertebral discs. The research was published in Biomaterials and the title of the paper is “Metformin facilitates mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular nanovesicles release and optimizes therapeutic efficacy in intervertebral disc degeneration”,
Research ideas:
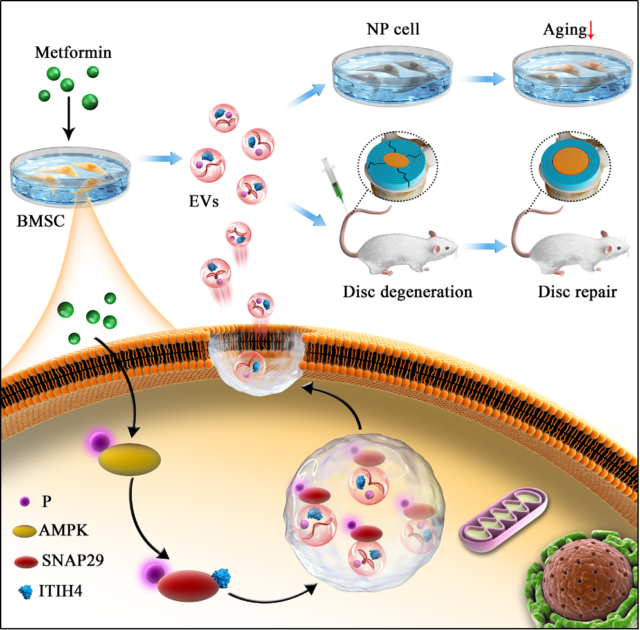
Figure Research schematic
The researchers studied the effect of metformin on MSC-EVs, focusing on the mechanism of EVs secretion. First, we compared the secretion of normal and metformin-treated MSC-EV, and the conclusion supports the hypothesis that metformin induces the release of EVs.
Then on the basis of in vivo and in vitro experiments, the therapeutic effects of metformin-treated MSC-EVs and normal MSC-EVs on NP cells were further compared, and proteomics analysis showed.
Finally, a model of intervertebral disc degeneration of the rat tail vertebra was constructed to compare the in vivo therapeutic effects of metformin-treated MSC-EV and normal MSC-EV in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration.
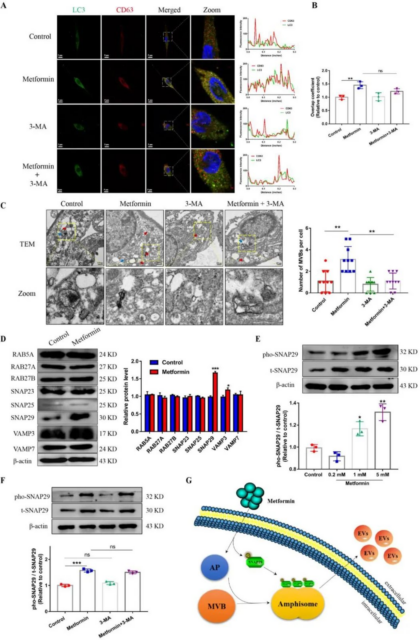
The results of vesicle marker protein level detection, transmission electron microscopy and particle size analysis showed that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) treated with metformin can release more vesicles.
Further research found that metformin enhanced the production of EVs through autophagy-related pathways, and was accompanied by phosphorylation of synaptosome-associated protein 29 (SNAP29 protein). Metformin not only affects the number of MSCs-EVs, but also their quality.
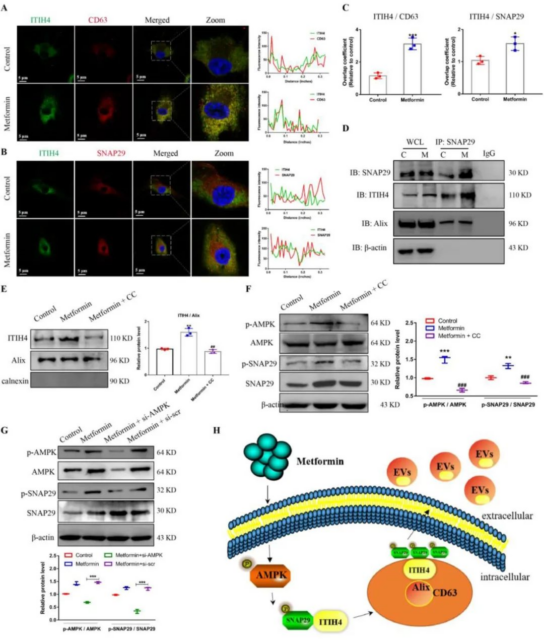
Proteomics analysis showed that MSC-EVs treated with metformin had higher levels of proteins related to cell proliferation in MSC-EVs compared with those without metformin treatment. The results show that metformin-treated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived external vesicles (BMSC-EVs) can improve the senescence of intervertebral disc cells both in vivo and in vitro.
Animal experiment
Animal model:
The acupuncture method was used to construct a rat model of intervertebral disc degeneration. Simply put, it is to puncture the intervertebral disc from the tail skin of the rat’s back to induce degeneration of the intervertebral disc.
Experimental design
24 SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups and administered separately: the blank control group was punctured with a 33-gauge needle; the IDD group was punctured with a 20-gauge needle and injected with PBS; in the C-EVs group, the normal control MSC-EVs were injected with a 20-gauge needle In the M-EVs group, MSCs-EVs treated with metformin were injected with a 20-gauge needle. The injection was repeated once a week for one month to compare the therapeutic effects of M-EVs and C-EVs in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration.
On the other hand, a model of intervertebral disc degeneration of the rat tail vertebra was constructed to compare the in vivo therapeutic effects of M-EVs and C-EVs in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration.
Experimental results show that MSC-EVs can restore the height of the intervertebral disc to a certain extent. MSC-EVs can improve the number and morphology of intervertebral disc tissue cells. The therapeutic effect of MSC-EVs (M-EVs) treated with metformin is better than that of MSC-EVs (C-EVs) not treated with metformin. MSC-EVs reduce matrix degrading enzymes (such as matrix metalloproteinases <MMPs>). It is one of the tissue characteristics of degenerative disc disease. MSC-EVs can delay the progress of intervertebral disc degeneration in the body to a certain extent, and the treatment effect of MSC-EVs (M-EVs) treated with metformin is better than that of MSC-EVs (C-EVs) not treated with metformin.
3. Summary
This study found that metformin not only affects the quantity of MSC-EVs, but also its quality, and emphasizes the relationship between autophagy and the release of MSC-EVs. Metformin can promote the production of EVs through autophagy-related pathways. In addition, metformin also promotes the transport of EVs in the body. This study reveals the potential of metformin in the treatment of stem cell vesicles, and also provides new ideas for the regeneration and repair of intervertebral discs.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



