Multivalent Nanobodies can neutralize a variety of COVID-19 mutant strains
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Multivalent Nanobodies can neutralize a variety of COVID-19 mutant strains
Multivalent Nanobodies can neutralize a variety of COVID-19 mutant strains. Multivalent Nanobodies have been developed, which can neutralize a variety of COVID-19 mutant strains; this is the institution that has rewritten the anti-epidemic process!
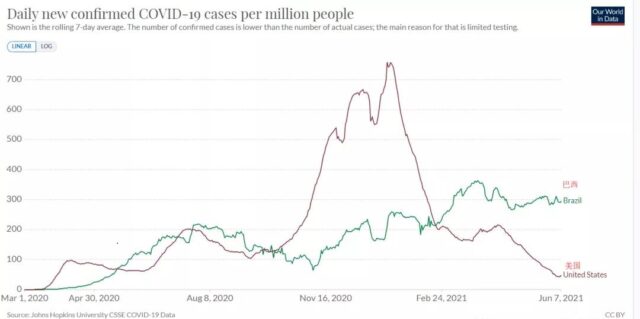
In the face of the once-in-a-century COVID-19 plague, what will happen to the United States without an efficient vaccine?
There is a high probability that it will be as continuous as Brazil, but it will be worse because the United States has a higher proportion of infections.
On April 9, 2021, Dr. Fauci, Chief Scientist of the White House and Director of the Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), wrote an editor’s note on the front page of Science, summarizing the COVID- 19 The main developer of mRNA vaccines.
The COVID-19 mRNA vaccine is mainly composed of two important parts: a lipid nanoparticle (LNP) carrier and an S-conformation antigen.
The main contribution of the LNP-mRNA vaccine vector was undoubtedly given to Katalin Karikó, the current vice president of BioNTech and a researcher at the University of Pennsylvania at the time, and his co-professor Drew Weissman at Penn.
Dr. Fauci made his main contribution to the design of the conformational S antigen to his colleagues, Peter Kwong and Barney Graham of the NIH Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Vaccine Research Center (VRC). They determined that the pre-fusion conformation of the new coronavirus spike protein (S protein) is highly immunogenic and created a method to stabilize this pre-fusion protein. This strategy has been applied to research on HIV, MERS and SARS before the development of the COVID-19 vaccine.
However, the new coronavirus is not so easy to deal with. Mutant strains that continue to mutate, become more infectious, or evade immune responses will become mainstream strains as they continue to spread.
Eli Lilly’s monoclonal antibody for the treatment of the new coronavirus has been revoked for emergency use because it cannot block the mutant strain.
It is necessary to develop new multivalent neutralizing antibodies against mutant strains.
On June 7, 2021, Peter Kwong of NIH VRC, who has done a great job in the development of COVID-19 vaccines, reported in Nature a nanobody that can neutralize a variety of SARS-CoV-2 mutant strains.
This study used camelid VHH (nanoantibodies), which are very popular in recent immunology and HIV research, and they can recognize epitopes that are not normally recognized by conventional antibodies. This study isolated anti-RBD Nanobodies from llamas, and designed, cloned and produced similar VHHs isolated from alpaca, dromedary and camel.
The study separated two groups of Nanobodies with high neutralizing activity: the first group suppressed the mutation and drift of viral antigens by identifying the RBD region that is highly conserved by coronavirus but is rarely targeted by human antibodies; the second group is directed against RBD-ACE2 crosstalk. The interface epitope (Are HIV colleagues familiar with the concept of the Kwong group?), it cannot effectively neutralize mutant strains containing E484K or N501Y mutations. But what is interesting is that the second type of Nanobody can effectively neutralize mutant strains that retain the spatial structure of the S antigen trimer, and has extremely strong neutralizing activity.
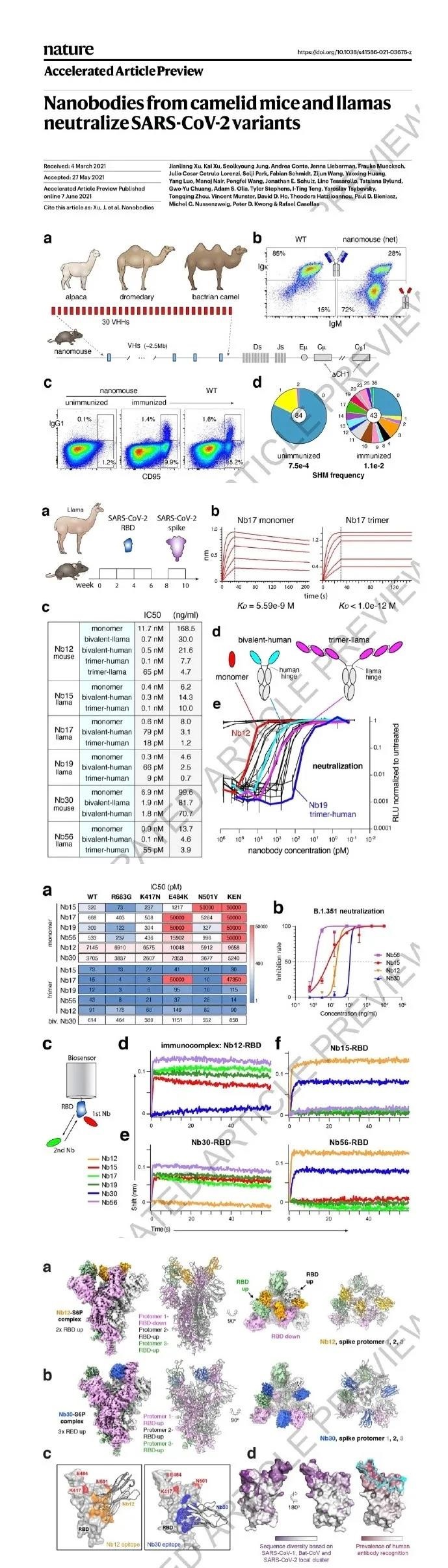
These findings show that multivalent Nanobodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 mutations through two different mechanisms: enhancing their affinity for the ACE2 binding domain, or recognizing conserved epitopes that human antibodies cannot recognize.
Editor’s note:
The innovation of biological sciences is the basis for mankind to ultimately control the COVID-19 epidemic and protect the health of patients.
When the previously approved therapeutic antibodies faced the challenge of virus mutant strains or even failed, the multivalent nanobodies studied by NIH VRC gave us new hope.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



