mRNA vaccine and adenovirus vaccine less effective against Delta variant?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
NEJM: mRNA vaccine and adenovirus vaccine less effective against COVID-19 Delta variant
mRNA vaccine and adenovirus vaccine less effective against Delta variant. Since the global outbreak of the COVID-19 epidemic in early 2020, various mutant strains have continued to appear.
Among them, the more important ones are the Alpha mutant strain that first appeared in the United Kingdom and the Delta mutant strain that first appeared in India.
Among them, the Delta mutant strain has become the main new coronavirus strain in the world. Studies have shown that these COVID-19 mutant strains may have stronger transmission and immune escape ability. Therefore, it is crucial to determine the current vaccine’s effect on these mutant strains. important.
The characteristic of the Delta mutant strain is that its spike protein (S protein) has mutation sites such as T19R, Δ157-158, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R and D950N. Among them, L452R and T478K mutations may lead to enhanced immune escape ability, while P681R mutation may lead to enhanced replication ability, resulting in higher viral load and stronger infectious ability.
On August 12, 2021, the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), the top of the four major international medical journals, published the UK’s real-world vaccine protection efficiency data.
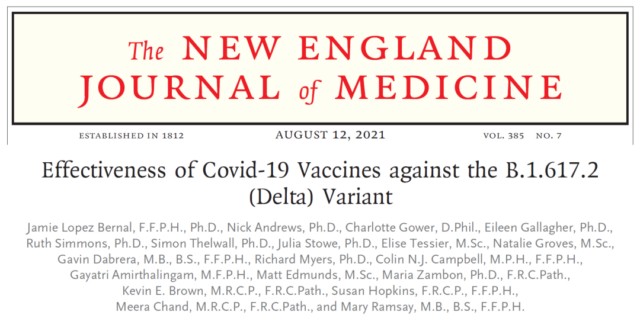
The study showed that although the mRNA vaccine (BNT162b2) and adenovirus vector vaccine (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) can still prevent the Delta mutant strain, the protection efficiency has been greatly reduced.
The protective efficiency of two doses of BNT162b2 vaccine against the Delta mutant strain was 88.0%, and the protective efficiency of two doses of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine was 67.0%.
The protective efficiencies of these two vaccines against the original strain of the new coronavirus are 95% and 90%, respectively. The protective efficiencies of Alpha mutant strains were 93.7% and 74.5%, respectively.
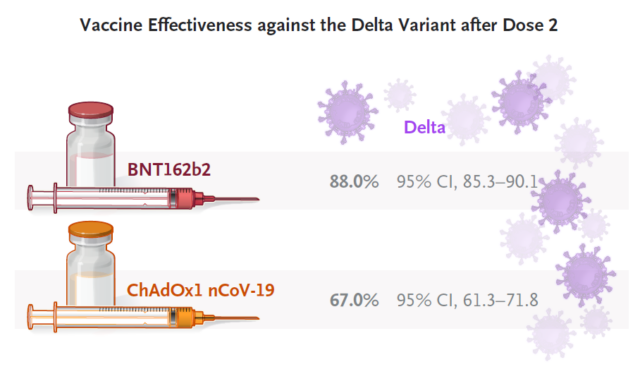
In addition, the study also pointed out that if only one dose of the mRNA vaccine (BNT162b2) or adenovirus vector vaccine (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) is administered, the protection efficiency is only 30.7%. With only one dose, the protective efficiency of the Alpha mutant strain was 48.7%. This reminds us that only one dose or the interval between two doses is not advisable.
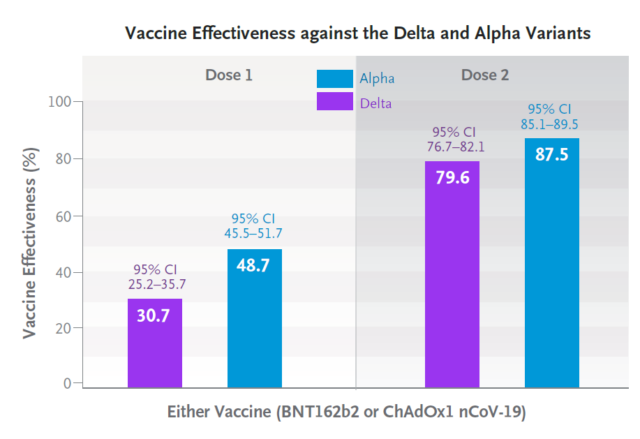
Finally, the research team stated that after two doses of the vaccine, compared with the Alpha mutant strain, the vaccine’s protective efficiency against the Delta mutant strain was reduced, but the decline was not large, indicating that the mRNA vaccine and adenovirus vaccine were against the Delta mutant strain.
The still has better protection efficiency. However, it should be pointed out that for these two vaccines, the protection efficiency of the Delta mutant strain is poor when only one dose is given, only 30.7%.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



