2021 ESMO: What are the new events in the hepatobiliary field?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
2021 ESMO: What are the new events in the hepatobiliary field?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
2021 ESMO: What are the new events in the hepatobiliary field?
The 2021 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) annual meeting will be held on September 16-21, 2021. The conference is hosted by the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO).
Up to now, a number of studies have published abstracts, and the field of hepatobiliary is of course no exception.
The 2021 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) annual meeting will be held on September 16-21, 2021. The conference is hosted by the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO).
Up to now, a number of studies have published abstracts, and the field of hepatobiliary is of course no exception.
Following the breakthrough of targeted immune combination in advanced liver cancer, the focus began to shift to adjuvant therapy for early liver cancer; combination therapy is no longer limited to systemic combined series of treatments, and local combined systemic treatments have also begun to get on track. New drugs and new therapies are emerging one after another, so let’s follow the editor to take a look~
Liver Cancer
1. In patients without MVI or EHS, The relative benefits of the “T+A” scheme remain unchanged

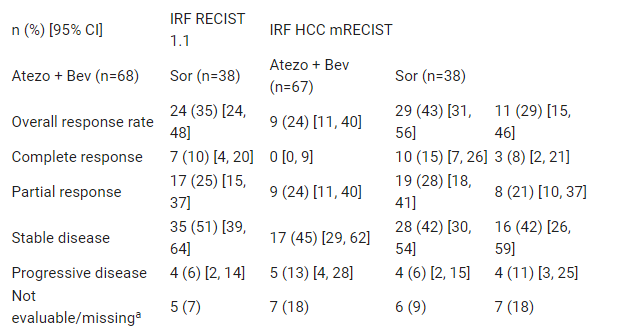
“T+A” first-line treatment has been approved in >70 countries. This study reports the exploratory efficacy and safety of patients without macrovascular invasion (MVI) or extrahepatic spread (EHS) after an additional 12 months of follow-up. At baseline, 111 patients had no MVI or EHS. As of the data cutoff on August 31, 2020, the mOS of the “T+A” group was 24.6 months, and that of the sorafenib group was 18.1 months; mPFS was 9.6 and 8.3 months, respectively.
According to the evaluation of RECIST 1.1 by IRF, 7 patients in the “T+A” group achieved complete remission (CR). Treatment-related grade 3/4 AEs occurred in 71 patients in the “T+A” group (49%) and 38 patients in the sorafenib group (47%).
Bleeding/bleeding AEs of any grade occurred in 34% (grade 3/4 11%) of the “T+A” group and 32% (grade 3/4 21%) of the sorafenib group.
“T+A” is the standard treatment for patients with unresectable liver cancer. In patients without MVI or EHS, the absolute results are improved compared to ITT. The safety results are consistent with the ITT population.
2. Update the Keynote-224 data again, Pembrolizumab first-line support for further research
This time, the researchers announced the latest results of untreated advanced HCC patients (cohort 2) based on an additional 6 months of follow-up. All 51 patients in cohort 2 received ≥1 dose of pembrolizumab.
The results of the study showed that the ORR was 16%, which was similar in most subgroups.
The median DOR was 16 months, 73% of patients had DOR ≥ 12 months; DCR was 57%. The median TTP was 4 months. The median PFS was 4 months, and the median OS was 17 months. The 24-month PFS rate was 15%, and the 24-month OS rate was 34%. No additional toxicity was observed, and 28 patients (55%) reported treatment-related AEs (TRAEs) (≥Grade 3, 16%).
One treatment-related death occurred in myocarditis with immune-related hepatitis.
Similar to the results of second-line treatment studies, the latest study results from Cohort 2 continue to show durable anti-tumor activity, promising OS, and manageable safety. These findings support further research on pembrolizumab-based liver cancer treatment options.
3. The ZGDH3 research subgroup data is re-announced, Older patients can still benefit from Donafinil
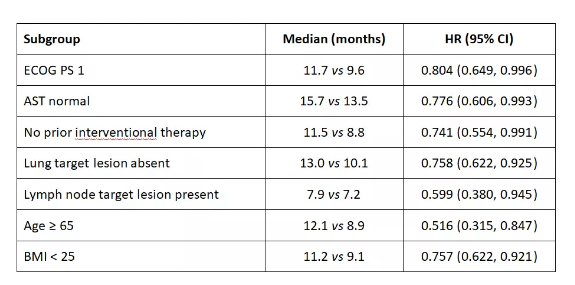
A total of 668 patients were included in the analysis (334 cases in each group). The results of the study showed that the OS benefit of the Donafenib group was superior to that of the Sorafenib group in most subgroups (point estimate of HR <1), and the difference was statistically significant in the following subgroups :ECOG PS score is 1 point (p=0.0462), AST is normal (p=0.0439), no previous interventional therapy (p=0.0433), no lung target lesion (p=0.0062), lymph node target lesion (p= 0.0277), age ≥65 years (p=0.0089), and BMI<25 (p=0.0054).
Among patients ≥65 years of age, the median OS of the Donafenib group and the Sorafenib group were 12.1 and 8.9 months, respectively, and the Donafenib group had the most significant benefit (HR 0.516, 95% CI 0.315~ 0.847).
4. KN046 combined with lenvatinib is used for Preliminary results of first-line treatment for advanced liver cancer announced

This is a phase II clinical trial conducted in China to evaluate the efficacy and safety of KN046 combined with lenvatinib in the treatment of advanced unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. As of April 8, 2021, a total of 25 patients were enrolled, with a median treatment duration of 10 weeks.
Among 21 evaluable patients, ORR was 57% and DCR was 95%. According to RECIST v1.1 and imRECIST, the same results were obtained. According to mRECIST, ORR increased to 76.2%, and DCR was still 95%. 64% of patients have experienced TEAE, 20% of which are grade 3 or above. 60% of patients have experienced TEAEs related to KN046, of which 8% were grade 3 or above.
KN046 combined with lenvatinib shows good safety and preliminary efficacy, including good anti-tumor activity, higher ORR and may further extend the survival time of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
5. Pembrolizumab and bavituximab: Phase II study of first-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma

Bavituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting phosphatidylserine (PS), which can modulate the activity of PS. Bavituximab can block the binding of PS to a variety of immune cell receptors (including TIM and TAM), block immunosuppressive signals, and reverse the PS-mediated immunosuppressive process, so that the immune system can recognize and fight tumor cells.
This phase II, open-label, multi-site trial enrolled patients with locally advanced or metastatic liver cancer who had not received systemic treatment confirmed histologically.
Among the 18 patients with evaluable safety, 4 patients had Grade 3 AEs, 1 patient had Grade 4 AEs, and 3 patients had Grade 5 AEs, but none of them was determined to be related to the study drug. Based on the data of 16 patients with evaluable remission, the overall remission rate (ORR) was 31.3% (5 confirmed partial remissions), and the disease control rate was 56.3% (5 partial remissions and 4 stable remissions).
Preliminary analysis shows that Bavituximab combined with pembrolizumab may have good anti-tumor activity in advanced HCC.
The latest data from the study, including its correlation with tumor biomarkers, will be formally displayed at the conference.
6. HAIC+Karelizumab+Apatinib: The triple plan demonstrates the strength of joint treatment

Combination of anti-angiogenesis and immune checkpoint blocking therapy has been proven to improve the clinical prognosis of advanced HCC. This phase II trial (NCT04191889) aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of transarterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) combined with carrelizumab and apatinib in the treatment of advanced liver cancer. 26 eligible patients were included in the study.
As of April 30, 2021, the median follow-up time was 8.87 months, and all patients had at least one post-baseline tumor assessment. According to RECIST v1.1, the determined ORR was 61.54%, which was a partial response (PR); the ORR estimated by mRECIST was 76.92%, with 2 cases of complete response (CR) and 18 cases of PR. Regardless of RECIST v1.1 or mRECIST, the disease control rate (DCR) was 92.31%.
The median time to response (mTTR) was 2.37 months (RECIST v1.1) or 1.67 months (mRECIST).
According to RECIST v1.1, the 6-month progression-free survival (PFS) rate is estimated to be 73.7%, and the 12-month overall survival rate is 90.7%. 69.23% of patients had ≥ grade 3 adverse events (AEs), among which neutropenia (38.46%), lymphopenia (34.62%), elevated ALT and AST (26.92%) were the most common.
In summary, the triple therapy of HAIC, apatinib and carrelizumab has good clinical efficacy and acceptable safety for BCLC-C HCC.
7. CA 209-678 research data update, Immune combined radiotherapy also has a place

At this meeting, the updated survival data of the CA209-678 study was provided, and the safety and efficacy results were analyzed again after a median follow-up of 24.8 months. In this study, eligible Child-Pugh Class A aHCC patients were treated with Y90-RE, followed by 240 mg of nivolumab, once every 2 weeks.
40 cases were enrolled, of which 36 cases can be evaluated. Based on mRECIST, the ORR was 41.7%, and the ORR in the field of radiotherapy was 58.3%; the ORR based on iRECIST was 36.1%.
The median time to remission was 3.8 months. The updated median PFS was 5.6 months, and the median OS was 16.9 months.
The most common pattern of progression is new intrahepatic lesions. 81% of patients experienced treatment-related adverse reactions (trAEs), of which 14% were G3/4, and no G5 trAEs occurred.
When comparing the ALBI scores on treatment and baseline, no significant changes were observed. Among the 19 patients with HBV DNA VL detected, 22 cases (61.6%) were hepatitis B, and the median HBV DNA VL was 120IU/mL.
All patients received antiviral treatment, and there were no cases of HBV reactivation. As of the data cutoff date of January 31, 2021, 5 patients are still receiving treatment.
8. Release of LEOPARD research data, HAIC+lenvatinib is effective
This is a multicenter, open-label, single-group, phase II trial to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of lenvatinib combined with HAIC in the treatment of advanced liver cancer (HCC). Among the 34 evaluable patients, the Independent Review Committee (IRC) evaluated ORRs based on mRECIST and RECISTv1.1 standards of 64.7% and 45.7%, respectively.
36 patients stopped treatment due to the following reasons: disease progression (24 cases, 67%), adverse events (9 cases, 25%), and others (3 cases, 8%).
The median progression-free survival and overall survival were 6.3 months and 17.2 months, respectively. The main grade 3-4 adverse events were elevated AST (34%), hyponatremia (25%), leukopenia (22%), elevated ALT (19%) and hypertension (11%).
There are no treatment-related deaths. It is necessary to further evaluate this program in a phase III trial.
9. Thermal ablation combined with Treprizumab, Treatment of advanced liver cancer can achieve complete remission

Preclinical studies have shown that thermal ablation can induce immunogenic cell death and enhance the effect of anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1).
This open-label Phase I/II trial evaluated the safety and effectiveness of ablation combined with teriprizumab in the treatment of advanced liver cancer (HCC).
Patients with advanced HCC who had received at least one systemic treatment failure were included and randomly divided into 3 groups. In group A, patients received teriprizumab monotherapy (240mg, Q3W).
In group B, patients received subtotal ablation, that is, 1-5 lesions were completely treated by thermal ablation, and the rest of the lesions remained intact. Teriplizumab (240 mg, Q3W) was started on the 3rd day after ablation. In group C, patients received teriprizumab (240 mg, Q3W) 14 days after ablation.
Forty-eight patients (16 cases in each group) were included in the study. 75% of patients experienced treatment-related adverse events (TRAE).
18.7% of patients in group A reported grade 3/4 TARE, and both groups B and C were 25.0%. There was 1 patient in group A and group B each discontinuing teriprizumab treatment due to TRAE. No TRAE leads to death.
The objective response rate (ORR) of group A was 18.8%, group B was 37.5%, and group C was 31.2%. Two patients (12.5%) in group B achieved complete remission (CR).
Therefore, it is recommended to start tolipa anti-treatment on the 3rd day after ablation for phase II evaluation.
10. Combination fights early liver cancer, Postoperative adjuvant treatment is safe and effective

Surgical resection is a radical treatment for liver cancer. However, the high recurrence rate after resection (up to 50-70% within 5 years) severely reduces the long-term survival rate of HCC patients. In particular, the survival rate of CNLC stage II and stage III liver cancer is still poor after resection.
In this single-center, open-label, prospective, phase II trial, patients receive carrelizumab (200 mg) + apatinib (250 mg/day) every 3 weeks. The primary end point is relapse-free survival (RFS): the secondary end point is safety and overall survival (OS).
The results of the study showed that among the 45 patients, there were 25 CNLC stage II patients and 20 CNLCI stage patients.
The median follow-up was 21.5 months. The median RFS was 11.7 months. The 1-year OS rate and 1-year RFS rate after surgery were 97.8% and 48.9%, respectively; the 2-year OS rate and 2-year RFS rate were 75.7% and 41.0%, respectively.
A total of 12 (26.7%) patients had adverse events, and 1 (2.2%) patients had grade 3 or 4 adverse events (grade 3 thrombocytosis and grade 4 leukocytosis). The most common adverse event was liver dysfunction (n=11/45, 24.4%). There were no deaths related to treatment.
It can be seen that this combination program has shown promising efficacy and is well tolerated in postoperative CNLC II-III HCC patients, and further research is necessary.
11. Local combined system: TACE+lenvatinib, Adjuvant treatment of patients with high risk of recurrence after surgery

This time, the researchers reported the latest results of the Lance study, which evaluated the effectiveness and safety of lenvatinib combined with TACE and TACE alone as an adjuvant treatment for patients with high risk of recurrence after liver cancer resection. The cohort has been expanded to 184 patients.
There were 92 cases in the lenvatinib+TACE group and 92 cases in the TACE group. The baseline clinicopathological characteristics between the two groups were well balanced. The median progression-free survival (DFS) in the lenvatinib + TACE group was 17.0 months, which was significantly longer than 9.0 months in the TACE group (P=0.0228).
The most common grade 3 or 4 adverse events (incidence ≥5%) were hypertension (19.6%), diarrhea (15.2%), bleeding gums (13.0%), hand-foot skin reactions (8.7%), joint pain (5.4%) ) And liver damage.
It can be seen that in the expanded cohort, lenvatinib combined with TACE showed a longer DFS than TACE alone for patients with a high risk of postoperative recurrence. There were no unexpected adverse reactions in the combination group.
12. New telomerase specific oncolytic virus OBP-301, Efficacy in advanced liver cancer

OBP-301 is a new, replication-competent adenovirus regulated by the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene (hTERT) promoter. Its replication, oncolysis and spread are limited to cells expressing the hTERT promoter, which is highly expressed in various human cancers including liver cancer.
Researchers evaluated the safety and effectiveness of intratumoral injection of OBP-301 in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). An open-label, phase I dose escalation trial (3+3 design) was conducted on 20 patients with advanced HCC who progressed after standard treatment. The results of the study show that single and multiple doses of OBP-301 are well tolerated.
The most reported TEAE related to OBP-301 was influenza-like illness (30.0%), followed by fever (15.0%), fatigue, decreased platelet count, abdominal distension and anemia (10.0% each). The overall intrahepatic mRECIST response was observed in 7 subjects (39%) with stable disease (SD) and 11 (61%) subjects with progressive disease (PD).
14 SD patients (78%) and 4 PD patients (22%) had the best target response. Multiple IT injections of OBP-301 are well tolerated in advanced HCC. Although the anti-tumor activity of the study drug alone cannot be proven, it is clear that the SD for the best local response is significantly higher than the overall response.
Biliary Tract Tumors
1. Nivolumab combined with chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of biliary tract tumors

In previous studies, modified gemcitabine and S-1 (GS) regimens were effective and safe for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (aBTC).
This time, the researchers reported the single-arm phase II clinical results of nivolumab combined with modified GS as the first-line treatment of aBTC patients.
A total of 48 patients were enrolled, with a median follow-up of 6.4 months. 1 patient showed pathological CR, 19 patients reached confirmed PR, ORR was 41.7%, and 22 patients were in stable condition (45.8%), and long-term disease control rate It was 77.1% (CR+PR+SD >12 weeks).
The median progression-free survival and overall survival were 8.0 months and not reached, respectively.
All grade 3/4 chemotherapy-related adverse events (AEs) were less than 7%; 14 patients (35.4%) had symptoms related to skin toxicity (14.6%), hypothyroidism, hypothyroiditis and pneumonia (both 6.3%) Immune-related AEs.
Two patients with grade 3 pneumonia recovered well without any treatment-related deaths.
Nivolumab combined with modified GS is a promising and safe solution, and it is worthy of further study for the treatment of Asian aBTC patients.
2. Pemigatinib: Chinese patient data released, DCR reached 100%

Pemigatinib is a selective FGFR inhibitor, showing a high degree of effectiveness and tolerability in patients with cholangiocarcinoma. It has been confirmed in the Fight 202 study that the ORR is 35.5%. What is released this time is its research data in the Chinese cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) population.
Among the 30 subjects with evaluable efficacy, 15 cases were evaluated by IRC with a confirmed response, with an ORR of 50%. The median follow-up time was 5.13 months, 13 patients still responded, the median DOR was not reached, and the median PFS was 6.3 months. The DCR is 100%. The most common TRAEs were hyperphosphatemia (73.5%), dry mouth (55.9%), and hair loss (50.0%). 14.7% of TRAEs were grade 3 or higher.
Three subjects developed SAEs, which were rectal polyps, abnormal liver function, and bile duct infection. There was no discontinuation of treatment and death due to TRAE. It can be seen that Pemigatinib is very effective and tolerable in patients with relapsed or metastatic CCA with FGFR2 fusion or rearrangement in China.
At present, the listing application of Pemigatinib has been accepted by NMPA, and we look forward to its approval as soon as possible to benefit Chinese patients!
3. New prodrug MIV-818, Phase I study in patients with hepatobiliary tumors

MIV-818 is administered as an oral capsule. MIV-818 is a targeted drug targeting the liver. Based on promising preclinical and clinical data, MIV-818 has the potential to become the first liver cancer targeted drug.
In addition to liver cancer, MIV-818 can also treat intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, which accounts for about 3-5% of liver cancer cases.
In addition, liver metastases from other tumor sites (colorectal cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and pancreatic cancer) are also the main causes of cancer-related deaths. MIV-818 has great therapeutic potential.
On May 8, 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted MIV-818 Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) for the treatment of the most common primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Nine patients can be evaluated in this phase I study, with a median age of 64 years, HCC (5 cases), mixed HCC/iCCA (1 case), iCCA (1 case), liver metastases from gastrointestinal solid tumors (LM , 2 cases), received a median of 2 systemic treatments before.
The initial dose of MIV-818 is 40 mg, for 5 consecutive days, 21 days as a cycle. The most common treatment emergency AEs occur in the blood system. Among the 9 patients, 1 patient experienced DLT (macular papules grade 3) in the first treatment cycle. The longest treatment time is 9 cycles (1 patient).
Tumor biopsy revealed selective, drug-induced DNA damage in tumor tissue, measured as phosphorylation of histone H2AX, while MIV-818 had little or no effect observed in healthy liver tissue. MIV-818 has acceptable safety and tolerability, and hematological inhibition is the most common AE.
Biomarker data from liver biopsy shows that MIV-818 has a selective effect on cancer cells. In the future, the effect of MIV-818 combined with other drugs in the treatment of HCC patients will be evaluated.
4. Phase II study of SHR1701 combined with Famitinib, For patients with treated biliary tract cancer (BTC)

SHR1701 is a bifunctional fusion protein that targets PD-L1 and TGF-β receptor II; Famitinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for multiple targets, including VEGFR 2/3, platelet-derived growth factor receptor Body beta and stem cell factor receptors.
Here, researchers report the safety and effectiveness of SHR1701 combined with Famitinib in the treatment of previously treated patients with advanced pancreatic cancer (PC) and BTC.
As of April 27, 2021, 10 patients and 4 patients were included in the PC group and BTC group. Among the 3 evaluable patients in the BTC cohort, 1 SD and 1 PR lasted 3.3+ months (tumor reduction>45%), ORR and DCR were 33% and 67%, respectively.
The most common grade 3 TRAE was increased bilirubin conjugates (2 patients), and there were no reports of grade 4/5 adverse events.
In patients with advanced PC or BTC, the combination of SHR1701 and Famitinib showed good activity and tolerable side effects. The full results will be announced at the conference.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



