Omicron-mRNA vaccine as booster: No more significant advantages
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Omicron-mRNA vaccine: No significant advantages against Omicron?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Omicron-mRNA vaccine as booster: No more significant advantages
Since its first identification in November last year, the Omicron mutant strain has continued to swept the world with its strong transmission ability.
Recently, the number of COVID-19 infections has soared again, and mass outbreaks have occurred in many places.
Compared with the original strain, the Spike protein of the Omicron mutant strain has many mutations, resulting in that the protection efficiency of the existing mRNA vaccine against the infection of the Omicron mutant strain is greatly weakened compared with other mutant strains.
The emergence of Omicron mutant strains has forced many new RNA drug development companies to develop mRNA vaccines specifically targeting Omicron mutant strains.
At the end of January this year, Pfizer and Moderna both announced that they had started clinical trials of the Omicron mRNA vaccine .
However, for these R&D companies that are eager to develop new mutant mRNA vaccines, they may face a very embarrassing situation, because some early animal data obtained so far show that after 2 injections of existing mRNA have been vaccinated On the basis of the vaccine, when the third mRNA vaccine booster is administered, the Omicron-mRNA vaccine booster does not have any significant advantages compared with choosing the existing mRNA vaccine booster .
Although many of the research articles in this area have not been peer-reviewed and are only preprints, these data provide some indication that a specific mRNA vaccine targeting Omicron mutants will not bring any Overwhelming defensive advantage.
「What we’re seeing coming out of these preclinical studies in animal models is that a boost with a variant vaccine doesn’t really do any better than a boost with the current vaccine」
In response to new mutant strains, mRNA vaccine booster becomes necessary
Many live virus and pseudovirus tests have shown that the neutralization ability of the sera of patients in the convalescent period of the COVID-19 against the Omicron mutant is reduced by 60-80 times compared with the original strain , while the sera of the original mRNA vaccine recipients are neutralized for the Omicron mutant strain.
The capacity has dropped 20-130 times compared to the original strain. In the first few months of mRNA-1273 vaccination, the vaccine protection efficiency is 30% (California data) or 37% (Denmark data), and the protection efficiency will be completely lost within six months.
Many studies have shown that Omicron mutant strains show reduced virulence in vivo after infecting humans, mice, and hamsters compared with previous new coronavirus mutant strains .
Any reduction in the natural pathogenicity of the virus may be attenuated to some extent in the context of diminished vaccine efficacy and enhanced transmission of Omicron mutant viruses in human populations worldwide . Therefore, these data suggest that limiting the spread of Omicron mutants is necessary .
The new coronavirus mRNA vaccines BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 showed very significant protection in preventing the infection of the original strain of the new coronavirus and reducing the incidence of severe illness.
The protective efficacy of mRNA vaccines declines in response to emerging mutant strains due to the time-dependent decline of vaccination-triggered immunity and the mutation of viral epitopes (different mutants).
After the initial immunization is completed, the booster vaccination can improve the body’s immunity and protection efficiency, and reduce the infection rate, hospitalization rate and mortality rate. However, different types of mutant strains of the virus have different transmissibility and virulence, therefore.
Selecting the timing and type of booster vaccination is a very important challenge for basic virus research and development and clinical treatment .
Omicron-mRNA vaccine boosts the immune effect of injection-rhesus monkey model
On February 4, 2022 , Robert A. Seder submitted the article mRNA-1273 or mRNA-Omicron boost in vaccinated macaques elicits comparable B cell expansion, neutralizing antibodies and protection against Omicron in BioRxiv , which showed that in an Indian rhesus monkey model On the basis of having received two doses of mRNA-1273 vaccine , either homologous booster mRNA-1273 or heterologous booster mRNA-Omincron can trigger significant antibody titers targeting various VOC mutants, including Omicron.
More importantly , the magnitude of the antibody titer increase caused by the two types of boosters was roughly equivalent , but the overall level of neutralizing antibody titers targeting various mutant strains in the serum inoculated with the Omicron heterologous booster Both were slightly lower than those inoculated with homologous booster mRNA-1273.
Indian rhesus macaques were vaccinated with 100ug mRNA-1273 vaccine at intervals of 0 and 4 weeks to complete the initial immunization . At weeks 6 and 41, titers of Binding antibody ( IgG ) targeting the S protein of various mutant strains in serum were determined.
The results showed that at the 6th week, the distribution of Binding antibody titers: WA1>Delta>Beta>Omicron. At the 41st week, the Binding antibody titers decreased significantly, and the geometric mean ( GMT ) of both WA1-targeting and Omicron-targeting Binding antibody titers decreased by 7 orders of magnitude ( GMT of 2×10^12^ and 2×10^8^ AUC). for WA1 and Omicron ).
Nine months after the initial immunization, that is, at the 41st week, the 50ug homologous mRNA-1273 booster or the heterologous mRNA-Omicron booster was re-inoculated , and the titer of the binding antibody targeting the S protein could be recovered to the sixth week. time level.
Compared with other types of mutants, the titer of Binding antibody targeting Omicron is still the lowest.
Binding antibody titers targeting various mutant RBD strains in serum, or neutralizing antibody titers by live virus or pseudovirus serum neutralization assays , yielded generally similar results. After Indian rhesus monkeys completed the initial immunization of mRNA-1273 vaccine at weeks 0 and 4, the neutralizing antibody titers targeting D614G in serum at weeks 6 and 41 were 4760 and 270, respectively; Neutralizing antibody titers to Omicron were 320 and 110, respectively.
At week 41, the neutralizing antibody titers targeting D614G and Omicron in the sera of Indian rhesus monkeys vaccinated with the mRNA-1273 homologous booster were 5360 and 2980, respectively, while those vaccinated with the mRNA-Omicron heterologous booster in India The titers of neutralizing antibodies targeting D614G and Omicron in rhesus monkey serum were 2670 and 1930, respectively.
The above test data is a very good thing for us, which means that the immune protection efficiency against various mutant strains can be improved by inoculating the existing homologous mRNA vaccine booster . Of course, since this study only tested the immune response after 4 weeks of booster vaccination, it is not clear how long the increased antibody titers in serum can last.
「It means we’re still able to cover all known variants with a boost of the current vaccine」
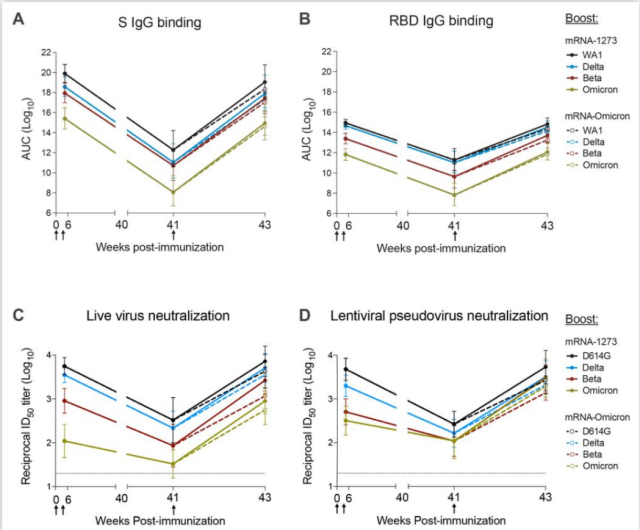
Kinetic characteristics of serum antibody responses after mRNA-1273 initial and booster immunizations
Omicron mRNA Vaccine Booster Immune Effect – Mouse Model
On February 9, 2022 , Michael S. Diamond submitted the article Boosting with Omicron-matched or historical mRNA vaccines increases neutralizing antibody responses and protection against B.1.1.529 infection in mice in BioRxiv . The article showed that in a mouse model, No matter inoculation with mRNA-1273 homologous booster needle or inoculation with Omicron-mRNA heterologous booster needle can improve the protection against Omicron mutant infection, but there is a slight difference in protection efficiency .
- The titers of neutralizing antibodies targeting the original WA1/2020 strain in the serum of mice inoculated with 2 doses of mRNA1273 could reach high, but the neutralizing antibody titers targeting the Omicron mutant were relatively low . Mice vaccinated with 2 doses of mRNA1273 developed infection and inflammation in the lungs when tested against the Omicron mutant.
- The serum of mice inoculated with 2 doses of Omicron-mRNA can effectively neutralize the Omicron mutant, but the neutralization ability of other types of new coronaviruses is limited . (Yesterday’s article COVID-19 | The immunogenicity of RBD mRNA vaccines of different mutant strains in mice also shows that after the first inoculation of Omicron RBD vaccine in mice, the body can induce the body to produce serum neutralizing antibodies targeting Omicron mutant strains, but cannot produce Serum neutralizing antibodies targeting other types of mutant strains)
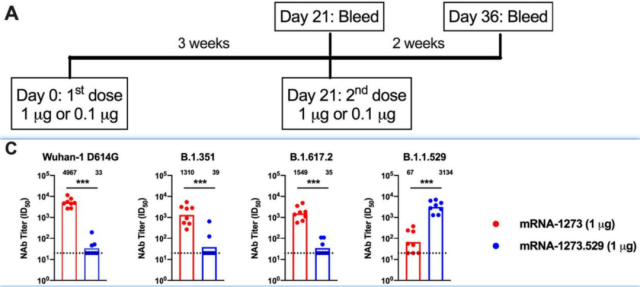 Serum neutralizing antibody titers after 2 doses of mRNA1273 or Omicron-mRNA vaccine
Serum neutralizing antibody titers after 2 doses of mRNA1273 or Omicron-mRNA vaccine
- After inoculation with mRNA1273 booster needle and Omicron-mRNA booster needle , the neutralizing antibody titer targeting Omicron mutant strain in serum can be increased, and the mice can be protected against Omicron mutant strain infection.
- Mice vaccinated with the Omicron-mRNA booster had relatively higher neutralizing antibody titers in serum and lower cytokine and viral loads in the lungs.
- Both the mRNA1273 booster and the mRNA127.529 booster can improve the body’s immunity against infection with Omicron mutant strains, but there is a slight difference in the immune efficiency between the two boosters.
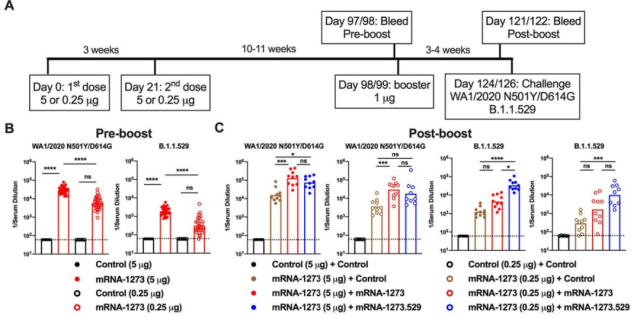
Omicron mRNA self-replicating vaccine booster immune effect-hamster model
On February 3, 2022 , Jesse H. Erasmus uploaded the article Replicating RNA platform enables rapid response to the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and elicits enhanced protection in naïve hamsters compared to ancestral vaccine in BioRxiv , which is less than two Within a short period of time, the self-replicating mRNA vaccine expressing the Spike protein of the Omicron mutant strain was quickly prepared, and the animal immunization test was also completed, and very interesting data were obtained: if the hamsters have been vaccinated with the original self-replicating mRNA vaccine, then the Omicron will be vaccinated again. – After the booster shot of the self-replicating mRNA vaccine, the neutralizing antibody titer targeting Omicron in the serum could not be increased , which indicates that the pre-existing immunity of the original target strain in the hamsters was not effective for the Omicron-self-replicating mRNA vaccine. The process of boosting acupuncture to induce the body to regenerate specific immunity causes interference .
In addition, they inoculated naive hamsters with 20ug of the original strain self-replicating mRNA vaccine or Omicron-self-replicating mRNA vaccine. On the 28th day, they infected the vaccinated hamsters with Omicron, and the result induced the body Serum homologous neutralizing antibodies were produced, but heterologous neutralizing antibody titers were barely detectable.
That is to say, hamsters who have never been vaccinated, if vaccinated with a dose of Omicron-self-replicating mRNA vaccine, can induce the body to produce serum neutralizing antibodies targeting Omicron, but cannot produce serum neutralizing antibodies targeting other mutants .
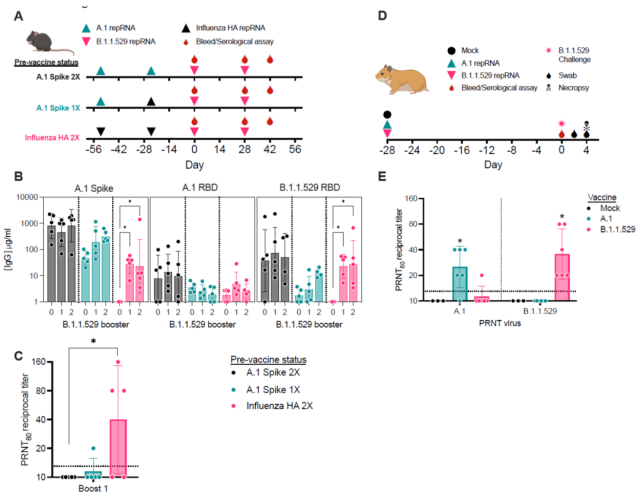 Serum antibody response after Omicron-self-replicating mRNA vaccine booster
Serum antibody response after Omicron-self-replicating mRNA vaccine booster
Summary
The differences in the immune responses triggered by homologous or heterologous booster shots of mRNA vaccines in the above studies indicate that Omicron-mRNA vaccine booster shots are not the only way to deal with Omicron mutants with high transmission efficiency .
This gives domestic mRNA vaccine research and development companies a point to consider when choosing targets.
As far as the early data of Omicron booster needles have been obtained, it seems that there is not much advantage in choosing to develop Omicron mRNA vaccines.
Judging from the data in yesterday’s article, the immunogenicity of different mutant RBD mRNA vaccines in mice , the development of Delta-mRNA is a better choice , because the sera of mice vaccinated with Delta RBD vaccine are not suitable for D614G, Beta, Delta , Omicron mutants also displayed very high neutralization capacity.
Of course, many of the immunological mechanisms of the booster need to be further explored. For example, what are the differences in the immune response of the body to the new mutant after different types of vaccine boosters?
Does this difference significantly improve the body’s ability to generate specific immunity against the new mutant strain?
If the difference is small, can direct vaccination with the original type of homologous strain vaccine improve the body’s immunity against mutant strains?
It is hoped that the clinical trials of Pfize and Moderna Omicron vaccines will address these issues, so that the timing and type of vaccine booster injections will provide important evidence .
Reference:
Financial Times:Covid success of mRNA vaccines opens way to a new generation of drugs
Omicron-mRNA vaccine as booster: No more significant advantages
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



