2022 ASCO: 11 important advances on cancer treatment
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
2022 ASCO: 11 important advances on cancer treatment
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
2022 ASCO: 11 important advances on cancer treatment.
This article will introduce 11 important advances in three major categories of breast cancer, gynecological tumors and skin cancer.

丨588
Neoadjuvant regimens of pyrotinib, letrozole, and dalcili can provide a new treatment paradigm without chemotherapy for triple-positive breast cancer patients
Although multiple targeted therapy regimens have revolutionized the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer, the efficacy of these regimens in triple-positive breast cancer (TPBC) remains limited, thus requiring continuous optimization of treatment strategies.
This MUKDEN-01 prospective clinical trial was designed to evaluate the efficacy of pyrotinib and letrozole plus dalcilis as a neoadjuvant regimen for TPBC, which is oral and chemotherapy-free for TPBC in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic The patient’s treatment provides convenience.
MUKDEN 01 is a multicenter, single-arm, prospective Phase II clinical trial conducted in 12 hospitals in China (NCT04486911).
Patients with untreated stage II-III tumors were eligible according to AJCC 8th edition criteria. The patients received a total of 5 cycles of treatment, every four weeks as a cycle. In each cycle, the patients were given oral pyrotinib 320 mg, letrozole 2.5 mg once a day for a total of 4 weeks; 3 weeks, followed by a week off.
The primary endpoint was pathological complete response (pCR) in breast and axilla (ypT0/is ypN0). Secondary endpoints included breast pCR (ypT0/is), residual cancer burden (RCB) score, change in Ki67 index at surgery compared to baseline, and safety.
A safety analysis was performed on all treated patients.
Between June 20, 2020, and September 6, 2021, the study screened a total of 68 patients and recruited 61 patients into the Phase 1 study.
After surgery, 18 of 61 patients (29.5%, 95% CI 18.5-42.6) achieved tpCR (ypT0/is ypN0) and 21 (34.4%, 95% CI 22.7-47.7) patients achieved bpCR (ypT0/is) ).
TPBC had a favorable pathological response to this combination therapy, with 54.1% of patients (33/61, 95% CI: 40.9-66.9) achieving RCB 0-1.
Mean Ki67 expression decreased from 38.7% (95%CI: 31.3-46.0) at baseline to 19.3% (95%CI: 13.6-25.0; p=0.0001) at surgery. The most common grade 3 adverse events (AEs) were neutropenia (35 [57%]), leukopenia (13 [21%]), diarrhea (9 [15%]) and oral mucositis (4 [7%]).
Five patients experienced grade 4 neutropenia (8%) and one patient experienced grade 4 AST elevation (2%), but there were no other SAEs and deaths throughout the study.
In TPBC, treatment with pyrotinib, letrozole, and dalcilli yielded comparable pCR rates compared with neoadjuvant treatment with dual HER2 antibodies plus standard chemotherapy.
The combination therapy was also well tolerated, providing a chemotherapy-free neoadjuvant therapy for TPBC patients.
To the investigators’ knowledge, this study is the first in TPBC to evaluate a neoadjuvant regimen of the HER2 TKIs pyrotinib and letrozole plus the CDK4/6 inhibitor dalcelli. Further validation in large-scale randomized controlled trials is necessary.
丨602
Neoadjuvant ipilimumab and nivolumab combined with paclitaxel in triple-negative breast cancer patients with poor response to anthracycline chemotherapy can achieve better ORR and pCR
This study investigated the efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant ipilimumab and nivolumab in combination with paclitaxel after poor response to anthracycline-based chemotherapy in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
This single-arm, multicenter Phase 2 study enrolled 34 patients at eight centers. The patients were aged ≥18 years, newly treated with stage 3 TNBC, and required residual tumor ≥15 mm or tumor 10 mm with a positive lymph node after 4 cycles of anthracycline therapy.
The subgroup with suboptimal response at baseline was defined as <50% tumor volume reduction after initial anthracycline chemotherapy.
The patient received neoadjuvant ipilimumab 1 mg/kg intravenously once every 6 weeks for 2 times, nivolumab 240 mg once every 2 weeks for 6 times; paclitaxel 80 mg/m² weekly for a total of 6 times 12 weeks, followed by surgery.
Nivolumab (480 mg, 4 times a week) was continued for 9 months postoperatively. The primary endpoint was pathological complete remission (pCR) in breast and axilla, and secondary endpoints were pCR in patients with unsatisfactory response, pCR in programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) positive patients (≥1% detected by SP142 method), breast Clinical response [objective response rate (ORR) as assessed by Response Evaluation Indicators in Solid Tumors (RECIST)], event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS).
From December 2018 to April 2020, 34 patients were enrolled and 33 were evaluable for the primary endpoint. The median age was 46.6 years.
At diagnosis, all patients were clinical stage III (AJCC v8), 16/34 (47%) were node-positive and 8/31 (26%) were PD-L1-positive.
At the start of the study (after anthracycline chemotherapy), the median tumor size on ultrasound was 28 mm (12-62). 16/33 (48%) were considered suboptimal responders.
Among all evaluable patients, the pCR rate (ypT0ypN0) was 24.2% (95% CI, 11.09-42.26), 37.5% (3/11) in PD-L1+ patients, and 23 in PD-L1- patients % (5/22).
Among patients with suboptimal anthracycline responses (< 50% tumor shrinkage), the pCR rate was 18.8% (95% CI, 8.52-75.51) (3/16).
Among all evaluable patients, the ORR was 57.6% (19/33) for breast and 43.7% (8/20) for those with suboptimal responses.
The number of patients with residual tumor burden (RCB) of grade 0, 1, 2, and 3 was 8 (24%), 1 (3%), 19 (57.5%), and 5 (15%), respectively.
With a median follow-up of 14 months, the estimated 12-month EFS was 85% and OS was 94%.
The hazard ratio (HR) for EFS was 0.62 in patients with pCR compared with patients without pCR, and the 12-month EFS was 100% and 75%.
During the neoadjuvant phase, 15/33 (45%) patients experienced at least one grade 3-4 adverse event.
The most common immune-related event was grade 1 or 2 pneumonitis (9/33, 27%), which usually occurred after the first dose of ipilimumab, accompanied by fever, and resolved thereafter. There was a case of grade 3 colitis.
In these high-risk patients, neoadjuvant ipilimumab and nivolumab combined with paclitaxel resulted in promising ORR and pCR rates regardless of PD-L1 status. The incidence of low-grade pneumonia is high. Follow-up continues.
丨1035
81.6% ORR in patients with HER2-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer treated with pyrotinib combined with nab-paclitaxel
For human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer, the standard treatment strategy is a combination of HER2-targeted drugs and taxanes.
This multicenter, single-arm, phase 2 trial was designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pyrotinib in combination with nab-paclitaxel in patients with HER2-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
This is a multicenter, single-arm, open-label Phase 2 trial (ChiCTR1900023653) conducted at seven centers in China.
Enrolled female patients were 18-75 years old with histologically or cytologically confirmed HER-2-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Physical Fitness Score (ECOG PS) of 0-1. Patients with primary resistance to trastuzumab and only bone metastases were excluded.
Eligible patients received pyrotinib (400 mg, po, qd) plus nab-paclitaxel (125 mg/m², iv, days 1/8/15) in each 28-day cycle until disease progression, unacceptable Toxicity, withdrawal of informed consent, or death. The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR), defined as the proportion of patients with a complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) according to RECIST version 1.1. Secondary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival, safety, and quality of life.
From December 2019 to December 2021, a total of 51 patients were enrolled. The median age was 55 years (range 35-72 years).
Twenty-three patients (45.1%) had an ECOG PS of 0. Ten patients with metastatic disease (19.6%) had previously received first-line therapy, and 28 (54.9%) had previously received trastuzumab.
More than half (29/51, 56.9%) were hormone receptor positive.
Visceral metastases occurred in 56.9% of patients (29/51), and 26 patients (51.0%) were postmenopausal. The data cutoff date for this analysis was January 21, 2022.
Of the 38 evaluable patients, 4 patients (10.5%) had CR, 27 patients (71.1%) had PR, 6 patients (15.8%) had stable disease, and 1 patient (2.6%) had progressive disease.
The confirmed ORR was 81.6% (95% CI, 65.1-91.7%). PFS data is immature. The most common grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events included neutropenia (14/51, 27.5%), diarrhea (10/51, 19.6%), fatigue (5/51, 9.8%) and peripheral neuropathy ( 4/51, 7.8%).
In patients with HER2-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer, pyrotinib combined with nab-paclitaxel showed promising antitumor activity and was well tolerated.
丨1071
Patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer receive higher survival benefit with goxatuzumab than standard single-agent chemotherapy
Treatment goals for patients with metastatic breast cancer include prolonging survival and improving quality of life (QoL).
Goxatuzumab (SG) is an antibody-drug conjugate composed of an anti-Trop-2 antibody conjugated to a cytotoxic payload, SN-38, via a proprietary hydrolyzable linker.
SG has received FDA approval for the treatment of patients with triple-negative breast cancer who have received ≥2 prior lines of chemotherapy (at least 1 line for metastatic stage).
In the pivotal Phase 3 ASCENT study (NCT02574455), SG versus physician’s choice (TPC) single-agent chemotherapy regimen in the primary analysis population of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer with no known brain metastases at baseline in second-line or above (2L+) showed a significant survival benefit and QoL. With further follow-up, the study provided final data on efficacy, including overall survival (OS), safety, and QoL.
Patients with relapsed or refractory metastatic triple-negative breast cancer who have received ≥2 lines of chemotherapy and at least 1 line in the metastatic stage were randomized 1:1 to the SG treatment group (10 mg intravenously on days 1 and 8). /kg every 21 days) or TPC (capecitabine, eribulin, vinorelbine, or gemcitabine) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) in patients without brain metastases independently assessed according to RECIST 1.1. Key secondary study endpoints include OS, safety and health-related QoL. A safety analysis was performed in patients who received ≥1 dose of study drug.
Of the 529 patients recruited, 468 were free of brain metastases at baseline (median age: 54 years [range 27-82]; median number of lines of prior therapy: 4 [range 2-17]).
As of February 25, 2021 (final lock-up), compared to TPC (n=233), SG (n=235) significantly improved median patient PFS (5.6 months vs 1.7 months; HR: 0.39; P<0.0001) , and median OS (12.1 vs 6.7 months; HR: 0.48; P<0.0001). At 24 months, the OS rate was 22.4% (95% CI, 16.8-28.5) in the SG group and 5.2% (95% CI, 2.5-9.4) in the TPC group.
In the safety analysis (n=482), SG (258 patients) vs TPC (224 patients) ≥ grade 3 critical treatment-related adverse events were diarrhea (11% vs 0.4%), neutropenia (52% vs 52%) 33%), anemia (8% vs 5%), and febrile neutropenia (6% vs 2%). No grade ≥3 neuropathy occurred, and one patient treated with SG developed grade 3 interstitial lung disease.
There were no treatment-related deaths in the SG group, and one patient in the TPC group resulted in a treatment-related death from neutropenic sepsis.
The incidence of treatment discontinuation due to adverse events was ≤3% in both groups. Compared with the TPC group, the SG group had clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvements in all five major health-related QoL domains.
This study analyzed the final lock library data based on the ASCENT study.
The study confirmed that SG has a survival advantage compared with single-agent chemotherapy in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer who have received ≥ 2 lines, and the safety is controllable. Quality is improved.
These findings once again demonstrate that SG can be an effective treatment option for this patient population.
丨1072
Apatinib plus chemotherapy in patients with HER2-negative advanced/metastatic breast cancer significantly improved PFS compared to chemotherapy alone
Apatinib is an oral, potent tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2).
A series of clinical studies have shown that anti-angiogenic drugs combined with chemotherapy can improve the efficacy of HER2-negative advanced/metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
Patients with HER2-negative MBC who received fewer than 2 lines of systemic therapy were included in this open-label, controlled, phase II trial.
Patients with measurable disease were randomized 1:1 to receive oral apatinib (250 mg once daily) with chemotherapy (A+CT) or chemotherapy alone (CT) until disease progression or intolerance toxicity.
The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by investigators and analyzed on an intention-to-treat basis.
Between August 2017 and January 2021, of the 80 patients who underwent randomization, 40 were assigned to receive A+CT and 40 were assigned to CT.
As of January 2022, 10 patients were not assessed for response or withdrew, 70 patients (36 A+CT patients, 34 CT patients) were ultimately included in the PFS event analysis, and 72 patients were included in the safety data analysis.
Median PFS was significantly longer in the A+CT group than in the CT group (182 days vs 63 days; p = 0.043); triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) subgroup (11 in the A+CT group and 14 in the CT group; 167 days vs 63) days, p = 0.637); HR+ subgroup (25 in A+CT group, 20 in CT group; 259 days vs 56 days, p = 0.054); patients with liver metastases (19 in apatinib group, 17 in chemotherapy group) ; 151 days vs 54 days, p = 0.191) for the median PFS. In A+CT group and CT group, serious adverse reactions (grade 3/4) were neutropenia (22.2% vs 13.9%), hypertension (11.1% vs 0.0%), leukopenia (8.3%) % vs 8.3%), hypokalemia (8.3% vs 2.8%), anemia (5.6% vs 11.1%), ALT (2.8% vs 8.3%), AST (0.0% vs 5.6%).
There was no proteinuria in either group. Treatment delays or dose reductions due to adverse events were 16.7% and 11.1%, respectively. The rates of treatment discontinuation due to adverse events were 23.5% and 8.8%, respectively.
In patients with HER2-negative MBC, apatinib combined with chemotherapy showed significant improvement in PFS and a manageable safety profile.
丨5510
Combination of bevacizumab + atezolizumab + Rucaparib for endometrial cancer that has recurred and progressed after prior therapy
Currently, treatment options for patients with metastatic and recurrent endometrial cancer are limited.
Patients with mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR) can be treated with pembrolizumab, while patients with normal MMR who have progressed after combination chemotherapy are often treated with a combination of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab.
This trial investigated the efficacy of a new triple-drug regimen for recurrent and progressive endometrial cancer.
In this multicenter, open-label, nonrandomized, phase 2 trial, patients with recurrent endometrial cancer (any histology included) who were reluctant to undergo curative surgery or radiation therapy after 1 or 2 treatments were included. All subjects initially received triple therapy with bevacizumab, atezolizumab, and Rucaparib.
The primary objective of this trial was to assess patients’ overall response rate (ORR), followed by progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
The total number of recruits was 30, and the first 6 subjects participated in the safety guidance.
The treatment of the patients continued until the disease progressed, toxic reactions occurred, or the clinician deemed it necessary to stop the treatment.
If the clinician and the subject agree that the subject would benefit from the treatment, the patient may continue the treatment even if there is progression.
Subjects were included in the analysis if they had received at least one cycle of treatment and had a post-treatment tumor assessment.
From July 2019 to June 2021, a total of 30 subjects were included in the study, of which 26 were evaluable for efficacy, and the median follow-up period was 14.9 months.
A total of 23 patients benefited from the treatment, including 1 (4%) complete remission (CR), 9 (39%) partial remission (PR), and 13 (57%) stable disease.
Overall median PFS was 5.3 months, median OS was 13.3 months, and median treatment duration was 4.4 months, with 4 subjects still on triple therapy.
The histological classification of tumors was as follows: serous tumors accounted for 50%, endometrioid carcinomas accounted for 20%, and sarcomas accounted for 13%. Among MMR-deficient patients, event-free survival was 11.9 months.
Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 50% of patients.
This trial is the first to use a non-chemotherapy-based triple therapy in patients with recurrent endometrial cancer. Preliminary results show that bevacizumab, atezolizumab and Rucaparib can be safely used in the treatment of patients with recurrent/progressing endometrial cancer.
This combination has certain clinical efficacy and controllable toxicity. Notably, MMR-deficient subjects responded better to treatment.
丨5512
Efficacy of Mirvetuximab-soravtansine (MIRV) in the treatment of folate receptor alpha (FRα) overexpressing platinum-resistant ovarian cancer
MIRV is an antibody-drug conjugate comprising a FRα-binding antibody, a cleavable linker, and a potent tubulin targeting agent (maytansinoid DM4).
This study (SORAYA) is a global single-arm, phase 3 clinical trial to evaluate MIRV in patients with FRα-expressing platinum-resistant ovarian cancer (PROC).
In this study, MIRV demonstrated broad antitumor activity in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer regardless of the number of lines of prior therapy or PARPi treatment.
At this conference, Prof. Ursula A. Matulonis gave a detailed introduction to the treatment response that is very important for clinical decision-making.
This trial enrolled patients with primary tumors with high FRα expression by immunohistochemistry (at least 75% of cells with PS2 staining intensity detected by Roche FOLR1) who had received 1-3 prior treatments, including bevacizumab.
In a 21-day cycle, patients received IV MIRV (6 mg/kg, adjusted ideal body weight) on day 1 of each cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Primary endpoint was investigator (INV) objective response rate (ORR) according to RECIST v1.1, key secondary endpoint was duration of response (DOR), additional endpoints included duration of response, CA-125 response, safety and tolerability sex.
A total of 106 patients were enrolled, of which 51% had received 3 lines of therapy, 48% had received 1-2 lines of therapy, and 48% had received PARPi therapy. The INV-assessed ORR was 32.4% (95% CI, 23.6%-42.2%), including 5 complete responses.
The median time to response was 1.5 months (1.0-5.6), and 71% of patients had tumor shrinkage.
At the time of the protocol-specified primary analysis (November 16, 2021), the median DOR was 5.9 months (95% CI, 5.6-7.7), and among the 15 responders receiving MIRV, the DOR continued to evolve.
Among 86 patients evaluable for CA-125 response (by between-group criteria for gynecologic cancers), responses were observed in 46.5% (95% CI, 35.7-57.6), the depth and duration of responses and the effect of dose adjustments , which will be provided when the data is updated.
The most common treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) included: blurred vision, keratopathy, nausea, with the incidence of all-grade and grade 3+ TRAEs being: blurred vision (41%, 6%), keratopathy (36%, 9%), nausea (29%, 0%). TRAEs resulted in dose delays in 32% of patients, dose reductions in 19%, and discontinuation in 7%; one patient discontinued treatment due to an ocular event. MIRV-tolerated adverse reactions included low-grade, reversible ocular and grade I TRAEs, which were managed with dose adjustment and supportive care.
Overall, the current treatment options for PROC patients are limited, and MIRV is the first biomarker-directed therapy to show antitumor activity in patients with high FRα expression.
These results confirm the clinical significance of MIRV for patients with FRα-high PROC, regardless of the patient’s prior treatment regimen or dose adjustment.
丨5551
Subgroup analysis of the phase 3 PRIME study: efficacy of niraparib maintenance as first-line platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer
In the PRIME trial, niraparib reduced the risk of disease progression or death in Chinese patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer by 55% compared with placebo (PBO) regardless of patient biomarker status (95% CI, 0.34 -0.60).
Since response to chemotherapy is thought to be associated with prognosis in patients with advanced ovarian cancer, a subgroup analysis of this pilot study aimed to better understand the effect of niraparib on patients based on response to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy (1L CT) .
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial enrolled patients with newly diagnosed stage III or IV ovarian cancer who had a complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) on 1L CT and received initial or intermittent Cytoreductive surgery regardless of postoperative residual disease status.
Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive niraparib or placebo, with a starting dose individualized based on baseline body weight and platelet count and based on germline BRCA mutation status (yes or no), tumor homologous recombination status ( were stratified by clinical response (CR or PR) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (yes or no), and 1L CT.
This prespecified exploratory analysis reported progression-free survival (PFS) and hazard ratios (HRs) based on clinical response on 1L CT. Data cutoff date is September 30, 2021.
Of the 384 randomized patients, 315 (82.0%) had complete remission after 1L CT, 212 in the niraparib group or 103 in the placebo group; 69 had a partial remission cases (18.0%), of which 43 and 26 were in the niraparib group or the placebo group, respectively. Baseline characteristics are listed in the table below.
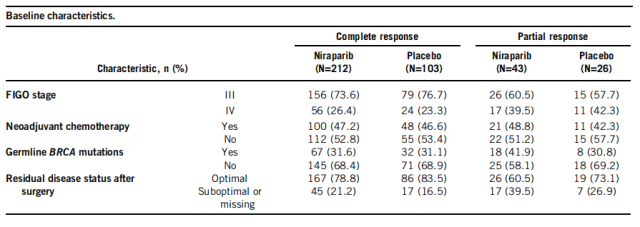
Baseline Characteristics
The median follow-up time was 27.5 months. In the complete remission population, niraparib significantly prolonged PFS compared with placebo, with a median PFS of 29.4 months in the niraparib group and 8.3 months in the placebo group, and a 55-55 reduction in the risk of disease progression or death % (95% CI, 0.32-0.61; P<0.001), in the partial response population, median PFS was 19.3 months in the niraparib group and 8.3 months in the placebo group, with a 55% reduction in the risk of disease progression or death ( 95% CI, 0.23 -0.86; P = 0.014).
In patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer, niraparib significantly prolonged PFS compared with placebo, regardless of response to chemotherapy and biomarker status . In addition, patients who achieved a complete response appeared to benefit more from niraparib than those who achieved a partial response.
丨9512
Combination therapy with toripalimab plus axitinib is superior to toripalimab or axitinib alone in patients with unresectable or metastatic mucosal melanoma
A phase IB clinical trial demonstrated the combination of toripalimab (T, a PD-1 antibody) combined with axitinib (A, a VEGF receptor inhibitor) in untreated unresectable or metastatic mucosa Good antitumor activity in melanoma.
This phase II clinical trial compared two-drug combination therapy with monotherapy.
In this randomized, controlled, phase II clinical trial, patients with unresectable or metastatic mucosal melanoma were stratified according to PD-L1 expression and were randomized 1:1:1 into three groups: Received T+A (toripalimab 240 mg IV every 3 weeks, axitinib 5 mg orally twice daily), T treatment (toripalimab 240 mg IV every 3 weeks) 3 weeks) or Treatment A (axitinib 5 mg orally twice daily).
After disease progression, patients in group T or group A can be crossed over to group T+A for treatment if they are eligible. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS). Secondary endpoints included objective response rate (ORR), duration of response (DOR), overall survival (OS) and safety.
From November 2019 to January 2022, 51 patients were randomly assigned to the three treatment arms (as of the preliminary efficacy analysis, 18 patients were assigned to T+A arm, 20 patients were assigned to arm T , and 13 patients were assigned to arm Group A ).
According to anatomical site, head and neck, gastrointestinal tract and gynecological mucosa melanoma accounted for 49.0% , 29.4% and 21.6% , respectively . For unresectable stage II or III , M1a , M1b , and M1c accounted for 3.9% , 23.5% , 17.6% , and 51.0% , respectively . T+A , T ,In group A , 55.6% , 45.0% , and 53.8% of patients were PD-L1 positive ( ≥1% PD-L1 expression in tumor cells and / or infiltrating immune cells ), respectively. There were 17 , 17 and 12 patients evaluable in groups T+A , T and A , respectively.
Twenty -four patients in either group T or group A crossed over to group T+A after disease progression .
At a median follow-up of 6.60 months, patients treated with T+A had higher median PFS compared with T or A (5.83 vs 2.80 vs 1.40 months; HR 0.538, 95% CI 0.237 to 1.221; HR 0.444, 95%CI 0.182 to 1.081; P=0.170), higher median ORR (35.3% (29.7% if crossover patients) vs 17.6% vs 8.3%), and higher DOR (82.4% (if crossover included) patients (70.3%) vs 52.9% vs 58.3%). Median OS was not reached.
Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) occurred in 80.4% of patients.
The most common TRAEs are mild (grade 1 or 2) and include diarrhea, proteinuria, hand-foot syndrome, fatigue, elevated transaminases, elevated bilirubin, hypertension, hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, and rash .
The proportions of patients with grade 3 or higher TRAEs in T+A, T, and A groups were 33.3%, 30.0%, and 30.8%, respectively.
Overall, the combination of toripalimab with axitinib compared with toripalimab or axitinib alone in the treatment of treatment-naïve patients with unresectable or metastatic mucosal melanoma was more effective. Good antitumor activity.
丨9525
Efficacy of atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab in patients with unresectable or metastatic mucosal melanoma
PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy is part of the standard of care in cutaneous melanoma, but has shown lower efficacy in mucosal melanoma.
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced mucosal melanoma.
This multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study used a Simon’s two-stage design.
Atezolizumab (fixed dose, 1200 mg ) and bevacizumab ( 7.5 mg/kg ) were administered intravenously every 3 weeks. The primary study endpoint was objective response rate ( ORR ) as determined by investigators according to RECIST v1.1 .
Secondary study endpoints included progression-free survival ( PFS ), overall survival ( OS ), duration of response ( DOR ), disease control rate ( DCR ) and safety of adverse events summarized using NCI-CTCAE v5.0 .
A total of 43 patients were included in the study, of which 20 ( 46.5% ) had unresectable mucosal melanoma and 23 ( 53.5% ) had metastatic mucosal melanoma. Median follow-up at data cutoff ( July 30 , 2021 ) was 13.4 months.
40 patients were evaluable for efficacy: In the phase I analysis set (n=22), the best confirmed ORR was 40.9% (9/22; 95% CI 20.7-63.7) according to RECIST v1.1 criteria, including 1 Complete remission (CR) and partial remission (PR) in 8 cases.
The ORR in the FAS population was 45.0% (95%CI, 29.3-61.5) (1 CR, 17 PR), and the DCR was 65.0% (95%CI, 48.3-79.4). The median PFS was 8.2 months (95%CI, 2.7-9.6), and the PFS rates at 6 and 12 months were 53.4% (95%CI, 36.6-67.6) and 28.1% (95%CI, 14.2- 43.9). Median OS (NR) was not reached (95%CI, 14.4-NR), and the 6- and 12-month OS rates were 92.5% (95%CI, 78.5-97.5) and 76.0% (95%CI, 57.1), respectively -87.5). The median DOR was 12.5 months (95% CI, 5.5-NR).
In terms of safety, 90.7% (39/43) patients experienced treatment-related adverse events, and 25.6% (11/43) patients experienced grade ≥ 3 adverse events.
Overall, atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab showed good efficacy and manageable safety profile in patients with advanced mucosal melanoma.
丨9578
The Peking University Cancer Hospital team found that temozolomide + cisplatin is more effective than high-dose interferon alpha-2b in the treatment of excised mucosal melanoma
Mucosal melanoma (MuM) is a rare cancer with an extremely poor prognosis for which there is currently no standard adjuvant therapy.
A phase 2 trial showed satisfactory efficacy of temozolomide in combination with cisplatin (chemotherapy) compared with high-dose interferon alfa-2b (HDI) therapy in patients with resected mucosal melanoma.
Peking University Cancer Hospital conducted a phase 3 trial to further compare the efficacy of the two treatments.
In this multicenter, randomized, controlled, phase 3 trial, patients who underwent total tumor resection with pathologically confirmed stage I-III mucosal melanoma were enrolled and were classified by primary site (head and neck and Non-head and neck) and disease stage (stage I/II vs. III) were randomized 1:1 to chemotherapy (oral temozolomide 200 mg/m²/d on days 1-5, and 1-3 Cisplatin 75 mg/m² intravenously every 3 weeks for 6 cycles) or HDI group (15×10 6 U/ m² intravenously on days 1-5 per week for 4 weeks, then 3 times per week 9×10 6 U for 48 weeks).
The total postoperative radiotherapy dose for head and neck MuM patients was 65-70 Gy/30-35 fx in the imaging target volume (GTV) and 60 Gy/30 fx in the clinical target volume (CTV).
The primary endpoint was recurrence-free survival (RFS), and secondary endpoints of the study included distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), overall survival (OS), and safety.
From February 2014 to June 2016, a total of 204 patients were treated, including 103 in the chemotherapy group and 101 in the HDI group. Baseline characteristics of the two groups of patients were generally similar.
The proportion of tumors by anatomic site in the chemotherapy and HDI groups was as follows: head and neck 38.8% vs 49.5%, gastrointestinal 35.9% vs 22.8%, and gynecological (vaginal) 25.2% vs 27.7%. The proportions of stage I/II and III in the chemotherapy group and HDI group were 68.9% vs 73.3% and 31.1% vs 26.7%, respectively.
The rates of CKIT, BRAF, and NRAS mutations in the chemotherapy group and HDI group were 7.0% vs 8.2%, 5.0% vs 8.2%, and 13.4% vs 15.8%, respectively.
In an intention-to-treat analysis, at a median follow-up of 64.8 months, patients who received chemotherapy had median RFS (15.5 months vs 9.9 months, HR=0.622, P=0.001), DMFS (19.5 months vs 12.7 months, HR =0.705, P=0.025) and OS (38.2 months vs 33.5 months, HR=0.832, P=0.270) were higher than those in the HDI group. Subgroup analysis showed improvements in RFS, DMFS, and OS with chemotherapy compared with HDI in multiple subgroups.
Toxicity was generally mild to moderate for both regimens. The most common adverse reactions were fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, leukopenia, neutropenia, hepatotoxicity, pyrexia, and anemia. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 23 patients (22.3%) in the chemotherapy group and 57 patients (56.4%) in the HDI group.
Compared with high-dose interferon alfa-2b therapy, temozolomide combined with cisplatin can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence and distant metastasis in patients with resected mucosal melanoma, and it is generally well tolerated.
2022 ASCO: 11 important advances on cancer treatment
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



