Japan: Over 10000 Applications for Health Damage from COVID-19 Vaccines
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Japan: Over 10000 Applications for Health Damage from COVID-19 Vaccines, Including 1,000 Cases in Individuals Under 20
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Japan: Over 10000 Applications for Health Damage from COVID-19 Vaccines, Including 1,000 Cases in Individuals Under 20
According to the relief system for health damage caused by vaccination, the number of applications for compensation for health damage after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine has exceeded 10,000 by the end of January this year.
Of these, over 6,000 cases have been recognized as health damage caused by vaccination, while approximately 3,000 cases are still under review.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare revealed these findings in a document summarizing the results of the examination.
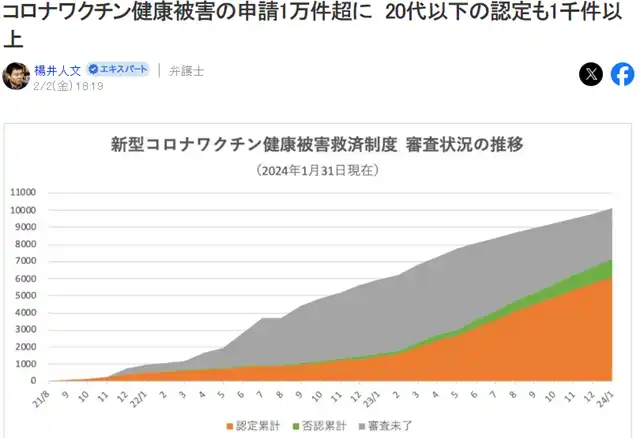
While 453 deaths have been certified so far, over 600 cases are still pending examination. The document was presented during the 12th Disease and Disability Certification Review Committee on February 24, 2023.
On January 15, for the first time, cases involving individuals under the age of 10 (6 and 9 years old) were publicly disclosed. According to the author’s analysis, it has been noted that the number of certifications for individuals under the age of 20, who have an extremely low risk of severe illness from COVID-19, has exceeded 1,000 cases, including 20 cases of death or disability. When considering the vaccination population under the age of 20, this translates to over 50 individuals per one million people being certified for health damage (Note 1). Prior to the pandemic, millions of people received vaccines such as influenza each year, and the number of examinations for health damage remained around 100 cases per year.
The government has decided to conclude the special vaccination program for COVID-19 in March of this year, transitioning to regular vaccinations for those aged 65 and above from April onwards. The categorization will also change to “Category B,” resulting in reduced compensation for health damage. Those outside the target group for regular vaccinations will have to bear the cost of vaccination themselves and will be excluded from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s compensation system for health damage (Note 2).
(Note 1) According to government announcements, the population of those under 20 who received one or more doses is 17,457,404 people (as of January 30). Based on the author’s database compiled from the open data of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s “Disease and Disability Certification Review Committee,” the number of health damage certifications for those under 20 is 1,047 (as of January 31).
(Note 2) If individuals outside the target group for regular vaccinations receive vaccinations at their own expense and experience health damage, they may be eligible for compensation under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act. However, the compensation amount is lower than that for regular vaccinations in Category B.
More than 75% of health damage certifications for myocarditis and pericarditis are concentrated in individuals under the age of 30.
Dual Examination from a Medical Perspective: Recognition Rate for Aftereffects is 40%
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare explicitly states on its website that the relief system is designed to promptly assist those in whom a causal relationship between vaccination and health damage is recognized.
Nevertheless, some physicians, influencers, and community notes on platforms such as Twitter have circulated opinions suggesting that the recognition of the relief system’s status is not based on a clear medical causation or is overly broad due to political reasons. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, however, explains that each case is carefully examined based on factors such as “the medical rationality of symptom onset,” “temporal proximity,” and “the lack of rationality to consider other causes” (Document, Page 3).
While it is stated that “strict causation is not required,” this is because “it is usually impossible to strictly prove causation” (same document). Thus, it emphasizes that not requiring strict causation is intended to avoid leaving all cases with strong suspicion of causation unresolved.
This method of determining causation is similar to the standards used in courts, and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare also explains, “Similar to precedents, a level of probability that does not raise doubts for the average person is required” (Document, Page 5).
To apply for compensation, individuals must gather their medical records, such as medical charts, and require cooperation from a physician. The process is not easily accessible, excluding minor side effects from examination. The system is not widely known, and even those who are aware often decide to abandon the application process. Particularly, the system presents a barrier, as the one-time death benefit is not available to surviving family members who are not financially dependent (for example, if a single individual living independently passes away).
The acceptance of applications is handled by local governments, and the “Vaccination Health Damage Investigation Committee,” composed of physicians, conducts the examination from a medical perspective. The results are then examined again by the “Disease and Disability Certification Review Committee,” mainly composed of physicians, in the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. In other words, there is a dual medical examination at the local and national levels (except for cases of anaphylaxis, which can be exempted from local examination).
From the documents of Setagaya Ward, Tokyo, some excerpts:
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s examination process denies cases where there are reasons to negate causation between vaccination and disease, among other factors. At present, about 15% of the examination cases have been denied. Initially, there were many certifications for anaphylaxis, but lately, cases other than anaphylaxis have increased, and the denial rate has risen. According to the author’s tally, there are 39 certifications and 59 denials for cases of “aftereffects,” with a denial rate of 60%.
The details of the examination are not disclosed, and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s explanation is not easily understandable. However, it is almost certain that careful judgments regarding the recognition or denial of causation are made based on medical perspectives for individual cases.
Interpreting the explanation of “strict proof is not required” as meaning “relief certification is unrelated to medical causation” not only underestimates the actual situation of the damage but also risks creating misunderstandings and misconceptions among recognized victims and their families.
Ongoing Examination of Increasing Death Cases: Current Situation with Very Few Reports
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has postponed the examination of death cases.
Even though 418 death cases had been forwarded to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare after completion of examination by local governments in November 2022, only about 11 cases had been examined (revealed by Junichiro Yamaoka’s report, ‘Report: Suspected Deaths from Adverse Reactions’). Since the strengthening of the examination system and the reclassification of COVID-19 to “Category 5,” numerous pending death cases are expected to undergo examination. However, due to the continuous increase in new applications, it has been found that there are more than 600 pending cases, as per the author’s investigation.
The author’s compilation. The number of applications accepted in May 2023 is from parliamentary replies, and data from September onwards is from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s publicly available documents.
The examination of COVID-19 vaccine cases has become unprecedented in scale, surpassing the capacity even with a significantly expanded system. Media reports by Asahi Shimbun and Yomiuri Shimbun at the end of last year highlighted the issue of the increasing number of examination cases, and
the media is not unaware of the situation. However, except for some local stations, major media outlets have hardly reported on the situation, despite the fact that the examination results are disclosed in public four times a month.
In the case of NHK, after reporting that the number of certifications for death cases reached 156 in August of the previous year, there has been no subsequent reporting.
Japan: Over 10000 Applications for Health Damage from COVID-19 Vaccines, Including 1,000 Cases in Individuals Under 20
References: https://news.yahoo.co.jp/expert/articles/699679f5b03858c7c384002dfb215059f6f4a157
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



