Chinese Scientists Synthesize New Nuclides Ruthenium-160 and Tungsten-156
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Chinese Scientists Synthesize New Nuclides Ruthenium-160 and Tungsten-156
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Chinese Scientists Synthesize New Nuclides Ruthenium-160 and Tungsten-156
Researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have recently synthesized the new nuclides ruthenium-160 and tungsten-156 for the first time. The relevant findings were published in the international academic journal Physical Review Letters on February 15.
Atomic nuclei are quantum many-body systems composed of protons and neutrons. Nuclei with different numbers of protons and neutrons have different properties, and scientists refer to them as nuclides. The synthesis and study of new nuclides are not only important for understanding the structure of matter but also provide important information for understanding the evolution of astrophysical environments, serving as important means to explore the mysteries of nature.
source: news.cn
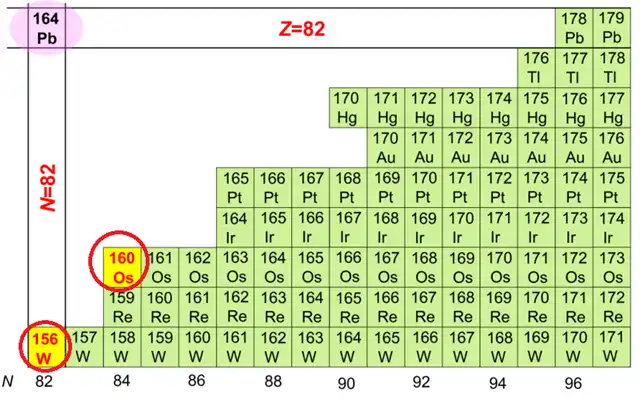
The research team relied on the Lanzhou Heavy Ion Accelerator and used the Inflatable Recoil Separator SHANS to synthesize the new nuclides ruthenium-160 and tungsten-156 through fusion-evaporation reactions. Ruthenium-160 (with 84 neutrons) exhibits α-radioactivity, while tungsten-156 (with 82 neutrons) exhibits β+ decay radioactivity. The team measured properties such as the alpha decay particle energy and half-life of ruthenium-160, as well as the half-life of tungsten-156.
Through a systematic analysis of the new measurement data and existing data, the researchers found that when the atomic number is greater than 68, the preformation probability of alpha particles in isotones with 84 and 85 neutrons gradually decreases, revealing an enhanced shell effect with 82 neutrons in neutron-deficient nuclides. Further research suggests that the reason for this enhanced effect is the gradual approach to the potentially more stable double magic nucleus lead-164 (with 82 protons and 82 neutrons).
This study provides the first clear indication of the evolution of the neutron shell with 82 neutrons on the neutron-deficient side and marks a new phase in China’s research on new nuclides in a new nuclear region.
Chinese Scientists Synthesize New Nuclides Ruthenium-160 and Tungsten-156
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



