WHO: Latest 2024-2025 Influenza Vaccine Strain Recommendations
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
WHO: Latest 2024-2025 Influenza Vaccine Strain Recommendations
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
WHO: Latest 2024-2025 Influenza Vaccine Strain Recommendations
The influenza virus can cause seasonal flu and even pandemics. It is an RNA virus with a complex classification and many subtypes, making it prone to mutations.
Vaccination is widely recognized as the best way to prevent the flu.
To ensure vaccine effectiveness, the World Health Organization (WHO) updates the vaccine strain components annually.
Changes in the 2024-2025 Northern Hemisphere Influenza Vaccine Strain Composition
To maintain vaccine effectiveness, it is necessary to regularly update the influenza virus vaccine components.
After analyzing global influenza virus epidemiology, pathogenesis, and vaccine serology, WHO announced the 2024-2025 Northern Hemisphere Influenza Vaccine Strain Recommendations on February 23, 2024.
Trivalent Chicken Embryo Cultured Vaccines:
- an A/Victoria/4897/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Thailand/8/2022 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Austria/1359417/2021 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus
Trivalent Cell-Cultured or Recombinant Protein Vaccines:
- an A/Wisconsin/67/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus
- an A/Massachusetts/18/2022 (H3N2)-like virus
- a B/Austria/1359417/2021 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus
Quadrivalent Chicken Embryo and Cell-Cultured or Recombinant Protein Vaccines (added to the trivalent vaccine components):
- a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (B/Yamagata lineage)-like virus Since March 2020, no naturally occurring B/Yamagata lineage virus has been confirmed. WHO considers it unnecessary to include the B/Yamagata lineage virus as a component of influenza vaccines and recommends its removal from influenza vaccine components. In areas still using quadrivalent vaccines, the inclusion of the B/Yamagata lineage component remains consistent with previous recommendations.
Comparison of 2023-2024 and 2024-2025 Northern Hemisphere Influenza Vaccine Strain Components reveals the main difference in the H3N2 virus strains:
|
Vaccine type |
2023-2024 |
2024-2025 |
|
Trivalent chicken embryo culture vaccine |
A/Darwin/9/2021 (H3N2)-like virus |
A/Thailand/8/2022 (H3N2) -like virus |
|
Trivalent cell culture or recombinant protein vaccine |
A/Darwin/9/2021 (H3N2)-like virus |
A/Massachusetts/18/2022 (H3N2)-like virus |
Recombinant Antigens are Key Materials for Vaccine Research
Critical target antigens play an important role in influenza virus-related vaccines, drugs, and even diagnostic reagents. Below, we have organized information on HA, NA, and NP proteins.
|
protein |
Function |
application |
|
HA (Hemagglutinin) |
Binds to sialic acid receptors on the host cell membrane to assist the fusion of the viral envelope and the host cell membrane; coagulation |
Basic research on influenza Flu vaccine development Anti-hemagglutinin antibody development Research on virus detection reagents |
|
NA (Neuraminidase) |
Hydrolyzes sialic acid receptors to promote release of mature virus particles |
Antiviral drug development Basic research on influenza Flu vaccine development Antibody R&D Research on virus detection reagents |
|
NP (nucleoprotein) |
Combines with influenza genetic material to participate in viral gene replication, transcription, and translation; maintains viral gene stability |
Antiviral drug development Basic research on influenza Antibody R&D Diagnostic product development |
Recombinant antigens from influenza vaccine strains can be applied in various stages of vaccine development, such as vaccine content testing, vaccine biological potency testing, and toxicity testing. Using recombinant antigens for ELISA testing can analyze the levels of total antibodies and neutralizing antibodies in immune sera after vaccination, and detect vaccine content using recombinant proteins as controls.
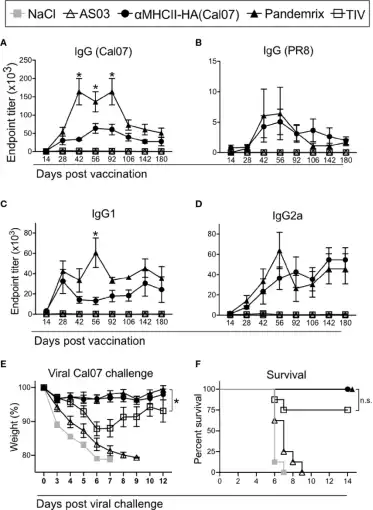
Using recombinant influenza HA protein to detect serum antibody levels in mice after vaccine immunization (picture from Andersen, et al.)
WHO: Latest 2024-2025 Influenza Vaccine Strain Recommendations
References:
[1]https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/recommended-composition-of-influenza-virus-vaccines-for-use-in-the-2024-2025-northern-hemisphere-influenza-season
[2] Andersen, et al. Pandemic Preparedness Against Influenza: DNA Vaccine for Rapid Relief.[J]. Frontiers in Immunology.2021.747032.
[3] Bangaru S , et al. A Site of Vulnerability on the Influenza Virus Hemagglutinin Head Domain Trimer Interface[J]. Cell, 2019.
[4] Kim M , et al. Inhibition of influenza virus internalization by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate.[J]. Antiviral Research, 2013, 100(2):460-472.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



