Intermittent fasting can prevent the disadvantages of a long-term high-fat diet
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
Intermittent fasting can prevent the disadvantages of a long-term high-fat diet
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Nature: Scientists have found that intermittent fasting can prevent the disadvantages of a long-term high-fat diet. The body will not gain weight and the cardiovascular system will be healthier.
Recently, a study published in the journal Nature Metabolism can be described as the ecstasy of high-fat diet lovers. The scientific team from the University of Southern California found in mice that as long as the fasting-mimicking diet is simulated for one week each month, the obesity, metabolic problems and cardiovascular problems caused by the high-fat diet can be greatly improved , Multiple indicators are no different from mice that have been on a healthy diet for a long time [1].
Let me talk about this simulated fasting diet first. This is a diet method developed by scientists in previous research. The diet mainly contains high levels of fat, with very few protein and carbohydrates. In previous animal studies, the short-term fasting diet simulation showed many benefits, such as prolonging life, reduce and delay the occurrence of cancer, alleviate autoimmune diseases and multiple sclerosis symptoms and reverse diabetes , regulation of intestinal flora Wait [2-7].
God, what kind of fairy rice.
In this research, scientists want to try to explore the effects of periodic and long-term simulated fasting. The mice in the study were divided into three groups. The control group ate a normal healthy diet with 10% energy derived from fat; the high-fat diet group (HFCD) had 60% of the food’s energy derived from fat; the simulated fasting group (FMD) is to eat a high-fat diet at ordinary times, and to simulate a fasting diet for 5 days every 4 weeks.
In these 5 days, the mice ate 50% of the usual food on the first day, and only 10% of the usual food for the remaining four days. Since mice are not particularly able to accept the jump from empty stomach to big fish and meat, from the 6th month, the researchers also arranged for the mice to make the transition to a healthy diet for two more days after the simulated fasting diet.
By the way, this experiment is different from the previous studies. The mice used are all female mice. Since female rats are not sensitive to obesity induced by high-fat diet, the diet formula used this time is also more “oily”, and the proportion of fat has increased from 45% to 60%.
It is conceivable that HFCD mice gained weight rapidly, and their median lifespan was shortened to only 570 days, while the control group was able to live 836.5 days. Interestingly, the median life span of FMD mice was 732 days, which was not significantly different from the control group (p=0.0630).
18 months after the experiment, the average weight of the control group, HFCD group, and FMD group were 30.73g, 60.63g, and 34.88g, respectively. The FMD group is only 13.5% heavier than the control group, and the HFCD mice are 97.29% heavier, which is really the best.
The researchers analyzed the metabolism of the mice and found that the FMD group was also quite excellent.
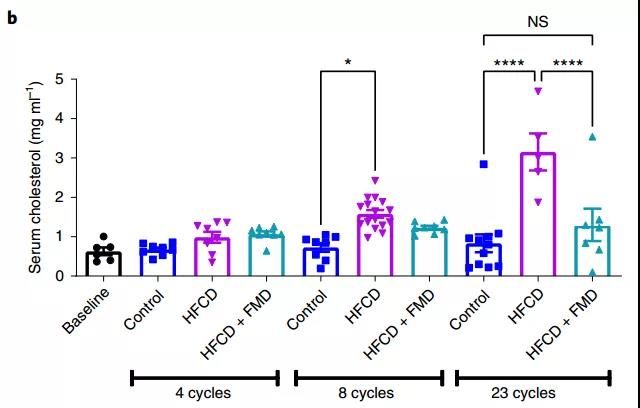
For example, when the mouse was 33 months old, the experiment had been conducted for 23 months. At this time, the cholesterol level of the FMD group was basically the same as that of the control group, while the HFCD group was almost 4 times that of the control group; in addition, the FMD was smaller. The data of liver disease markers alanine aminotransferase, blood sugar, and serum leptin are also much better than those of HFCD mice.
In other words, a simulated fasting diet once a month can effectively prevent hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, and hyperleptinemia caused by a high-fat diet.
The researchers also found that the cardiovascular system of FMD mice is also healthier than that of HFD. Data such as capillary density and myocardial hypertrophy are similar to those of the control group and much better than HFD, indicating that FMD can promote angiogenesis and prevent Heart damage caused by HFCD.
Why does FMD have such a “magic effect”?
The researchers analyzed the RNA data of the heart and visceral adipose tissue of 21-month-old mice and found that the expression of genes related to mitochondrial metabolism, acetyl-CoA biosynthesis and NADH dehydrogenase activity in HFCD mice was down-regulated, while FMD could effectively restore or partially Restore their expression.
At the same time, FMD mice do not eat retaliatory food after hungry as we think. They actually eat very “restrained”, and in general they consume less calories. In addition, a 5-day simulated fasting diet will also bring continuous ketogenic effects, which all contribute to the final health benefits.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



