First epidemiological study: Omicron with significant immune escape
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
First epidemiological study: Omicron with significant immune escape
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
First epidemiological study: Omicron with significant immune escape.
[Heavyweight] The first epidemiological study of Omicron causing superinfection, showing that the phenomenon of immune escape is more significant.
On December 2, 2021, Pulliam of Stellenbosch University in South Africa and others uploaded the first research paper on Omicron mutant strains on bioRxiv, the title is “Increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection associated with emergence of the Omicron variant in South Africa” (The increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 superinfection in South Africa is related to the Omicron mutant ).
This blockbuster study describes the epidemiology of Omicron’s repeated infections .
In a cohort of 2,796,982 patients previously infected with SARS-CoV-2, the study found 35,670 repeat infections before November 27.
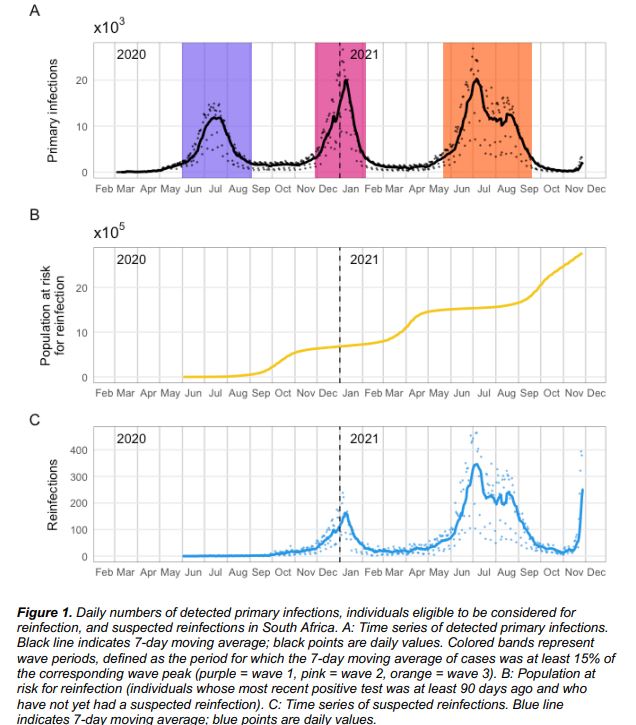
Studies have found that, compared with wild-type strains, Beta and Delta mutant strains increase the risk of initial infection (first infection) in the population , but do not increase the risk of reinfection, that is to say, the immunity formed after initial infection is against reinfection. Still valid. Omicron is contrary to the prevalence of the above two mutant strains.
The study found that Omicron did not increase the risk of initial infection in the population, and even the risk of initial infection in the population was reduced; but it increased the risk of reinfection .
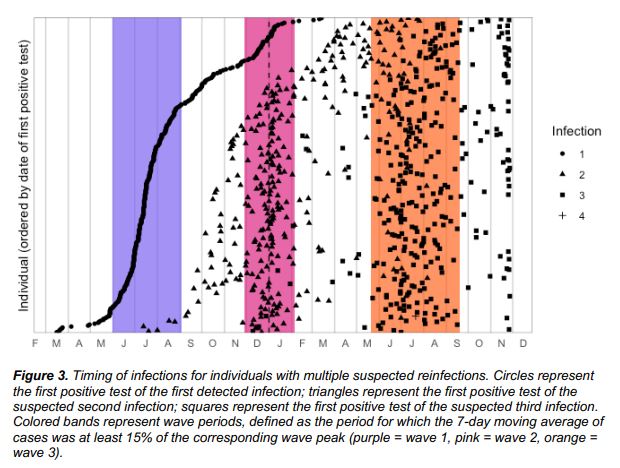
In the second and third peaks dominated by Beta and Delta mutant strains, the hazard ratios of repeated infections were 0.75 and 0.71, respectively. In South Africa’s recent fourth peak led by Omicron, the hazard ratio of repeated infections rose to 2.39 .
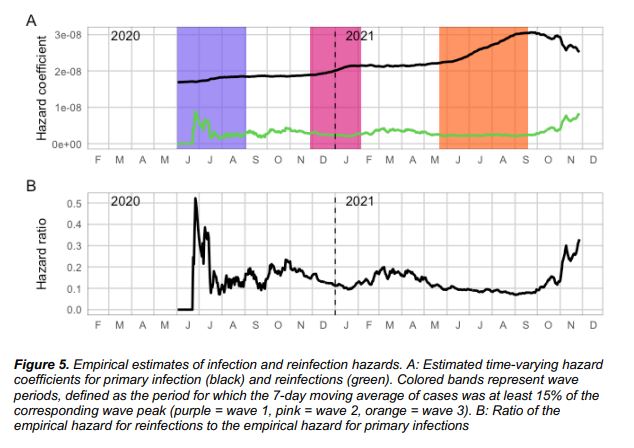
In other words, the immune escape phenomenon of Omicron may be more significant .
Therefore, it is critical to continue to monitor its epidemic and conduct serological research.
references:
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.11.11.21266068v2.full.pdf
First epidemiological study: Omicron with significant immune escape
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



