MDT should be actively promoted to treat craniopharyngioma
- WHO Releases Global Influenza Vaccine Market Study in 2024
- HIV Infections Linked to Unlicensed Spa’s Vampire Facial Treatments
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
MDT should be actively promoted to treat craniopharyngioma
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
MDT should be actively promoted to treat craniopharyngioma.
The multidisciplinary team (MDT) model, in which complex diseases are discussed by senior experts from multiple disciplines, is an advanced diagnosis and treatment model widely respected in the international medical field, and it is also an important component of the hospital’s superior discipline medical system.
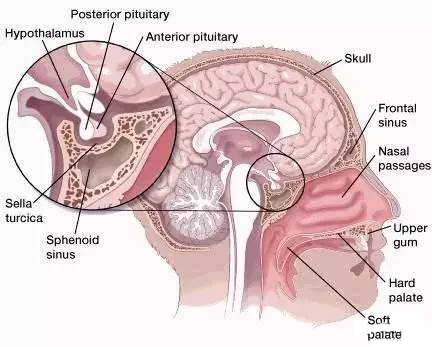
Craniopharyngioma (Craniopharyngioma, CP) is an internationally recognized benign tumor that is difficult to cure due to its deep location and adjacent to important structures.
As in developed countries, some countries’s craniopharyngioma has different treatment strategies, low radical cure rates, and poor quality of life.
The application of effective MDT plays an irreplaceable role in improving the quality of CP diagnosis and treatment, breaking down the barriers between disciplines, and making up for the lack of personal ability.
Actively promoting the application of MDT in CP patients has become a top priority.
Application of MDT model is a requirement of CP disease attributes
CP originates from the residual cells of Rathke’s tube epithelium or metaplasia outside the nervous system, and belongs to epithelial tumors in the sellar area and parasellar area.
On the one hand, it is difficult to avoid the high mortality rate caused by hypothalamic injury by en bloc resection of the tumor. On the other hand, only radical resection of the tumor can be cured.
Therefore, all methods used for malignant tumors are used for the treatment of CP, which is defined by the WHO as incurable intracranial benign tumors.
Even today after more than 30 years of clinical application of magnetic resonance imaging, the tumor cure rate of CP is still less than 30%, and the mortality rate is as high as 15% to 40%.
Although the perfect operation can completely remove the tumor and avoid the damage of important structures, it is recognized as the only way to cure CP patients.
However, due to the variability of tumor origin and growth mode, fear of hypothalamic injury, partial tumor resection and adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy are still the mainstream strategies for treatment of CP at home and abroad.
As a result, most patients still sacrifice the endocrine function of the hypothalamus in exchange for prolonging survival time.
These patients are not only prone to relapse, but also obesity and difficulty in retreatment caused by pituitary and hypothalamic dysfunction caused by radiotherapy and chemotherapy have actually caused the patients to lose the chance of continuing to survive.
Currently, the standardized mortality rate of CP is as high as 19.4.
CP is divided into two histological types of ameloblastic craniopharyngioma (adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma, ACP) and squamous craniopharyngioma (PCP), and there are two peaks of incidence in adolescents and middle-aged and elderly patients.
Different ages, genders and histological types make obvious differences in patients’ symptoms, treatment strategies and prognosis.
The literature shows that children and female patients have a standardized mortality rate of 1.55 for all CP patients, which is significantly different from adult male patients.
CP can occur from the pharynx along the neurohypophysis, pituitary stalk, and Rathke’s tube remnants, especially when it originates from the distal part of the pituitary gland near the funnel of the hypothalamic nodule.
Due to the enlargement of the tumor, the soft membrane is weak and easy to cause tumor pushing Submerged into the hypothalamic tissue to grow; due to individual differences in the surrounding inner arachnoid, the hypothalamus and its nucleus at the bottom of the three ventricles have different displacements and distortions, which are the key to the difficulty of CP treatment.
Both the perioperative and protracted mortality of CP remain high.
The mortality of the first operation is between 0-16%, and the mortality of patients with recurrence is as high as 10.5%-40.6%, which is the highest mortality of tumors in the sellar area.
The main cause of early death is the dysfunction of vital organs caused by electrolyte disturbances in the internal environment, while long-term deaths are mostly caused by cardiovascular diseases caused by long-term hypothalamic and pituitary function decline. The standardized mortality rate is 3~ 19 times.
It can be seen that maintaining and restoring the function of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus in CP patients is the main task throughout the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative procedures.
To sum up, there are three main factors that lead to incurable and poor quality of life in CP patients:
- Complications of adjuvant therapy such as radiation that cannot be removed completely;
- Hypothalamic function and endocrine dysfunction caused by important structural damage;
- Total resection and protection of important structures are more difficult for repeated operations.
Therefore, it is necessary to improve the preoperative diagnosis and formulate the best individualized treatment strategy; strive to achieve complete removal of the true tumor under the protection of the important surrounding structures during the initial treatment, and perioperative safety and perfect hypothalamic and pituitary function reconstruction are indispensable.
For CP, a rare and difficult disease that accounts for less than 4% of intracranial tumors, it is difficult for individuals and teams to gain sufficient knowledge and experience in a short period of time.
This makes the diagnosis and treatment of CP have a stronger demand and dependence on MDT. From the discovery of craniopharyngiomas to diagnosis and treatment, there are many disciplines involved: pediatrics, ophthalmology, endocrinology, neuropsychiatry, imaging, anesthesiology, pathology, tumor radiotherapy, rehabilitation and neurosurgery.
Adolescent patients also need obstetrics and gynecology. Division and Andrology Intervention. It can be seen that the high-level diagnosis and treatment of CP is actually the performance of personal skills and the overall high-level work of the hospital.
Requirements and tasks of MDT teams
The neurosurgery team is the main body of CP. Even with a senior surgical history, it is impossible to complete this difficult treatment task with high quality without the experience of handling no less than 10 cases of CP each year.
In addition to the rich experience in the treatment of sellar disease and the skills of safe total tumor resection, young patients who also have difficulty in recurring surgery, worsened hypothalamic endocrine dysfunction after radiotherapy, and irreversible damage, and who fail to complete tumor resection may lose complete cure.
A clear understanding of opportunities is also crucial. In addition, a deep understanding of the peculiarities of this disease is also a basic requirement for all members of the CPMDT team.
The imaging team understands and provides high-quality images that clarify the diagnosis of CP, clarify the relationship between the tumor and the surrounding tissues, and specify the direction and law of the displacement of important structures of the hypothalamus in different individuals at a high level.
This is the premise for high-quality diagnosis and treatment of CP.
The radiotherapy and oncology team fully understand the origin of CP and the growth mode of tumors.
On the one hand, chemotherapy and radiotherapy can indeed delay the recurrence and growth rate of tumors. On the other hand, it is necessary to understand that the incidence of endocrine disorders in patients after radiotherapy has increased from 80%.
To 100%, and the number and extent of the affected axis have increased significantly, and the mortality rate of reoperation has also doubled.
This is the basis for positioning the role and status of the radiotherapy and chemotherapy team in CP treatment.
There are two main tasks of the pathology team: 1. To clarify the pathological diagnosis; 2. To clarify the relationship between the tumor and surrounding structures, especially the hypothalamus, pituitary stalk, and normal pituitary.
In terms of definitive diagnosis, in addition to distinguishing different types (ACP and PCP), it is more important to identify some diseases similar to CP in sellar area, such as Rathke’s cyst squamous epithelial metaplasia, Rathke’s cyst with xanthoma-like variant lesions.
Histopathology is easy to ignore and the important task is to clarify the true histological relationship between tumor and surrounding structures.
Re-recognizing CP at the molecular and genetic level in histology is the key to determining its therapeutic level and future development.
Endocrinology: CP accounts for about 10% of intracranial tumors in children. The quality of life of middle-aged and elderly patients, the growth and development of children, and the maintenance of fertility are long-term and difficult problems.
The degree and number of axis of CP endocrine disorders are variable, and the mortality rate of cardiovascular diseases caused by obesity related to hypothalamic endocrine dysfunction is 40%.
The difficulty in the reconstruction of the hypothalamic and pituitary endocrine function in CP patients is actually a problem faced by the endocrinology discipline and the direction to be overcome in the future.
Anesthesia and neurocritical medicine: CP patients have poor surgical tolerance. About 18% of patients can develop diabetes insipidus during surgery, which leads to rapid changes in the water and electrolyte environment during the perioperative period, which can lead to cognitive and consciousness disturbances, and in severe cases.
It is possible that blood pressure and heart rate vital signs are disordered, which is the main cause of death during the perioperative period.
ICU management is centered on the protection and reconstruction of brain function, and CP patients will experience hypothalamic pituitary dysfunction caused by decreased stress ability.
Understanding the patient’s injury mode will help increase the patient’s surgical tolerance and reduce postoperative treatment difficult.
It is of practical significance for anesthesia and neurosurgery to participate in MDT work and move forward to participate in preoperative evaluation and treatment strategy formulation.
The significance of improving CP treatment level
In addition to benefiting patients, the pursuit of safe total resection of CP can greatly improve neurosurgery skills, and the high-quality long-term survival of CP cured patients not only has the iconic significance of the overall medical level, but also guides the disease.
The research on hypothalamus is a fortress problem in brain science-the working mode of brain function with emotion and the solution of bionics are of decisive significance.
It is the fundamental purpose of CP to perform MDT to allow every young patient to have a chance to be cured, and for older patients to survive with high quality, and every treatment process must adopt the concept of MDT to achieve high-level treatment of CP.
The common requirements of CP for MDT members are: fully understand the origin of CP, pathological properties, high mortality caused by wrong treatment, the complexity of hypothalamic pituitary function reconstruction and the difficulty of reoperation.
On this basis, you can be qualified to be a member of the MDT of CP only if you are competent in your own professional problems and handling capabilities.
The mutual promotion and influence between MDT is a way to build a high-level medical team, and it also determines that CP should be treated in a large-scale neurosurgery center with a high level.
Because CP is a difficult problem that depends on the overall high-level MDT.
In the future, on the AI doctor assistance platform, obtaining the CP knowledge graph under massive data through MDT is the only way to comprehensively solve the difficulties of CP treatment.
MDT should be actively promoted to treat craniopharyngioma
(source:internet, reference only)
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



