COVID-19: Self-assembled nanoparticle protein vaccine candidate
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
COVID-19: Self-assembled nanoparticle protein vaccine candidate
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
COVID-19: Self-assembled nanoparticle protein vaccine candidate. A self-assembled nanoparticle protein candidate vaccine based on the receptor binding domain of the new coronavirus spike protein.
The n COVID-19 epidemic is still raging around the world. As of January 16, 2021, the COVID-19 epidemic has caused more than 2 million deaths worldwide. The prevention and control of the COVID-19 virus is still the number one issue of world public health security.
As one of the most important methods for epidemic prevention and control, the development of new coronavirus vaccines has attracted worldwide attention. According to statistics, there are more than 300 new coronavirus vaccines under research in the world. Among them, the vaccines that have entered clinical applications are mainly inactivated virus vaccines with relatively mature technology and relatively new virus vector vaccines and nucleic acid vaccines.
With the maturity of recombinant protein technology, the value of subunit protein vaccines in vaccine research and development has become more and more affirmed. It directly stimulates the immune system in the form of recombinantly expressed antigens, and has its own uniqueness in safety, preparation process and immune effect The advantages.
Spike protein (S protein), as an important surface glycoprotein of the new coronavirus, mediates virus adhesion and cell fusion by directly binding to human angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) receptors.
Among them, the S protein receptor binding domain (RBD) is the key region that directly binds to ACE2. Blocking its binding to the receptor can significantly inhibit the infection efficiency of the virus, so it is considered one of the most valuable vaccine targets.
However, because the RBD monomer of the S protein has a weak ability to stimulate the immune response, it is difficult to generate sufficient protective antibodies using RBD monomer as an antigen.
Therefore, how to enhance RBD without increasing the complexity of vaccine production and maintaining high protein stability The immune effect of the drug and improving its ability to stimulate the body to produce protective antibodies have become important issues in the development of RBD vaccines.
In response to this problem, recently, the research group of Professor Zeng Musheng from the Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University, the research group of Professor Zhao Jincun of Guangzhou Medical University and the research group of Guangdong Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention Ke Changwen jointly published a title of Rapid Development of ACS NANO.
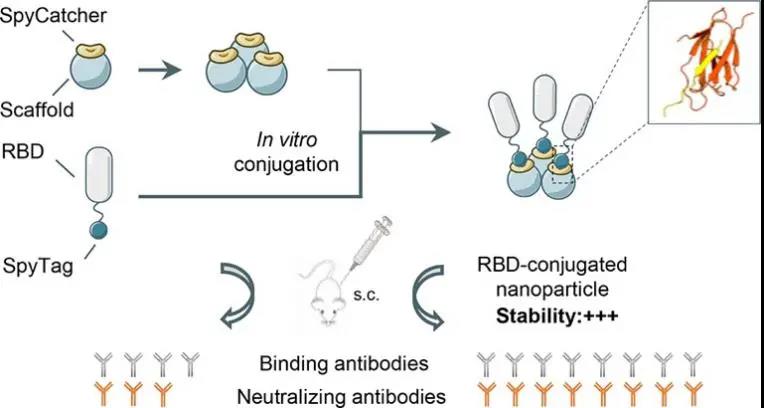
SARS-CoV‑2 Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Self-Assembled Nanoparticle Vaccine Candidates (rapid research and development of self-assembled nanoparticle vaccine candidates based on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain), designed several articles based on The SpyTag-SpyCatcher covalent protein coupling system is a nanoparticulate RBD vaccine, and its immune effect is verified through animal experiments.

The study uses three different sizes of nanoparticles as the skeleton in the design, including regular octahedral 24-mer ferritin (Ferritin), regular dodecahedral 60-mer mi3 nanoparticle protein (mi3) and regular icosahedron.
The 120-mer I53-50 nanoparticle protein (I53-50), using the amide bond formed by SpyTag-SpyCatcher, incubate RBD with these three nanoparticle proteins in vitro to couple the RBD protein to these three different nanoparticle proteins.
The surface of the particle. The three designed RBD-coupled nanoparticle vaccines not only maintain the spatial conformation of RBD, but also significantly enhance protein stability and enhance its antigenicity.
These characteristics give these three RBD-coupled self-assembled nanoparticles a stronger immune effect, and the protective effect induced by them can be up to 120 times more than monomeric RBD antigen.
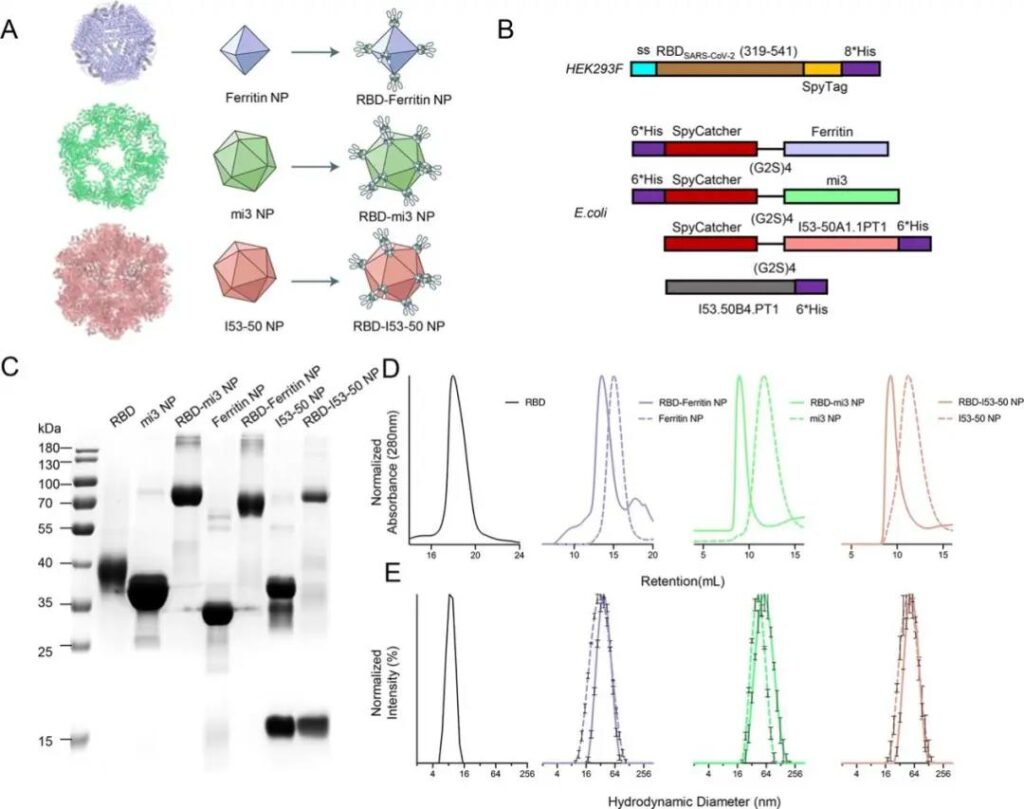
In terms of protein expression, in view of the uncertainty of the current recombinant expression of the fusion protein, the researchers used two different expression systems.
The RBD-SpyTag protein was expressed in the HEK293F eukaryotic expression system, and the SpyCatcher was expressed in the E. coli prokaryotic expression system. Ferritin, mi3 and I53-50 self-assembled nanoparticles.
Then the RBD was covalently coupled with three kinds of nanoparticles in vitro, and further purified by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to obtain stable RBD-coupled nanoparticles, followed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and differential fluorescence scanning (DSF) Test the uniformity and stability of nanoparticles.
After verifying the reliability of the physical and chemical characteristics of the nanoparticles, the researchers further evaluated the difference between their antigenicity and RBD monomers.
Through ELISA and kinetic testing, the results show that compared with RBD monomer, RBD-coupled nanoparticles can significantly increase the affinity to receptor ACE2 and neutralizing antibody CB6, and as the size of the nanoparticles increases, the The binding ability is enhanced.
These results highly suggest that nanoparticleization has an important immune-enhancing effect on the RBD region of the new coronavirus S protein.
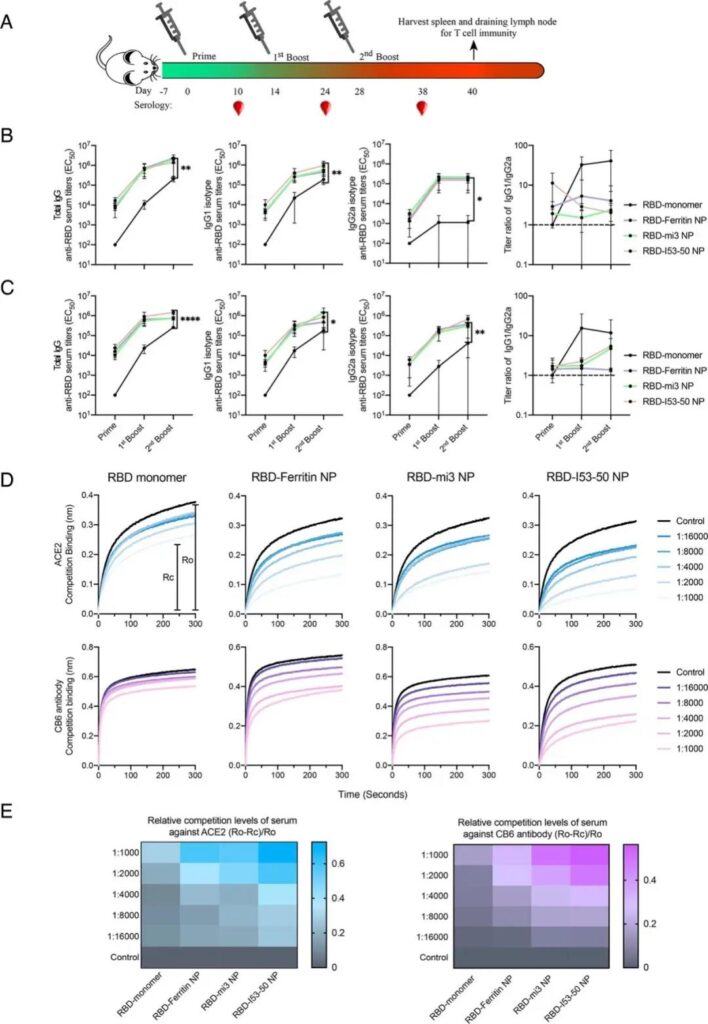
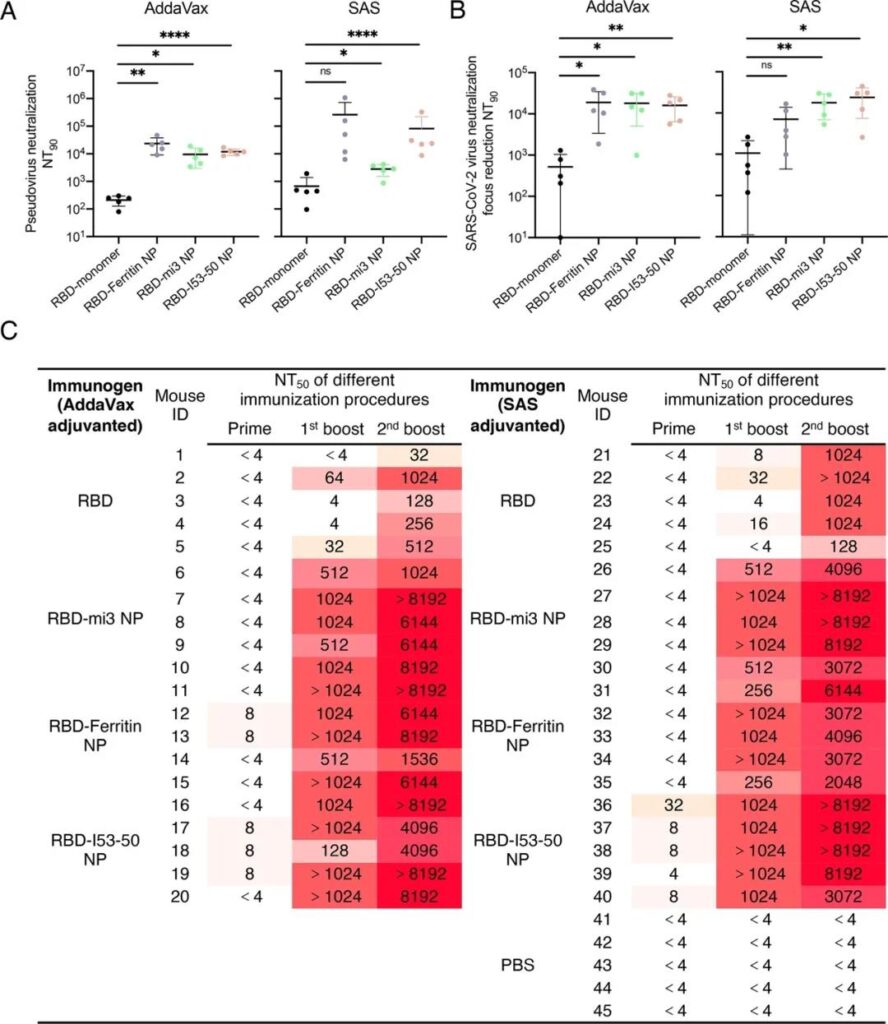
Subsequently, the researchers conducted animal immunization experiments in BALB/c mice. The RBD monomer containing 5μg of equal mass RBD and three different RBD-coupled nanoparticles were mixed with AddaVax or Sigma adjuvant system to immunize the mice.
Show that compared with monomer RBD, nanoparticles can significantly induce higher titers of antibodies against RBD, and passed three independent virus neutralization experiments (SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization test, SARS-CoV-2 Live virus plaque reduction neutralization experiment and SARS-CoV-2 live virus cytopathic neutralization experiment) confirmed that nanoparticles can significantly increase the titer of neutralizing antibodies, up to 120 times that of monomer RBD.
In order to explain this phenomenon, the researchers used the biofilm layer interference (BLI) technology to conduct an experiment on mouse serum/monomer RBD binding to ACE2, and found that the serum of mice inoculated with RBD-coupled nanoparticles was compared with monomer.
RBD can significantly inhibit the ability of receptor ACE2 to bind to RBD, which highly suggests that the antibodies induced after immunization with RBD conjugated nanoparticles can better neutralize the RBD on the surface of the virus, thereby reducing the chance of binding to ACE2 and infection.
In summary, this research has developed three different RBD-coupled nanoparticle proteins, the immune effect of which is significantly improved compared to monomer RBD, and the use of two different expression systems greatly improves the preparation of RBD nanoparticles.
With the convenience and scalability of particles, the three nanoparticle skeleton proteins proposed by the research can be further used in the development of other pathogen vaccines in the future, which not only provides new ideas for the research of new coronavirus vaccines, but also prevents nanoparticles from other pathogens. Protein vaccine design provides an important platform.
COVID-19: Self-assembled nanoparticle protein vaccine candidate
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



