PNAS: China medical team is developing mRNA cancer vaccine
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
PNAS: China medical team is developing mRNA cancer vaccine
PNAS: China medical team is developing mRNA cancer vaccine. PNAS: Sun Yat-sen University develops a new cancer vaccine based on mRNA.
The study used in vitro antigen presentation cell screening system to screen, and found that a lipid material C1 has both efficient mRNA delivery/expression function and the “self-adjuvant” characteristic of activating the natural immune signal of dendritic cells, and developed based on this A new mRNA nano-tumor vaccine based on lipid material C1

In the war with the COVID-19 virus, two mRNA vaccines quickly approved by Europe and the United States have attracted great attention because of their fast and efficient characteristics. In fact, Moderna and BioNTech, which have successfully developed these two mRNA vaccines, have been deeply involved in mRNA vaccines (especially in the field of tumor vaccines) for many years and have carried out multiple clinical trials.
In the current basic and clinical experimental studies, tumor vaccines using in vitro synthesized mRNA as the antigen component have shown great potential in inducing anti-tumor immunotherapy for tumors. Such tumor vaccines can use the translation function of antigen-presenting cells in the body to express mRNA into corresponding tumor antigen protein short peptides, and stimulate antigen-presenting cells to process and present antigens and activate T cell immunity, thereby inducing The body produces a specific anti-tumor immune response.
Due to the easily degradable characteristics of mRNA and its own physical and chemical characteristics, special delivery tools are needed to transport it to specific parts/organs of the human body to exert its effects. However, the current carriers used for mRNA delivery, such as lipid nanoparticles (LNP) or adenovirus, are still not safe and effective enough, and adjuvant components are still needed to activate the body’s immunity, which limits their preparation and efficiency. Therefore, the development of mRNA tumor vaccines urgently needs more safe and effective functional delivery vehicles.
Recently, Xia Xiaojun’s research team from Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center and Wu Jun’s research team from the School of Biomedical Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, published a title in PNAS magazine: “
Delivery of mRNA vaccine with a lipid-like material potentiates antitumor efficacy through Toll-like receptor 4 signaling” research paper.

The study reported that a class of cationic lipid material C1, as a nano-delivery carrier for antigen-encoding mRNA, can efficiently deliver and express mRNA encoding tumor antigens. At the same time, the nanocarrier itself can activate the natural immune receptor signal of antigen-presenting cells to achieve The dual function of mRNA delivery vector and “self-adjuvant”; Nano-tumor vaccines that deliver mRNA encoding tumor antigens with C1 have achieved good preventive and therapeutic effects in a variety of animal tumor models.
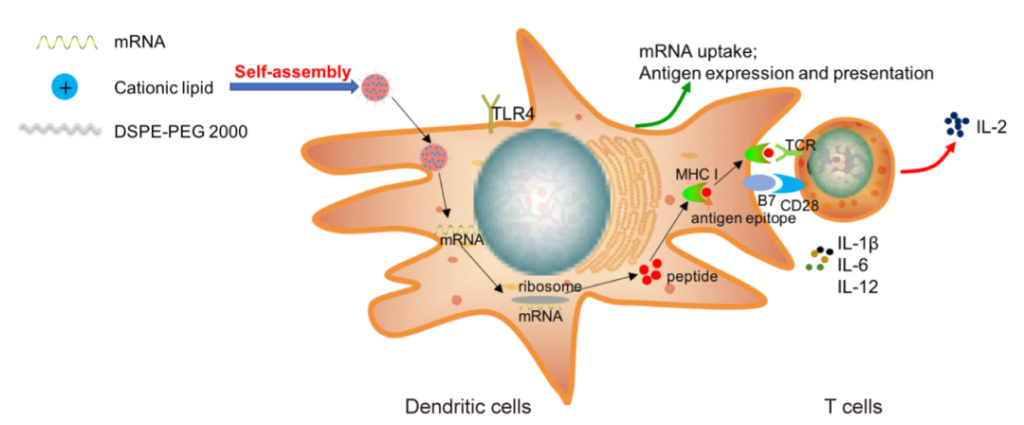
In this study, the author used PAMAM dendrimer as the main raw material and carried out ring-opening reactions with 1,2-epoxyhexane of different chain lengths to obtain a series of cationic lipids. The obtained materials were combined with mRNA is made into lipid nano-vaccine particles through self-assembly; then through in vitro antigen presentation experiments, a C1 material with a 12-carbon tail is screened, which can efficiently deliver antigen-encoding mRNA to dendritic cells and stimulate the tree Distrite cells translate mRNA into antigen peptides and present them to T cells, inducing T cell activation.
The mode of action of mRNA nano-tumor vaccine
At the same time, C1-based lipid-like nano-vaccine particles themselves can promote the expression of IL-12 and other type I cytokines in dendritic cells by activating the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway of dendritic cells And secretion, thereby promoting the activation of dendritic cells and the ability of antigen presentation.
Finally, the authors used a variety of mouse tumor models to verify the in vivo anti-tumor effects of C1 mRNA tumor vaccines. The results showed that in tumor prevention and treatment models, the C1 mRNA vaccines all showed significant anti-tumor effects and showed good biological performance. safety.
In summary, the study used an in vitro antigen presentation cell screening system to screen and found that a lipid material C1 has both efficient mRNA delivery/expression functions and “self-adjuvant” properties that activate the natural immune signal of dendritic cells. Based on this, a new mRNA nano-tumor vaccine based on lipid material C1 was developed, which provides a potential new immunotherapy for the treatment of different types of tumors, and provides vaccines for infectious diseases and gene therapy methods that rely on mRNA delivery An effective delivery vehicle and design ideas.
The research team is currently testing the development of a new coronavirus mRNA vaccine based on the C1 delivery system.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



