Lung cancer immunotherapy: New drug Libtayo reduces mortality rate by 43%
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Lung cancer immunotherapy: New drug Libtayo reduces mortality rate by 43%
Lung cancer immunotherapy: New drug Libtayo reduces mortality rate by 43%. Although lung cancer has temporarily retreated to the top spot in the global cancer incidence, the number one cancer mortality rate is still lung cancer.
Recently, the US FDA announced the approval of a new adaptation of the PD-1 inhibitor Libtayo (Cemiplimab-rwlc) for the first-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with high PD-L1 expression (≥50%). The tumors of these patients must be metastatic or locally advanced tumors, not suitable for surgical resection or final radiotherapy/chemotherapy, and the tumors do not carry EGFR, ALK or ROS1 aberrations.
In a pivotal trial, Libtayo was significantly better than chemotherapy in prolonging overall survival. This means that Libtayo has become another immune drug approved for the treatment of lung cancer patients with high PD-L1 expression after K and T drugs.
▌Lung cancer with the top mortality rate
Whether in the world or in China, lung cancer is still the leading cause of cancer deaths. In 2020, there will be approximately 2.2 million newly confirmed cases worldwide.
Lung cancer is mainly divided into small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, and NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. 75% of NSCLC patients are already at an advanced stage when they are diagnosed, and in newly diagnosed cases, tumor cells with PD-L1 expression ≥50% account for about 25% to 30% of the total.
As the main cause of cancer deaths worldwide, patients with advanced NSCLC still need more treatment options.
▌PD-1 inhibitor: Libtayo

Libtayo is a fully human monoclonal antibody drug targeting PD-1. By binding specifically to PD-1, it can reactivate T cell receptor signals, enhance the human immune system’s ability to kill cancer cells, and achieve natural anti-cancer effects.
As early as 2018, Libtayo was approved for the first time for the treatment of adult patients with advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC).
In early February of this year, Libtayo was approved to treat patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) who had previously been treated with Hedgehog protein pathway inhibitors (HHI) or were not suitable for HHI treatment.
In all approved indications, the recommended dose of Libtayo is 350 mg intravenous infusion every 30 minutes every three weeks until the disease progresses or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
It is worth mentioning that Libtayo has also been approved for clinical trials in China for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic NSCLC in combination with chemotherapy or as a single agent.
▌The risk of death is reduced by 43%! The test data is amazing
This approval is based on positive data from an open-label, randomized, multi-center Phase 3 clinical trial (called EMPOWER-Lung 1).
The trial enrolled 710 patients with advanced NSCLC with high PD-L1 expression (≥50%) and were randomly assigned to receive Libtayo first-line monotherapy or platinum-containing chemotherapy. The primary endpoints are OS and PFS, and secondary endpoints include overall remission rate, duration of remission, and quality of life.
The test data recently published in the “Lancet” magazine showed:
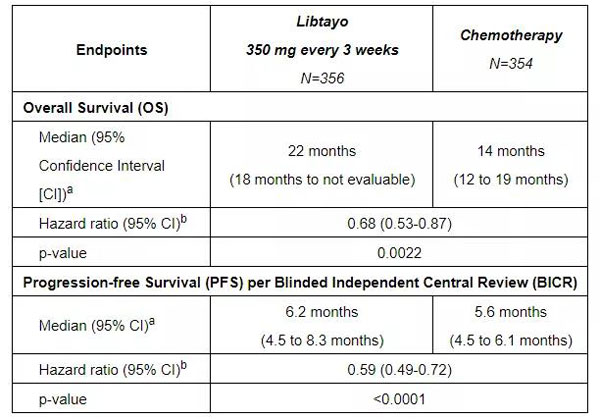
◆ In patients with tumor PD-L1 expression ≥50%, compared with the chemotherapy group, the Libtayo treatment group reduced the risk of death by 43%, and it was safe and well tolerated.
◆ The median overall survival (OS) of the Libtayo treatment group was 22 months, while that of chemotherapy was 14 months.
◆ Libtayo monotherapy can also improve patients’ progression-free survival (PFS). PFS was 6.2 months in the treatment group and 5.6 months in the control group.
It is worth noting that this trial allows patients initially assigned to the chemotherapy group to be transferred to the Libtayo group for treatment after the disease has progressed. Therefore, currently about 70% of patients in the chemotherapy group are transferred to the Libtayo group during the trial.
This is the third indication that Libtayo has obtained in the United States. This approval means that patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer have ushered in an effective new immunotherapy regimen.
▌List of first-line immunotherapy approved for non-small cell lung cancer (China and the US):
◆ United States
In October 2016, the US FDA approved Pembrolizumab (Drug K) for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with high PD-L1 expression.
In May 2017, the FDA approved bolizumab (drug K) in combination with pemetrexed and carboplatin for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, regardless of PD-L1 expression level.
In October 2018, the US FDA approved pembrolizumab (drug K) combined with carboplatin, paclitaxel/albumin paclitaxel for the first-line treatment of squamous non-small cell lung cancer, regardless of PD-L1 expression level.
Drug K has completed full coverage of non-small cell lung cancer.
In May 2020, the FDA approved the PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab (drug O) combined with the CTLA-4 inhibitor ipilimumab (drug Y) and platinum-containing dual-agent chemotherapy for first-line treatment of EGFR and ALK negative Of metastatic or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer, regardless of PD-L1 expression level.
In May 2020, the FDA approved atelizumab (T drug) as a single-agent first-line treatment for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with high PD-L1 expression and negative EGFR and ALK.
◆ China
In March 2019, the National Food and Drug Administration approved drug K combined with chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of EGFR and ALK-negative non-squamous advanced non-small cell lung cancer, regardless of PD-L1 expression level.
In October 2019, the National Food and Drug Administration approved K drug as a single-agent first-line treatment of PD-L1-positive non-small cell lung cancer without combined chemotherapy.
In November 2019, the State Food and Drug Administration approved K drug combined with chemotherapy (carboplatin + paclitaxel) for the first-line treatment of advanced squamous non-small cell lung cancer.
In June 2020, the National Food and Drug Administration approved the domestic PD-1 inhibitor carrelizumab (erika) in combination with pemetrexed and carboplatin for the use of non-EGFR and ALK-negative, unresectable locally advanced or First-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.
In January 2021, the National Food and Drug Administration approved the domestic PD-1 inhibitor tislelizumab (Bezian) combined with paclitaxel and carboplatin for the first-line treatment of locally advanced or metastatic squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Tilelizumab became the first domestic PD-1 approved as a first-line treatment for advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma.
In February 2021, the National Food and Drug Administration approved the domestic PD-1 inhibitor Sintilimab (Daboshu) combined with pemetrexed and platinum-based chemotherapy for EGFR and ALK-negative, non-resectable locally advanced or metastatic disease First-line treatment for patients with sexual non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



