Bispecific Nano-Antibody activates type 1 NKT cells
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Bispecific Nano-Antibody activates type 1 NKT cells
Bispecific Nano-Antibody activates type 1 NKT cells. Although NKT only accounts for about 1% of T cells, in addition to its direct tumor killing activity, it also has multiple functions such as immunosuppressive cells to clear the tumor microenvironment and helper T effector cell activation.
NKT cells are natural killer T cells in the body, which recognize lipid antigens presented by β2M-CD1d, and are mainly divided into type 1 and type 2 NKT cells.
Type 1 NKT cells recognize α-GalCer and express CD1d restricted semi-invariant αβTCR, including the invariant α chain (mouse Vα14-Jα18, human Vα24-Jα18), plus the limited variable β chain (mouse Vβ8 , Vβ7, Vβ2, human Vβ11). It accounts for about 1% of human T cells.
NKT cells mainly perform anti-tumor immune activity through three mechanisms:
- Directly lyse CD1d-expressing tumor cells (such as multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukemia, etc.)
- Lysis of immunosuppressive cells expressing CD1d (such as TAM, MDSCs, etc.)
- Activated antigen-presenting cells such as DCs, etc., participate in T cell activation.
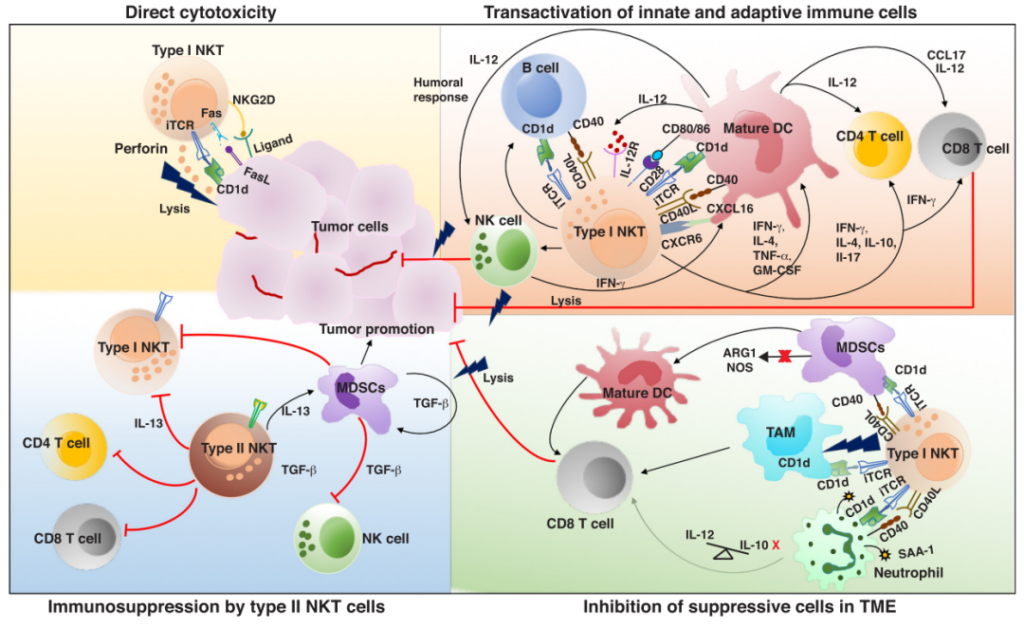
NKT biological activity (reference 1)
Agonistic bispecific nanobody
The classic MHC-antigen peptide-TCRT cell activation pathway makes it difficult to develop agonistic antibodies. The reason is the polymorphism of TCR and MHC molecules, and strict MHC restriction.
CD1d is a non-classical MHC molecule, and NKT-TCR is relatively constant. Therefore, researchers from the Amsterdam Cancer Center in the Netherlands and other units constructed the CD1d-NKTTCR bispecific antibody VHH1D12-CD1d-NKT TCR, which showed anti-tumor activity. The results were published in Nature Cancer.

Main findings in studies
1. CD1d specific antibody (VHH1D12) activates type I NKT cells
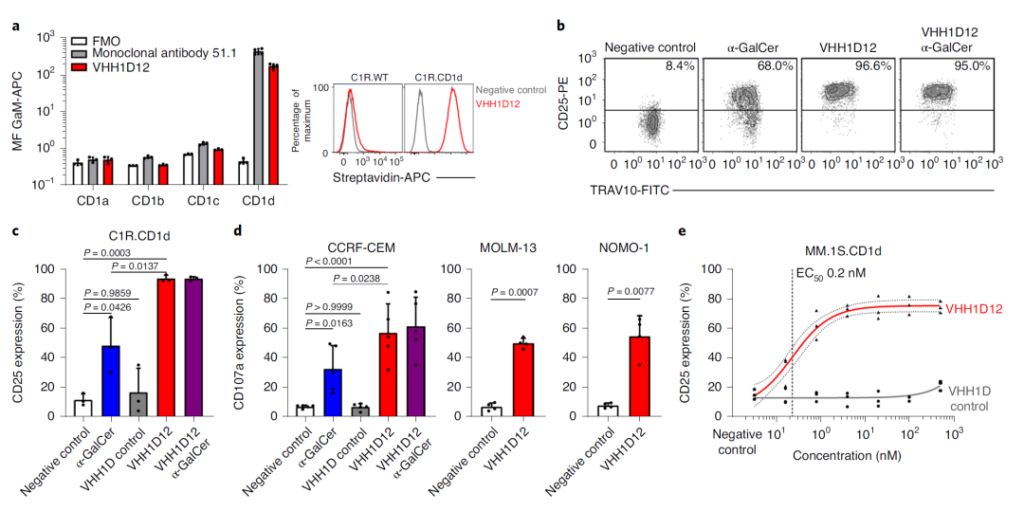
2. VHH1D12 selectively activates type I NKT cells to enhance their affinity for CD1d (weak) agonistic antigen
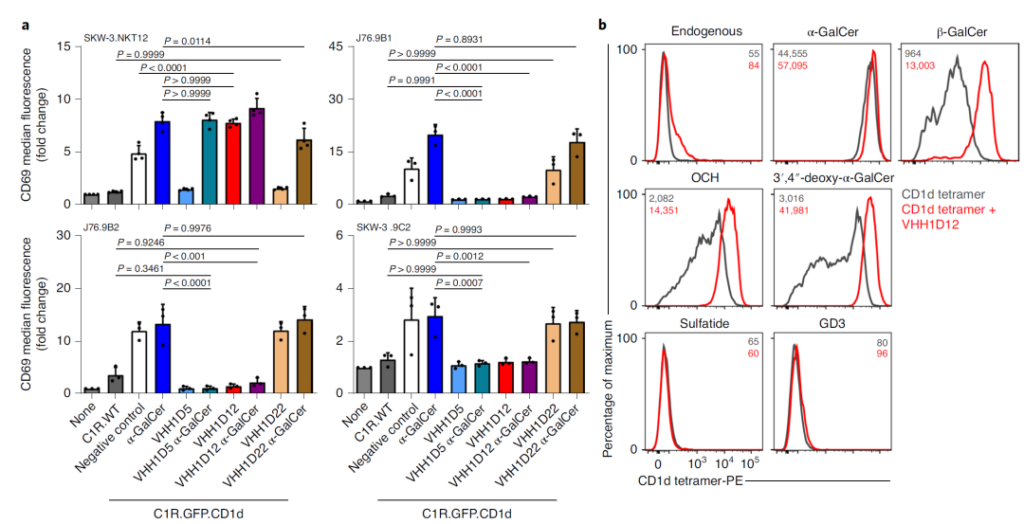
3. In vitro, VHH1D12 can induce type I NKT cell proliferation and cytokine production, and lyse CD1d-expressing tumor cells.
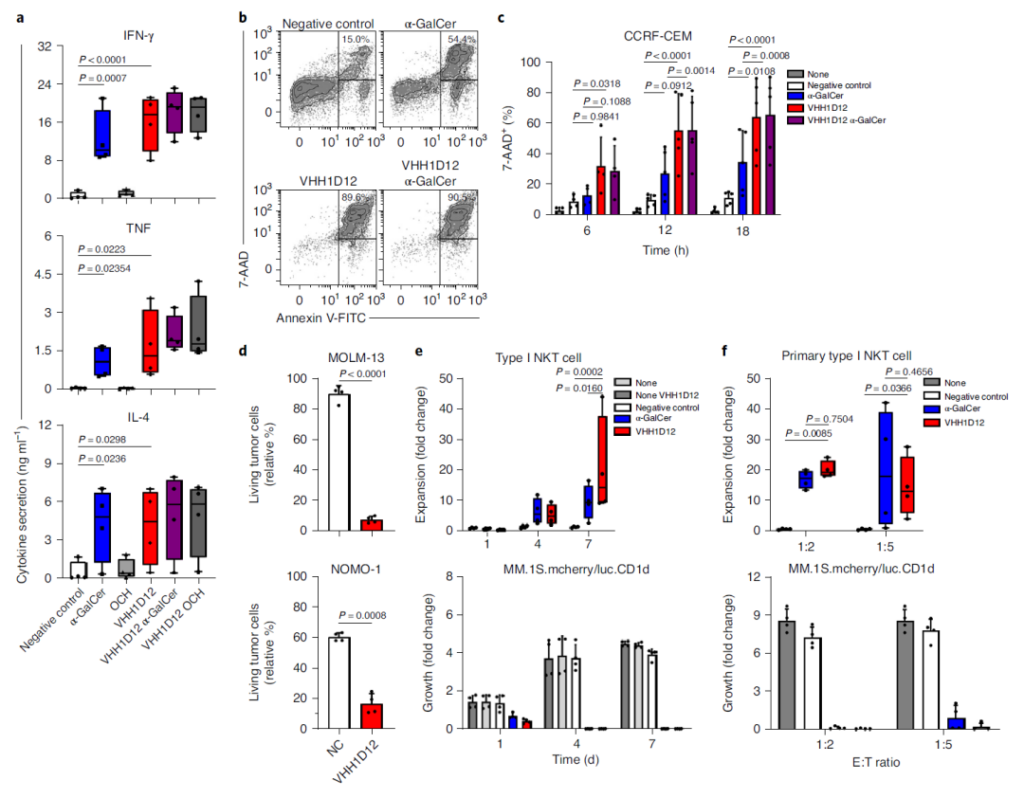
4. VHH1D12 induces the activation of type I NKT cells and is cytotoxic to tumor cells of patients expressing CD1d.
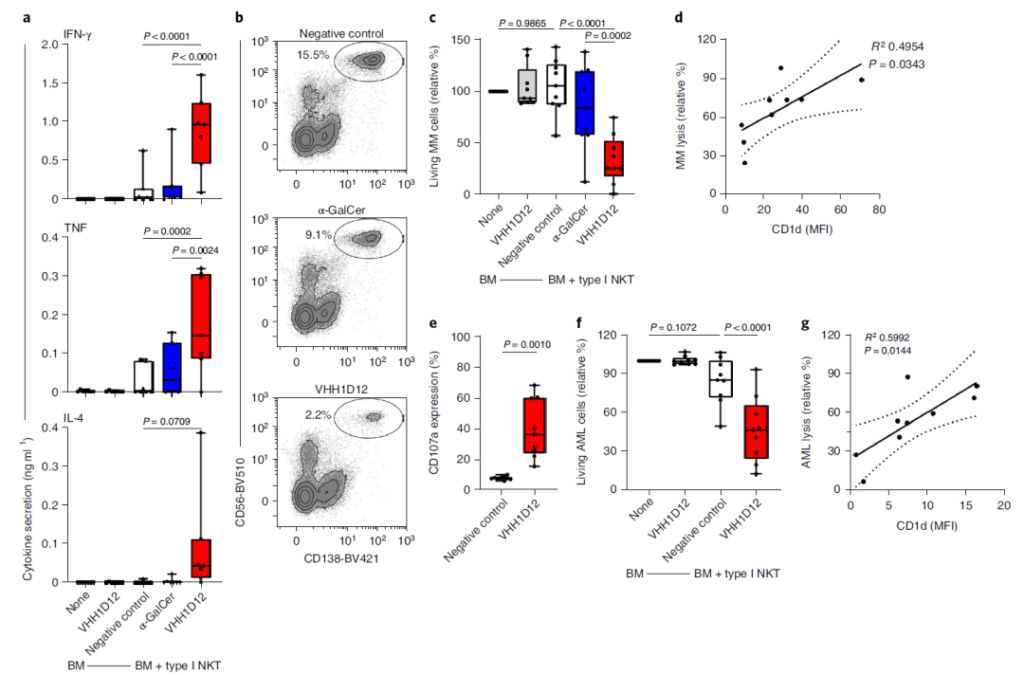
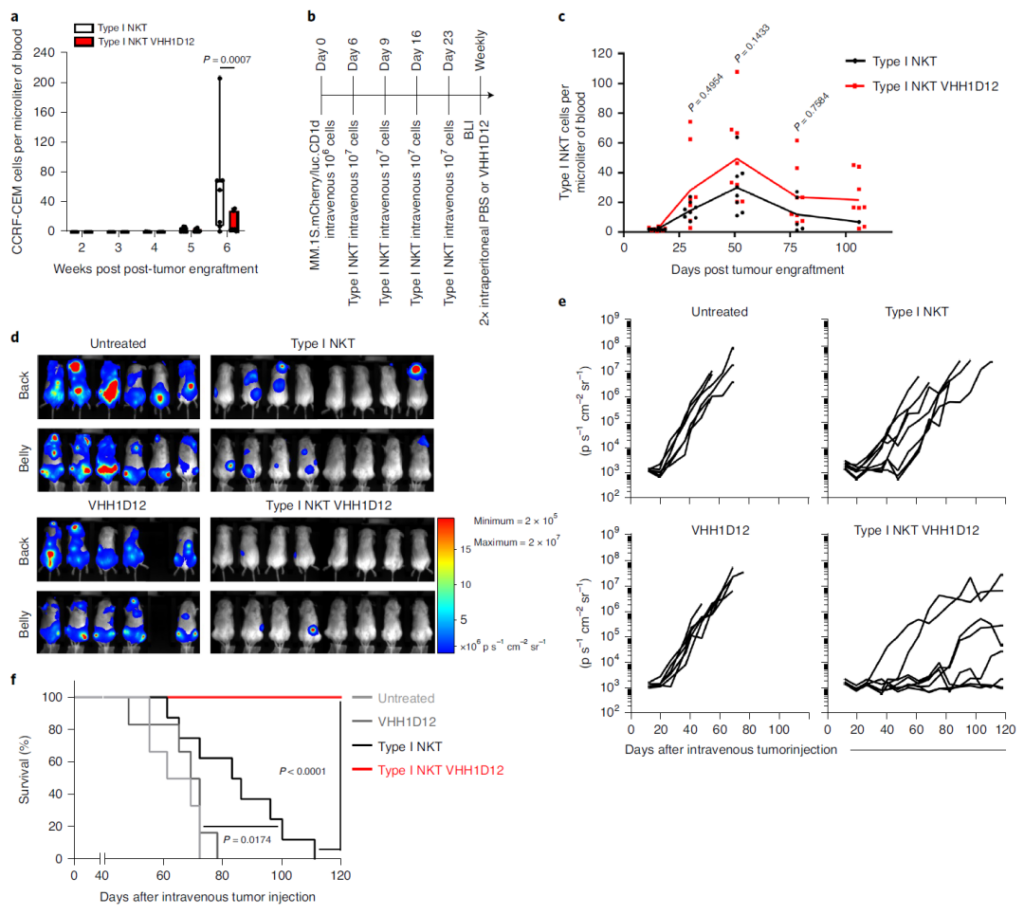
5. In the MM mouse model, VHH1D12 induces the anti-tumor activity of type I NKT cells and increases the survival rate
Summary
Although NKT only accounts for about 1% of T cells, in addition to its direct tumor killing activity, it also has multiple functions such as immunosuppressive cells to clear the tumor microenvironment and helper T effector cell activation. Therefore, it has attracted widespread attention in recent years.
The agonistic bispecific antibodies of CD1d and NKT-TCR can activate NKT cells. Both in vitro cell killing tests and mouse models have shown good anti-tumor activity. In the future, clinical studies are needed for further verification.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



