Reprogram lipid metabolism to prevent T cell senescence and enhance cancer immunotherapy
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Reprogram lipid metabolism to prevent T cell senescence and enhance cancer immunotherapy
Reprogram lipid metabolism to prevent T cell senescence and enhance cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy, including immune checkpoint blocking therapy and adoptive T cell therapy, the emergence of immunotherapy has brought gratifying results for certain types of cancer patients, but the overall effective rate still varies with cancer types, and most cancer patients Tumor immunotherapy did not respond.
One of the key determinants of the therapeutic efficacy and immune response of immunotherapy is the functional status of existing T cells or imported T cells in the suppressive tumor microenvironment. If the patient’s T cell functional status is abnormal or depleted , Then the cancer will continue to develop.
Therefore, further understanding of the mechanisms that lead to abnormal T cell function in the suppressive tumor microenvironment is essential for tumor immunotherapy.
Today, the team of Professor Guangyong Peng of St. Louis University School of Medicine published a research paper titled: Reprogramming lipid metabolism prevents effector T cell senescence and enhances tumor immunotherapy in the journal Science Translational Medicine, a subsidiary of Science.
This study confirms that tumor cells and regulatory T cells (Treg) in the tumor microenvironment can induce changes in lipid metabolism and senescence of T cells by promoting the expression of phospholipase A2-IVA, leading to tumor immune escape. Inhibiting phospholipase A2-IVA can reprogram T cell lipid metabolism, prevent T cell senescence, and enhance anti-tumor immunity and immunotherapy effects.
These findings confirm the link between T cell senescence and lipid metabolism regulation in the tumor microenvironment, indicating that targeting lipid metabolism can further improve the effect of cancer immunotherapy, and also provide a new target for tumor immunotherapy.
The functional status of T cells is a key determinant of effective anti-tumor immunity and immunotherapy. The research team found that T cell senescence driven by malignant tumor cells and regulatory T cells (Treg) is a common feature in cancer development, and the senescence of T cells leads to a decrease in the ability to kill cancer cells.
Senescent T cells have an active glucose metabolism function, but their lipid metabolism is not balanced. This unbalanced lipid metabolism can lead to changes in the expression of lipid-metabolizing enzymes, which in turn changes the types of lipids and the accumulation of lipid droplets in T cells. Cell metabolism (including lipid metabolism) guides the survival, proliferation and effector functions of T cells.
Tumor cells and regulatory T cells (Treg) induce the changes in lipid metabolism and senescence of T cells by promoting the expression of phospholipase A2-IVA in T cells.
The research team conducted verification in mouse models of melanoma and breast cancer. The test results showed that inhibiting phospholipase A2-IVA can reprogram the lipid metabolism of effector T cells, prevent T cells from aging, and enhance anti-tumor immunity and immunotherapy effect.
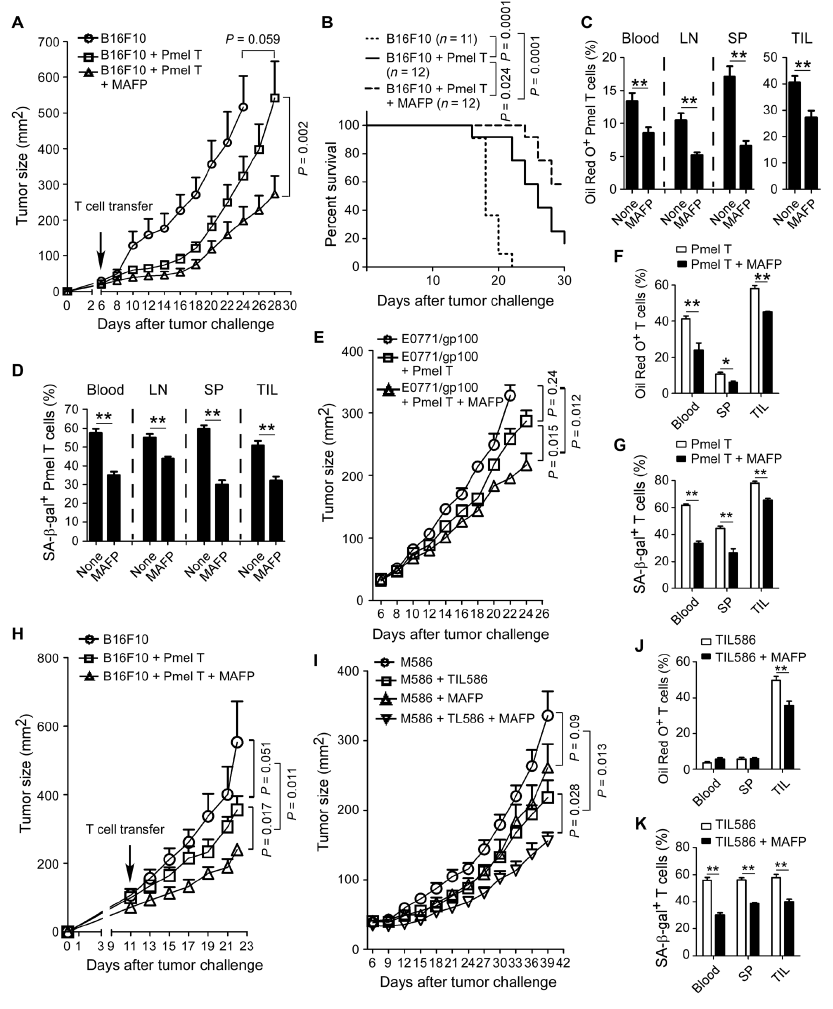
Overall, this study confirmed that tumor cells and regulatory T cells (Treg) in the tumor microenvironment can induce changes in lipid metabolism and senescence of T cells by promoting the expression of phospholipase A2-IVA, leading to tumors. Immune to escape. Inhibiting phospholipase A2-IVA can reprogram T cell lipid metabolism, prevent T cell senescence, and enhance anti-tumor immunity and immunotherapy effects.
These findings confirm the link between T cell senescence and lipid metabolism regulation in the tumor microenvironment, indicating that targeting lipid metabolism can further improve the effect of cancer immunotherapy, and also provide a new target for tumor immunotherapy.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



