Harvard: Vitamin D and fish oil reduce risks of autoimmune diseases by 25-30%
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Harvard: Vitamin D and fish oil reduce risks of autoimmune diseases by 25-30%
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Harvard: Vitamin D and fish oil reduce risks of autoimmune diseases by 25-30%.
The impact of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acid nutritional supplements on health has long been a research focus in various disciplines. However, most studies have focused on whether supplementing these nutrients can prevent cardiovascular diseases and cancer, and few studies have explored its effects on autoimmune diseases.
Recently, the research team at Harvard University brigham and Women’s Hospital (Harvard University brigham and Women’s Hospital) focused on heavy research related to vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids (VITAL trial).
The latest results indicate that for people who can’t sun or eat fish all day, supplementing with vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acid supplements may be the best potential option for preventing autoimmune diseases.
The results of the study were recently announced at the 2021 College of Rheumatology (ACR 2021) annual meeting.
This research is based on supplementary analysis done by VITAL research. In more than 5 years, the VITAL study conducted a rigorous placebo-controlled trial to explore the preventive effects of omega-3 and vitamin D supplementation on related diseases, including the independent and synergistic effects of these two nutritional supplements.
In the study, the researchers included 25,871 men and women with an average age of 67.1 years from across the United States during the period 2011-2014, of which 71% were non-Hispanic whites. The researchers divided the participants into four groups and took supplements/placebos until the end of 2017:
- Supplement vitamin D 2000IU/day + omega-3 fish oil capsules 1g/day,
- Supplement vitamin D+omega-3 placebo,
- Supplement omega-3 + vitamin D placebo,
- Supplement two placebos.
In this analysis of the incidence of autoimmune diseases, participants are required to report autoimmune disease events diagnosed by doctors every year. The primary endpoint is the total incidence of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, autoimmune thyroid disease, psoriasis, etc.
During a median follow-up of 5.3 years, the researchers found:
117 participants in the vitamin D group (supplemented alone or in combination with omega-3) and 150 participants in the vitamin D placebo group were diagnosed with autoimmune diseases. Compared with no vitamin D supplementation, 5-year vitamin D supplementation was associated with a 22% reduction in the risk of autoimmune diseases (HR=0.78, p=0.04).
123 participants in the omega-3 fatty acid group (alone or in combination) and 144 participants in the omega-3 fatty acid placebo group were diagnosed with autoimmune diseases. Compared with no supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids, supplementation of omega-3 fatty acids for 5 years is associated with a 15% reduction in autoimmune diseases (HR=0.85).
After adjusting for factors such as age, gender, race, and other supplements, the analysis found that:
- Vitamin D supplementation alone is associated with a 32% reduction in the risk of autoimmune diseases;
- Supplementing omega-3 fatty acids alone is associated with a 26% reduction in the risk of autoimmune diseases;
- Simultaneous supplementation of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids is associated with a 31% reduction in the risk of autoimmune diseases.
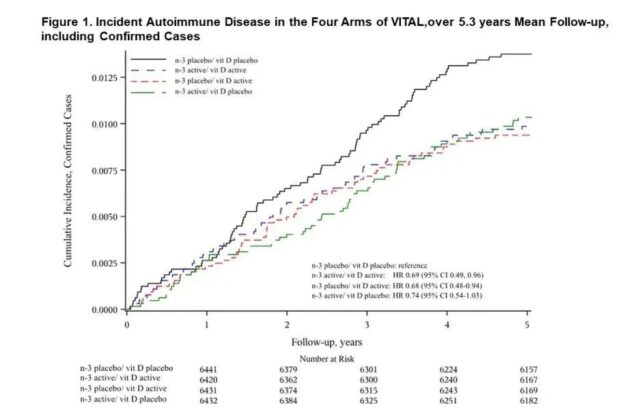
With an average follow-up of 5.3 years, in the VITAL study, the number of participants in the four groups who had autoimmune diseases. In general, compared with the double placebo group, participants in all three supplement groups had a 25% to 30% lower risk of autoimmune disease. (Image source: Reference [1])
The researchers also observed that the longer the supplementation time, the more obvious the effects of vitamin D and Omega-3. Excluding the primary endpoint data for the first 2 years, it was found that 137 patients in the vitamin D group were diagnosed with autoimmune diseases, and the risk of autoimmune diseases was reduced by 39% (HR=0.61) in the vitamin D-supplemented participants; omega supplementation Participants with -3 fatty acids had a 10% reduction in the risk of autoimmune diseases (HR=0.90).
The presenter of the paper, Dr. Karen H. Costenbader of Brigham & Women’s Hospital, pointed out: “It does take a long time for people to take supplements to see a reduction in risk, especially vitamin D, but this It has biological significance. Autoimmune diseases will slowly develop over time, although taking supplements today will not immediately reduce the risk of tomorrow’s disease.”
In addition, the researchers observed an interaction between vitamin D supplementation and body mass index (BMI): Among participants with low BMI, vitamin D supplementation had a stronger preventive effect on autoimmune diseases (P=0.02).
The paper concluded that supplementation of vitamin D and/or omega-3 fatty acids for 5 years can reduce the incidence of autoimmune diseases in the elderly by 25% to 30%. After taking the supplement for 2 years, the effect of vitamin D is stronger.
Dr. Costenbader pointed out: “The results of this study have very high clinical significance because these nutritional supplements may be non-toxic and well tolerated. At present, there are no other known effective therapies that can reduce the incidence of autoimmune diseases. “
Cheryl Koehn, an arthritis patient shared: “Although she did not participate in this study, her specialists have recommended herself to take vitamin D (1000 IU per day) for many years.” Dr. Fatma Dedeoglu, a rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital, also shared Said, “I would also recommend that patients consider taking vitamin D supplements.”
The researchers also pointed out that the study may also have certain limitations: the lack of data on high-risk or nutritionally deficient populations, in these populations, supplementary nutritional supplements may have a greater impact. Moreover, participants are limited to the elderly, and these supplements may also have health benefits for people of other age groups.
Reference
[1]Vitamin D and Marine n-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation and Prevention ofAutoimmune Disease in the VITAL Randomized Controlled Trial. retrieved ACRConvergence 2021, from https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vitamin-d-and-marine-n-3-fatty-acid-supplementation-and-prevention-of-autoimmune-disease-in-the-vital-randomized-controlled-trial/
[2]Vitamin D and Omega-3 Supplements Reduce Autoimmune Disease Risk. RetrievedNovember 07, 2021, from https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/962462
Harvard: Vitamin D and fish oil reduce risks of autoimmune diseases by 25-30%
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



