Does the detection of antibody levels know the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccine?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Does the detection of antibody levels know the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccine?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Does the detection of antibody levels know the protective efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine? “Science” publishes new results.
In the past year, the COVID-19 vaccine has provided an important means for epidemic prevention and control.
With the prevalence of new variants of the virus and potential changes in immunity after prolonged vaccination, additional booster shots have been put on the schedule by many people.
One of the direct purposes of strengthening needles is to stimulate the body to produce higher levels of neutralizing antibodies.
The relationship between the level of antibodies and the protective effect of vaccines has also attracted more and more attention.
However, there are currently no tools specifically used to detect neutralizing antibodies after vaccination with the COVID-19 vaccine; more importantly, the concentration of the COVID-19 neutralizing antibody will definitely protect the vaccinated from infection, and there is still a lack of recognized standards. .
Recently, “Science” published the results of a clinical trial, providing important data on the relationship between the level of antibodies induced by the COVID-19 vaccine and the protection against infection.
In this phase 3 clinical trial called COVE, the researchers evaluated the antibodies induced by participants vaccinated with mRNA-1273, a vaccine developed by Moderna.
Data shows that the level of antibodies can be used to predict the efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine. The higher the level of antibodies, the stronger the protection of the vaccine against COVID-19.
The researchers pointed out that identifying and verifying protection-related immune markers will help us measure the immunity required to fight infection, reliably guide the optimization of the COVID-19 vaccination program, and the clinical evaluation and supervision of more new vaccines in the future approve.
The researchers collected the blood of the test participants after the second shot of the vaccine and 4 weeks after they were vaccinated, and tested the binding antibodies (IgG bAb) and neutralizing antibodies against the viral spike protein (Spike) and antibody binding domain (RBD). Antibody (IgG nAb).
In previous rhesus monkey challenge experiments, these four antibody markers have been shown to be related to the protection of the vaccine, and can effectively inhibit virus replication after rhesus monkeys are exposed to the new coronavirus.
The researchers further evaluated the correlation between each antibody marker and the risk of COVID-19 in this clinical trial.
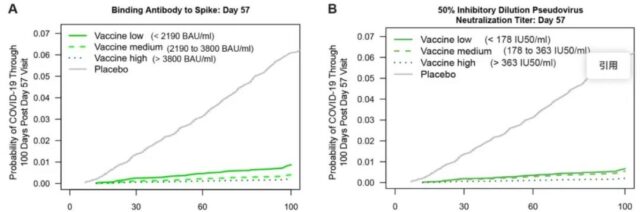
▲The relationship between different antibody levels and the cumulative incidence after vaccination (picture source: reference [1])
The results of the study showed that the evaluated binding antibodies and neutralizing antibodies were negatively related to the risk of COVID-19 within 4 months after the second dose.
Taking any one of these antibody markers as an indicator, compared with people with negative antibody values (undetectable), the risk of infection is about 10 times lower for those who are in the top 10% of vaccinators with antibody values.
After 4 weeks of vaccination, the vaccinators whose neutralizing antibody titer levels (50% neutralizing titer test) were 10, 100, and 1000, predicted the vaccine efficacy to be 78%, 91%, and 96%, respectively.
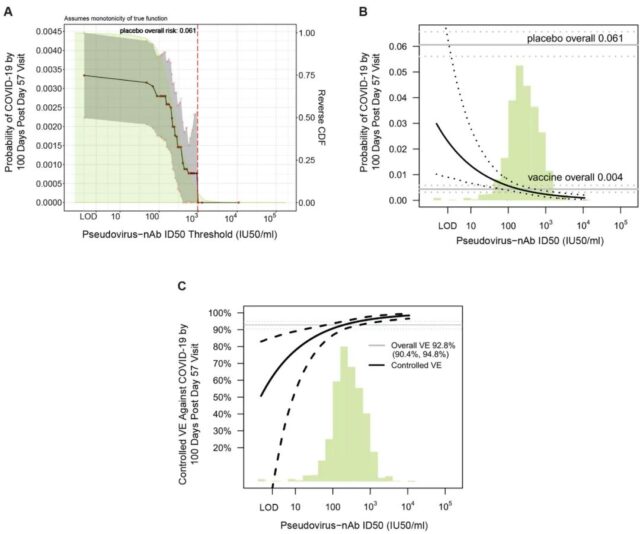
▲Using the level of neutralizing antibody titer as an indicator to evaluate the risk correlation of COVID-19 (picture source: reference [1])
Based on these results, the researchers proposed a continuous model in which the protective efficacy of the vaccine gradually increases as the level of antibody markers increases.
Reference
[1] Peter B. Gilbert et al., (2021) Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Science Doi:10.1126/science.abm3425 (2021).
[2] Antibody levels predict vaccine efficacy, new analysis shows. Retrieved Nov. 29, 2021 from https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/935775
Does the detection of antibody levels know the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccine?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



