The Lancet: Oral Antiaging Drugs Restore Human Antiaging Proteins
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
The Lancet: Oral Antiaging Drugs Restore Human Antiaging Proteins
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
The Lancet: Oral Antiaging Drugs Restore Human Antiaging Proteins
Aging is a natural process, all people will gradually age with age, it seems to be an irreversible natural law.
However, in recent years, with the acceleration of global aging, countries around the world have set off an upsurge in anti-aging research, and various anti-aging drugs and therapies have been discovered one after another, such as niacinamide, metformin and senolytics therapy.
In 2015, Dr. James Kirkland from the Mayo Medical Center in the United States published a paper in the journal Aging Cell [1] , reporting a drug combination that selectively kills senescent cells – Senolytics .
Senolytics therapy consisting of dasatinib and quercetin selectively induces senescent cell death . Among them, dasatinib can clear senescent human adipocyte progenitor cells, while quercetin can kill senescent human endothelial cells and mouse bone marrow stem cells, and the combined effect of the two is stronger.
Alpha-Klotho is an anti-aging protein in the body that reduces the harmful changes that come with aging and disease. Decreasing α-Klotho is associated with many age-related diseases, while increasing α-Klotho has therapeutic potential. However, there is currently no strategy for increasing α-Klotho that is easily translated into clinical applications.
Recently, researchers from Mayo Medical Center James Kirkland published a research paper entitled: Orally-active, clinically-translatable senolytics restore α-Klotho in mice and humans in the journal eBioMedicine [2] .
This study demonstrates that an orally available, clinically translatable drug combination that selectively kills senescent cells, Senolytics , is able to selectively clear senescent cells in naturally senescent mice, diet-induced obese mice and mice with senescent cell transplants , increasing α-Klotho levels .
In addition, increased levels of α-Klotho in the urine were also observed in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) treated with Senolytics.
This study shows that Senolytics can restore the expression level of the anti-aging protein α -Klotho by targeting senescent cells. It opens up new avenues for anti-aging research and clinical applications.

Senescent cells are a key driver of aging in the body, and eliminating senescent cells can delay or alleviate many age-related diseases .
The James Kirkland team established Unity Biotechnologyan anti-aging drug research and development company around Senolytics , to advance clinical trials. The company has been listed on Nasdaq. The company’s investors also include the world’s richest man and Amazon founderBezos.

In the new study, the research team validated the effects of Senolytics in naturally aging mice , mice with diet-induced obesity and mice transplanted with senescent cells.
In mice , oral administration of Senolytics resulted in specific clearance of senescent cells and increased levels of α-Klotho in lobes, kidneys, and brains of mice .
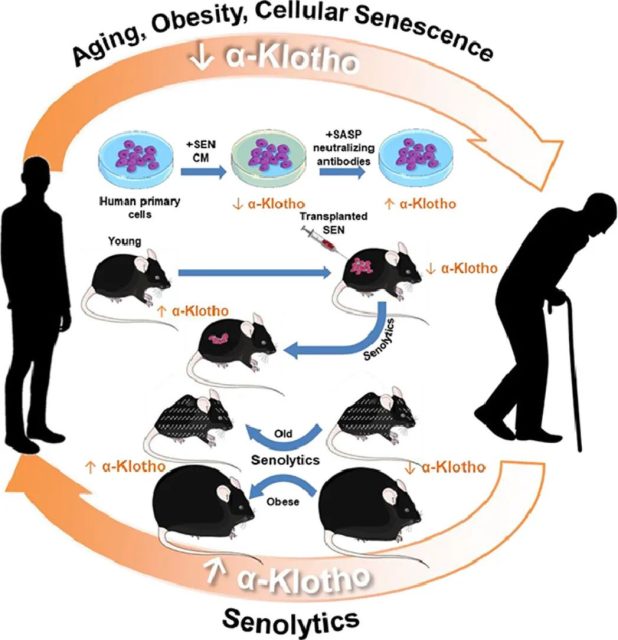
The research team further validated it in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) treated with Senolytics and found that α-Klotho levels in their urine were also increased.
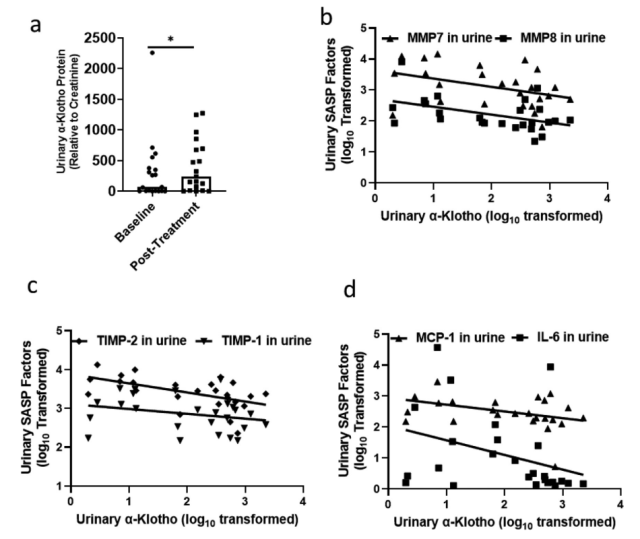
This study shows that Senolytics is able to restore the expression level of the anti-aging protein α-Klotho by targeting senescent cells. It opens up new avenues for anti-aging research and clinical applications.
Reference:
1.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/acel.12344
2.https ://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103912
The Lancet: Oral Antiaging Drugs Restore Human Antiaging Proteins
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



