Why human ability to heal after injury becomes worse and worse?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Why human ability to heal after injury becomes worse and worse?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Why human ability to heal after injury becomes worse and worse? Nature Aging: Can young blood really rejuvenate? Its extracellular vesicles are the key.
As we age, our muscles gradually become smaller and weaker, and our ability to heal after injury becomes worse and worse. What is the reason behind this?
December 7, 2021, researchers from University of Pittsburgh published a report entitled: Regulation of skeletal muscle Aged Regeneration by circulating extracellular vesicles in Nature Aging.
The study found that the decline in muscle function and impaired muscle repair in elderly mice may be driven by extracellular vesicles (EV) .
Extracellular vesicles (EV) deliver the mRNA of a longevity protein called Klotho to muscle cells, thereby promoting the regeneration and repair of muscle cells.
However, the extracellular vesicles (EV) in the aging blood The mRNA of Klotho protein decreased significantly, which explains why the ability of muscle regeneration decreases with age.
These findings indicate that extracellular vesicles (EV) mediate the beneficial effects of young blood , suggesting that we can use them as therapeutic drugs to counteract the functional defects caused by aging.

The leader of the study, Dr. Fabrisia Ambrosio of the University of Pittsburgh , said these findings are very exciting and help us understand the biological mechanisms of muscle regeneration and how muscles weaken with age.
More importantly, these findings suggest that we can use extracellular vesicles as therapeutic drugs to counteract the functional defects caused by aging.
This new research is based on decades of research. For a long time, many studies have found that when an aging animal is replaced with the blood of a young animal, many cells and tissues will regain their youthful state, but what exactly are the components in the blood? This effect has always been controversial.
Extracellular vesicles (EV) refer to vesicle-like bodies with a double-layer membrane structure that are shed from the cell membrane or secreted by the cell, with diameters ranging from 40nm to 1000nm.
Extracellular vesicles are mainly composed of microvesicles (MV) and exosomes (Exosome) .
Extracellular vesicles are widely present in various body fluids, carrying a variety of cell-derived proteins, lipids, DNA, mRNA, miRNA, etc., and are involved in processes such as intercellular communication, cell migration, angiogenesis, and immune regulation.
Considering that extracellular vesicles (EV) shuttle between blood and other tissues, and they carry a large amount of information including nucleic acids and proteins, they can also transmit this information to target cells and tissues. Therefore, the research team began to investigate whether extracellular vesicles (EV) contribute to muscle regeneration.
The research team collected serum from young mice, then removed blood cells and clotting factors, and injected the remaining blood into old mice with muscle injuries.
Compared with older mice that received placebo treatment, mice that received young serum showed enhanced muscle regeneration and functional recovery .
However, when extracellular vesicles (EV) were removed from these serums , this recovery effect Disappeared, which indicates that these extracellular vesicles mediate the beneficial effects of young blood .
Further research found that these extracellular vesicles (EVs) carry mRNA encoding the anti-aging protein Klotho and deliver it to muscle progenitor cells , which are a type of stem cells that are important for skeletal muscle regeneration.
The extracellular vesicles (EV) collected from the blood of old mice carry less Klotho mRNA than those in young mice, so the muscle progenitor cells of old mice produce less Klotho protein.
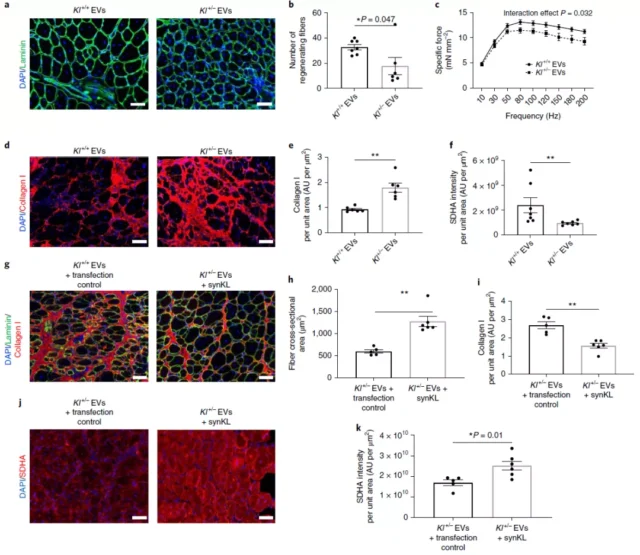
Prior to this, the Fabrisia Ambrosio team has confirmed that Klotho protein is an important regulator of muscle progenitor cell regeneration, and Klotho protein will decline with age.
Therefore, as age increases, muscle function begins to decline, and after injury The repair ability also declines.
And this new study shows for the first time thatThe substances carried in extracellular vesicles (EV) will change with age, resulting in less important information transmitted to stem cells.
This indicates that extracellular vesicles (EV) have the potential to be developed as a new therapy for the treatment of damaged muscle tissue.
In addition to muscles, extracellular vesicles (EV) can also help reverse other effects of aging.
Previous studies have shown that young blood can improve the cognitive ability of old mice .
In July 2020, Science published a research paper from the University of California, San Francisco.
The study showed that old mice that lie still for a long time can recover their brains and regenerate after receiving plasma injections from young mice that exercise regularly. The magical effect.
The study showed that after the mice exercise, a protein called GPLD1 secreted by the liver enters the blood, thereby mediating this miraculous effect of “transfusion for youth”.

It is reported that the Fabrisia Ambrosio team has received a donation to explore the potential of extracellular vesicles (EV) in reversing age-related cognitive decline.
Paper link:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-021-00143-2
https://science.sciencemag.org/content/369/6500/167
Why human ability to heal after injury becomes worse and worse?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



