CureVac/GSK Announced Preclinical Data of Bivalent mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
CureVac/GSK Announced Preclinical Data of Bivalent mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
CureVac/GSK Announced Preclinical Data of Bivalent mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
On April 21, 2022 , CureVac/GSK announced the preclinical data of the co-developed bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccine , and uploaded the preprint on BioRxiv : Low-dose bivalent mRNA vaccine is highly effective against different SARS-CoV-2 variants in a transgenic mouse model , this low-dose ( 5ug ), bivalent mRNA COVID-19 vaccine without modified nucleotides has a good protective effect in preclinical mouse and rat models, this vaccine contains half of Spike-Beta mRNA and half the Spike-Delta mRNA.
A few days ago, Moderna announced the clinical phase 2/3 data of the bivalent vaccine mRNA-1273.211. The doses are 50ug and 100ug, containing half of Spike-WT mRNA and half of Spike-Beta mRNA. mRNA-1273.211 triggers the targeting of Omicron mutants.
Neutralizing antibody titers were only 2-fold higher than mRNA-1273 and did not seem to see a very significant advantage of the bivalent vaccine. Today, let’s take a look at the specific mouse model data of the CureVac bivalent COVID-19 mRNA vaccine.
CureVac-mRNA construct
The biggest feature of CureVac-mRNA vaccine is that it does not use chemically modified nucleotides, and the full-length Spike encoded by the CDS sequence comes from CV2CoV.351 ( Beta ), CV2CoV.617 ( Delta ), and CV2CoV ( original strain ).
The 0.5 ug bivalent vaccine includes 0.25 ug Spike-Beta and 0.25 ug Spike-Delta . LNP was licensed from Acuitas Therapeutics . The specific cap structure, UTR sequence, has not been published in the article.
Vaccination and challenge trial design
On days 0 and 28, K18-hACE2 mice were vaccinated with intramuscular injection of low-dose 20ul/0.5ug CV2CoV ( original strain vaccine ), 0.5 μg CV2CoV.351 ( Beta variant vaccine ), 0.5 μg CV2CoV.617.2 ( Delta variant vaccine ), 0.25µg CV2CoV.351 + 0.25µg CV2CoV.617.2 ( Beta and Delta combination vaccine ), unimmunized control group was injected with 20 μl NaCl.
Serum was collected on day 0 ( Prime ) and day 28 ( Boost ), day 56, respectively . On day 56, for groups of vaccinated mice, 4 mice per group were sacrificed prior to challenge for analysis of cellular immune responses in lung and spleen. The remaining mice were used for B.1.351 or B.1.617.2 challenge .
Four days after challenge, mouse oral samples were collected . Ten days after challenge, mice were dissected and organ samples were collected including lung, spleen, inferior turbinate, brain, cerebellum.
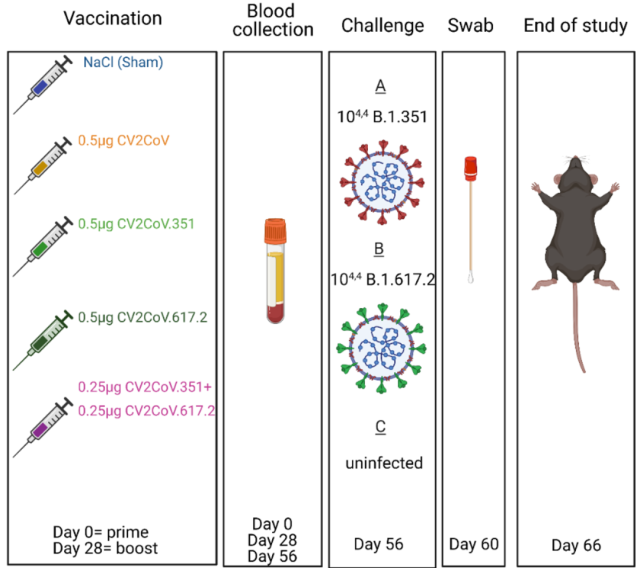 Mouse Vaccination and Challenge Trial Design
Mouse Vaccination and Challenge Trial Design
Severity and mortality
All vaccinated mice did not experience death caused by the new coronavirus after challenge, nor did they experience significant weight loss .
In contrast, unvaccinated mice, the saline-injected control group, were significantly reduced in survival and body weight after infection with Beta strain and Delta strain ( all mice in the Beta strain group lost weight, and the infection 67% of the mice in the Delta strain group lost weight ).
The above data show that in mice, mice vaccinated with the original strain mRNA vaccine, Beta variant strain mRNA vaccine, Delta variant strain mRNA vaccine, and Beta/Delta bivalent mRNA vaccine can trigger very good preventive and protective effects.
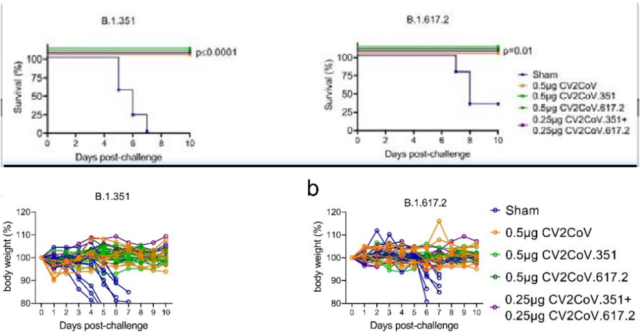 Mortality and body weight changes after challenge was completed in different vaccine groups and control groups
Mortality and body weight changes after challenge was completed in different vaccine groups and control groups
Viral load
In the vaccinated mice group, after the challenge was completed, except for a few cases, no novel coronavirus genomic RNA or subunits were detected in the oral samples collected on the 4th day and the lung , brain and cerebellum samples collected on the 10th day Group RNA ( subgenomic RNA ) .
In the group of mice vaccinated with monovalent vaccine, the degree of inhibition in the inferior turbinate ( conchae ) of SARS-CoV-2 varied by strain, but all showed inhibition of viral replication compared to the unvaccinated group.
Replication of the Delta strain was completely inhibited in the inferior turbinate of all vaccinated groups of mice , with no detectable viral subgenomic RNA .
The inhibition of the Betla strain in the inferior turbinate in the mice vaccinated with the bivalent vaccine was roughly equivalent to that in the group of mice vaccinated with the Spike-Betla mRNA vaccine .
From the above data, it can be found that the replication ability of new coronavirus variants in the inferior turbinate is different, but it is generally more difficult to suppress and clear than the lungs.
Even in the case of specific vaccines, it is still impossible to completely clear some new coronaviruses in the inferior turbinate. Replication of mutant strains.
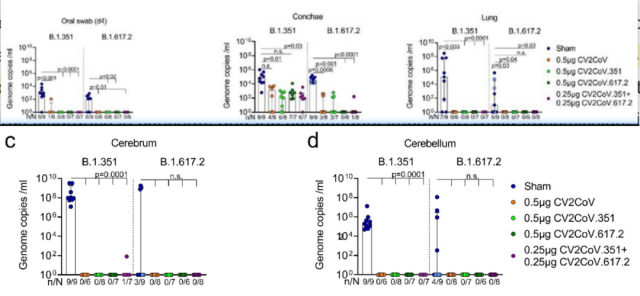 Virus replication in vivo after infection with different new coronavirus strains in mice vaccinated with different vaccines
Virus replication in vivo after infection with different new coronavirus strains in mice vaccinated with different vaccines
Serum antibodies
Serum RBD-binding antibody titers were generally high in all vaccinated mouse groups and did not differ significantly from each other , nor did they decay before and after challenge.
Although the mRNA content of the corresponding variant contained in the bivalent vaccine is only half of that of the monovalent vaccine (0.25 µg vs. 0.5 µg), for the homologous new coronavirus variant , the serum neutralizing antibody triggered by the bivalent vaccine corresponds to the vaccination The monovalent vaccine triggers the same titer .
Before and after the challenge, the serum neutralizing antibody titers triggered by the bivalent vaccine group were significantly higher than those triggered by the original strain vaccine , and were not related to the type of infection variant .
Neutralizing antibodies targeting homologous strains were at higher levels in serum antibodies triggered by the monovalent vaccine .
In addition, in the rat model , inoculated with 8 μg CV2CoV ( Spike-WT mRNA ), 8 μg CV2CoV.617.2 ( Spike-Delta mRNA ), 4 μg CV2CoV + 4 μg CV2CoV.617.2 ( Spike-WT mRNA and Spike-Delta mRNA ), 4µg CV2CoV.351 + 4µg CV2CoV.617.2 ( Spike-Beta mRNA and Spike-Delta mRNA ), all four groups of vaccines can trigger relatively high serum neutralizing antibody titers targeting the Delta strain .
In contrast, compared with serum neutralizing antibody titers targeting the Delta strain, the targeting triggered by the group of mice vaccinated with the other vaccines , except for the group of mice vaccinated with the Beta and Delta combination bivalent vaccine (a 2-fold increase) The serum neutralizing antibody titers of Omicron BA.1 were significantly decreased ( 9-4 times ) in different degrees.
4µg CV2CoV.351 + 4µg CV2CoV.617.2 ( Spike-Beta mRNA and Spike-Delta mRNA ) was more effective than 4µg CV2CoV + 4µg CV2CoV.617.2 (Serum neutralizing antibody titers targeting Omicron BA.1 triggered by Spike-WT mRNA and Spike-Delta mRNA) were high ( 8-fold ).
The above data show that the bivalent vaccine has a more efficient broad-spectrum neutralization ability in response to different mutant strains than the serum neutralizing antibodies triggered by the original strain vaccine or the monovalent vaccine .
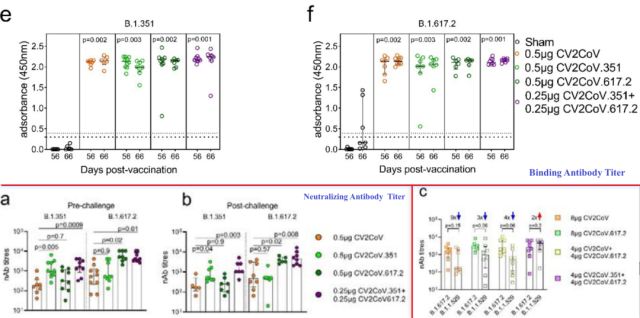 Serum binding antibody and neutralizing antibody titers of mice vaccinated with different vaccines
Serum binding antibody and neutralizing antibody titers of mice vaccinated with different vaccines
Cellular immunity
Both monovalently vaccinated and bivalently vaccinated mice elicited strong Spike-specific CD4 + and CD8 + responses compared to unvaccinated mice , with pulmonary CD45iv-CD8 + T cells having more 2-3 log boost .
To further characterize the T cell response, a higher proportion of TRM cells ( resident memory T cells ) were identified in the lung by surface markers of lung resident T cells .
It was also found that mRNA vaccination can also induce the production of CD8 + T cells in the lungs that secrete large amounts of IFNγ and granzymes.
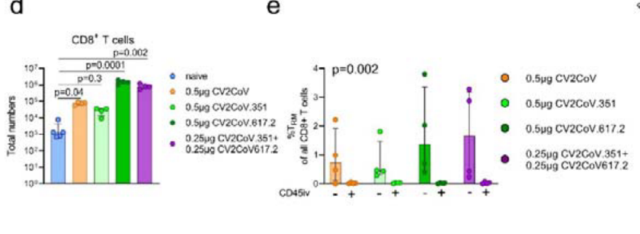
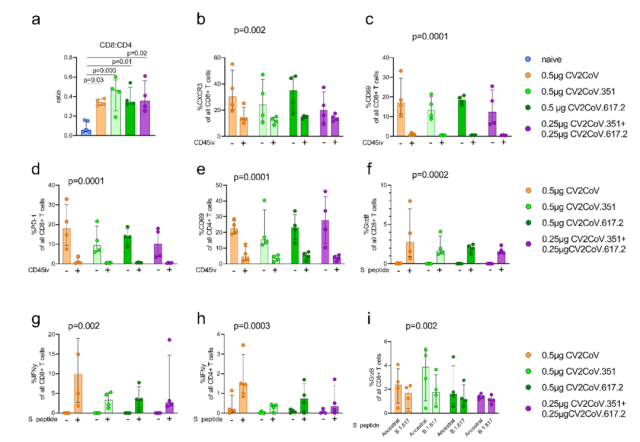 Both the vaccinated mice triggered strong CD4 + and CD8 + responses, and a large number of TRM cells were present in the lungs
Both the vaccinated mice triggered strong CD4 + and CD8 + responses, and a large number of TRM cells were present in the lungs
Summary
To summarize the clinical data obtained in the mouse model of the CureVac-mRNA vaccine:
1. Inoculation of Spike-WT mRNA vaccine/Spike-Beta mRNA vaccine/Spike-Delta mRNA vaccine/Spike-Beta+Delta mRNA bivalent vaccine shows good protective effect in the face of Beta variant strain or Delta variant strain .
2. The replication ability of the new coronavirus variant in the upper respiratory tract is different, and the new coronavirus is generally more difficult to clear in the inferior turbinate than in the lungs . Beta/Delta variant replication was undetectable in the oral cavity, lung, brain and cerebellum of all vaccinated mice after challenge.
In all groups of vaccinated mice, Delta variant replication was undetectable in the inferior turbinate of mice after challenge. In all the mice in the vaccinated group, the replication of the Betla strain variant was detected in the inferior turbinate of the mice after challenge, but the virus replication ability was inhibited compared with the unvaccinated group.
The inhibition of the Betla strain in the inferior turbinate in the mice vaccinated with the bivalent vaccine was roughly equivalent to that in the group of mice vaccinated with the Spike-Betla mRNA vaccine.
3. Serum binding antibody titers triggered by all vaccinated mice were roughly equivalent, with no significant differences. Mice vaccinated with the monovalent vaccine elicited serum-neutralizing antibodies against the Beta/Delta variant, but produced significantly different serum-neutralizing antibody titers .
Inoculation with the bivalent vaccine , although the Spike mRNA content of the corresponding variant strain contained was halved, the titer of serum neutralizing antibody triggered by the monovalent vaccine was the same as the titer of serum neutralizing antibody triggered by the monovalent vaccine .
For example, when faced with the Beta variant, the serum neutralizing antibody titers triggered by the Spike-Beta mRNA vaccine and the Spike-Beta+Delta mRNA bivalent vaccine were comparable, compared with the Spike-WT mRNA vaccine/Spike- Delta mRNA vaccine triggers 2-10 times higher.
4. The serum neutralizing antibody titers of the Omicron-targeting strain triggered by the inoculation of Spike-Delta mRNA vaccine were 3 times lower than that of the Delta-targeting isotype .
The serum neutralizing antibody titers triggered by the Spike-Beta+Delta mRNA bivalent vaccine against the Omicron strain were 8-fold higher than those of the Spike-WT+Delta mRNA bivalent vaccine .
5. Compared with the unvaccinated mouse group, both the monovalently vaccinated and bivalently vaccinated mouse groups can trigger strong Spike-specific CD4+ and CD8+ responses to generate lung-resident TRM cells.
From the above data, it can be seen that the CureVac COVID-19 bivalent vaccine has an advantage over the monovalent vaccine when dealing with different variants.
This shows that in the optimization and upgrading of vaccines, the use of bivalent or multivalent vaccines can trigger heterologous protection effects and improve the broad-spectrum neutralization ability of serum neutralizing antibodies against different mutant strains .
Considering the flexibility of encapsulating mRNA during the preparation of mRNA vaccines, this makes mRNA vaccines have significant advantages in R&D and production when dealing with current different new coronavirus variants.
CureVac/GSK Announced Preclinical Data of Bivalent mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.




