FDA approves first re-dose gene therapy: $630000 a year
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
FDA approves first re-dose gene therapy: $630000 a year
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
FDA approves first re-dose gene therapy: $630000 a year.
On May 19, 2023, FDA approved Beremagene Geperpavec (B-VEC) , a herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) -based topical gene therapy developed by Krystal Biotech , under the trade name Vyjuvke.
For the treatment of wounds in patients 6 months of age and older with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) with mutations in the COL7A1 gene.

It is reported that this is the first topical gene therapy approved by the FDA, the first gene therapy that can be administered repeatedly, and the first gene therapy for the treatment of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) .
Because the gene therapy is administered topically, it requires long-term repeated administration and cannot provide a one-time cure like previous adeno-associated virus (AAV) -based gene therapies.
According to Krystal Biotech , the treatment costs $24,250 per bottle, and the average patient uses 26 bottles per year, which means that the annual treatment cost is as high as $630,000, and it still costs $ 485,000 after government-mandated discounts .

Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa, DEB) is a rare hereditary skin disease caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, which encodes type VII collagen (C7) , and the skin of patients is prone to bullae , Blood blisters, these patients are also known as “butterfly babies”, describing their skin as fragile as a butterfly, which will break when touched.
It is one of the most painful diseases in the world , and patients are prone to infection, skin cancer, and even death.
Beremagene Geperpavec (B-VEC) is an investigational herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) -based topical gene therapy designed to treat malnutrition by delivering the COL7A1 gene to restore expression of type VII collagen (C7) Epidermolysis bullosa type.
On December 15, 2022, the research team of Stanford University School of Medicine published a research paper entitled: Trial of Beremagene Geperpavec (B-VEC) for Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa in the New England Journal of Medicine ( NEJM) .
The results of this phase 3 clinical trial showed that topical B-VEC therapy can significantly promote complete wound healing in patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa at 3 and 6 months.

This is a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial involving 31 patients aged 6 months or older who were confirmed by genetic sequencing to have dystrophic bullous disease caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene Epidermolysis .
The research team selected a pair of skin wounds for each patient, matching them based on wound size, area and appearance. Each patient’s wound pair was then randomly assigned to receive Beremagene Geperpavec (B-VEC) or placebo for a period of 26 weeks.
B-VEC therapy uses herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) as a gene delivery vehicle to deliver the COL7A1 gene into cells, and pioneered the innovative use of a gel- based topical drug delivery method to spread in patients Apply to skin wounds, then protect with a bandage.
The primary endpoint of this Phase 3 clinical trial was complete healing of treated wounds compared to untreated wounds at six months of treatment. Secondary endpoints included complete wound healing at 3 months and change in pain severity at re-dose (bandage replacement) .
Results of the trial showed that at six months, 67 percent of B-VEC-treated wounds had healed completely, compared with 22 percent of placebo-treated wounds. At 3 months, 71% of B-VEC-treated wounds were completely healed, compared with 20% of placebo wounds.
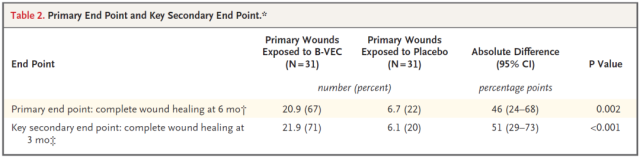
Overall, the results of this phase 3 clinical trial showed that topical B-VEC therapy significantly improved complete wound healing in patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa at 3 and 6 months. Pruritus and mild systemic side effects were observed in patients during treatment.
Krystal Biotech was founded in 2015 and listed on Nasdaq in 2017, with a current market capitalization of about $2.5 billion. The company is focused on developing gene therapies for serious rare diseases caused by single gene deletions or mutations.
In addition to B-VEC therapy, the company also has several gene therapies in the clinical stage, respectively treating autosomal recessive ichthyosis (Project No. KB105) and cystic fibrosis (Project No. KB407) with TGM1 gene defect , and anti-aging skin treatments based on type 3 collagen .
Paper link :
https://www.krystalbio.com/
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2206663
FDA approves first re-dose gene therapy: $630000 a year.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



