Eli Lilly new drug for Alzheimer’s disease achieved 35% reduction in cognitive decline
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Eli Lilly new drug for Alzheimer’s disease achieved 35% reduction in cognitive decline
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
JAMA: Eli Lilly new drug for Alzheimer’s disease achieved 35% reduction in cognitive decline.
On July 17, 2023, Eli Lilly published a paper entitled : Donanemab in Early Symptomatic Alzheimer Disease The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 Randomized Clinical Trial in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) .
Revealed data from Phase 3 clinical trial of highly anticipated Alzheimer’s disease candidate Donanemab , showing the drug achieved a 35% reduction in cognitive decline compared to placebo and patients progressed to the next stage of the disease risk fell by 39% . Lilly said the drug is expected to be approved in the first half of 2024.

Affected by the clinical trial results of the blockbuster weight- loss drug Tirzepatide and the Alzheimer’s disease candidate drug Donanemab , Eli Lilly’s market value has continued to rise recently, and its current market value has exceeded US$420 billion, making it the world’s No. 1 pharmaceutical company in terms of market value. one.

Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) , commonly known as ” Alzheimer’s disease “, is a serious neurodegenerative disease. Patients usually have symptoms of memory loss and learning ability weakening, accompanied by emotional regulation Impairment and loss of motor ability greatly affect the development of individuals, families and even society.
Currently, about 50 million people worldwide suffer from Alzheimer’s disease. As the average human life expectancy increases and the aging society intensifies, the prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease is also increasing. It is estimated that by 2050, the number of patients with Alzheimer’s disease will increase to more than 150 million .
However, drug development for Alzheimer’s disease has been accompanied by failures. International pharmaceutical giants including Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Roche have invested tens of billions of dollars in research and development, but with little success.
Two Alzheimer’s disease monoclonal antibody drugs on the market
Until June 7, 2021, the FDA announced the accelerated approval of the monoclonal antibody drug Aducanumab ( trade name Aduhelm) jointly developed by Eisai and Biogen for the treatment of mild Alzheimer’s disease. cognitive impairment (MCI) and mild Alzheimer’s disease. This is the first new drug for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease approved by the FDA since 2003.
However, the approval of the drug is full of controversy. Clinical trials have shown that this monoclonal antibody can clear β-amyloid (Aβ) in the brain , but there is not enough evidence that it can slow or stop the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Disease progression.
In addition, the drug also has multiple side effects risks. Among the 1029 patients in the 10mg/kg dose group, 425 patients (41.3%) experienced amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) problems, and 362 patients (35.2%) ARIA cerebral edema developed, and 94 of them developed associated symptoms such as headache, confusion, dizziness and nausea.
ARIA microbleeds were seen in 197 patients (19.1%) , and superficial siderosis in ARIA was seen in 151 patients (14.7%) . Of those patients who experienced side effects, 14 were severe.
On January 6, 2023, the FDA approved another Alzheimer’s disease drug, Lecanemab (trade name Leqembi), jointly developed by Eisai and Biogen , for the relief of mild and early-stage Alzheimer ‘s disease. Cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s patients.
image
The approval of Lecanemab is based on the results of the Phase III clinical trial published in the ” New England Journal of Medicine ” (NEJM) on November 29, 2022.
The results of this clinical trial for nearly 1,800 patients with early Alzheimer’s disease showed that, The drug slowed the rate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s patients by 27% .
However, adverse reactions in clinical trials have also caused controversy.
Cerebral hemorrhage occurred in 17.3% of patients receiving the drug (compared to 9% in the placebo control group) , and brain swelling occurred in 12.6% of patients (vs. 1.7% in the placebo control group). ) .
The drug candidate, Donanemab , developed by Eli Lilly , is a monoclonal antibody that targets β-amyloid (Aβ) modified by pyroglutamate at the 2nd position of the N-terminus.
In this Phase 3 clinical trial of TRAILBLAZWE-ALZ 2, the main analysis population (1182 patients) had intermediate levels of tau protein and clinical symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, which means they were in more advanced Alzheimer’s disease disease state.
In contrast, the two Alzheimer’s disease monoclonal antibody drugs approved by Eisai and Biogen are both in clinical trials in patients with early and mild Alzheimer’s disease.
The primary endpoint of this Phase 3 clinical trial of donanemab is based on the Integrated Alzheimer’s Disease Rating Scale (iADRS) , which combines two widely used Alzheimer’s disease measures to detect disease progression and treatment response .
The scale takes into account activities of daily living such as driving, hobbies and other things that are critical to quality of life.
Results showed that the clinical trial met its primary endpoint, with donanemab slowing the decline in cognitive function in patients by 35% compared to placebo .
In addition, the clinical trial also met several secondary endpoints. Within 18 months of Donanemab treatment, the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR-SB) showed that the decline in cognitive function in patients slowed down by 35%. Eisai and Biogen’s approved lecanemab in phase 3 clinical trials is 27%.
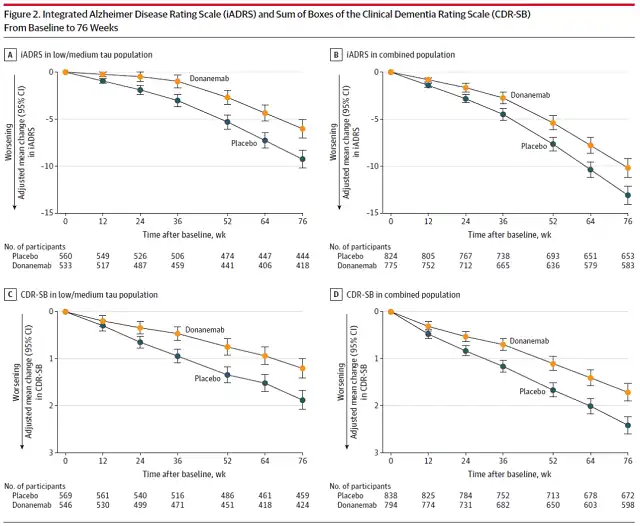
Analysis of other secondary endpoints showed that 47% of patients in the Donanemab treatment had no decline in CDR-SB scores within one year, compared with 29% in the placebo group.
Fifty-two percent of patients completed treatment within 1 year of protein plaque clearance in the brain , and 72% completed treatment within 18 months.
Patients who received the treatment also experienced a 40 percent slower rate of decline in their ability to perform activities of daily living at 18 months.
Compared with a placebo, those who received the treatment had a 39 percent lower risk of progressing to the next stage of Alzheimer’s disease.
All of these secondary endpoints demonstrate the clinical benefit of donanemab .
Aducanumab, which was previously approved by Eisai and Biogen, only reduced amyloid plaques in the brain, but did not really improve or slow down cognitive decline, that is, no clinical benefit was observed, which also led to the approval of Aducanumab caused great controversy.
Lilly said donanemab significantly reduced the risk of patients progressing to the next stage of the disease, in addition to showing the best effect in slowing cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease patients so far observed in phase 3 clinical trials , Alzheimer’s disease progression to the next stage (from mild cognitive impairment to dementia, or mild dementia to moderate dementia) means a huge decline in the patient’s quality of life.
Side effects are also worthy of attention
It should be pointed out that the two previously approved monoclonal antibody drugs Aducanumab and Lecanemab, as well as Donanemab introduced in this article, have observed amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA ) in clinical trials , including ARIA brain swelling (ARIA-E) , ARIA cerebellar hemorrhage (ARIA-H) , etc. Usually ARIA is asymptomatic, but in rare cases it can lead to serious or life-threatening events.
According to news released by Lilly, in this phase 3 clinical trial, 3 patients experienced ARIA-related deaths. ARIA-E occurred in 24% of patients compared with 6.1% in the placebo group; ARIA-H occurred in 31.4% of patients compared with 13.6% in the placebo group.
Most ARIA cases are mild to moderate and resolve or stabilize with appropriate management, Lilly said. The incidence of severe ARIA was 1.6%. The potential clinical benefits of donanemab are encouraging, although like many effective treatments for debilitating and fatal diseases, there are associated risks that can be serious and life-threatening.
Paper link.
Eli Lilly new drug for Alzheimer’s disease achieved 35% reduction in cognitive decline
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



