Breakthrough Nebulized LNP Technology for Efficient mRNA Delivery to Lungs
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Breakthrough Nebulized LNP Technology for Efficient mRNA Delivery to Lungs
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Breakthrough Nebulized LNP Technology for Efficient mRNA Delivery to Lungs
Nucleic acid-based drugs, known for their flexibility in encoding therapeutic proteins for the treatment, prevention, or vaccination against various diseases, have seen significant advancements with the development and optimization of viral carriers like lentiviruses, adeno-associated viruses (AAV), and non-viral carriers such as lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
These carriers have greatly propelled the field of nucleic acid drugs.
However, current nucleic acid drug delivery systems tend to accumulate in the liver, and diseases affecting the lungs, including COVID-19, influenza, cystic fibrosis, primary ciliary dyskinesia, α-1 antitrypsin deficiency, asthma, and lung cancer, urgently require an effective carrier to deliver mRNA specifically to the lungs, enhancing the prevention and treatment of pulmonary diseases.
As of now, research on pulmonary-targeted mRNA delivery has primarily been conducted in mice using polyethyleneimine (PEI) and lipid nanoparticles (LNP) with minimal clinical trials in humans.
Notably, a clinical trial by Translate Bio involving LNP-delivered mRNA through nebulization for the treatment of cystic fibrosis did not show significant improvement in lung function post-treatment, highlighting the need for further advancements in lung-targeted delivery systems.
On November 20, 2023, the team led by Daniel Anderson at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology published a research paper titled “Combinatorial development of nebulized mRNA delivery formulations for the lungs” in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
The study introduces the most efficient nebulized LNP formulation to date for delivering mRNA to the lungs, offering a promising carrier for gene therapy of pulmonary diseases.

The potential of in vivo mRNA delivery holds promise for treating and preventing various genetic and infectious diseases, including its outstanding efficacy in COVID-19 protection when administered intramuscularly as an mRNA vaccine based on lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Beyond infectious disease vaccines, mRNA technology is also utilized in tumor therapeutic vaccines, protein replacement therapies, and gene editing.
Challenges in nebulized mRNA delivery based on lipid nanoparticles (LNP) are associated with several nebulization and lung-specific barriers:
- Nebulization induces strong shear forces that can disrupt nanoparticle structures and induce aggregation.
- Transfecting bronchial epithelium requires penetration of the mucus layer, presenting challenges in diffusion space and chemical obstacles.
- While nanoparticle uptake is most effective at the basolateral side of polarized lung epithelial cells, tight junctions at the basolateral side make it challenging for delivered LNPs to enter.
To address nebulization challenges, the research team first optimized LNP component ratios to enhance stability. Further improvements in LNP stability were achieved through rational design of buffer conditions and excipients.
Subsequently, the team used an air-liquid interface (ALI) culture to screen a lipid library for mRNA delivery to lung epithelium.
ALI culture demonstrated good predictive capability and yielded two candidates with outstanding in vivo performance—IR-117-17 and IR-19-Py.
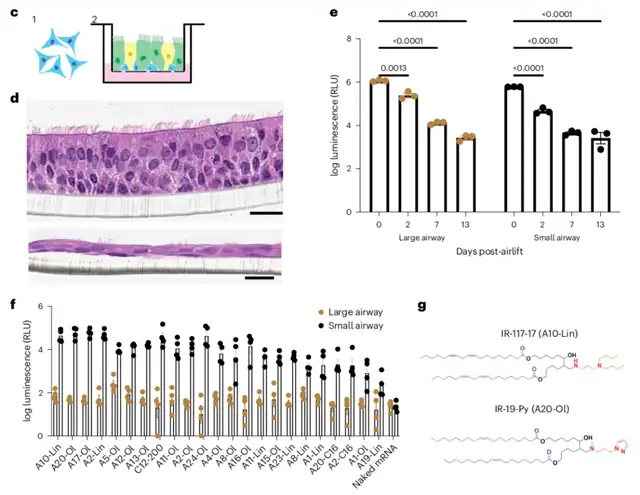
When nebulized under optimized conditions, both lipids significantly outperformed the state-of-the-art mRNA delivery carriers to the lungs and nasal cavity.
Nebulized IR-117-17 LNP demonstrated a 300-fold improvement in mRNA delivery to the lungs compared to LNPs and a 45-fold improvement in delivering to the upper airways compared to previously reported hyperbranched poly (β-amino ester) (PBAE).
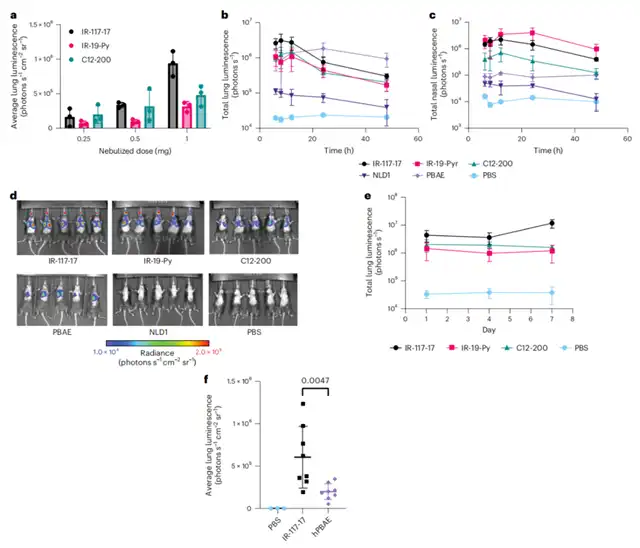
Inhalable mRNA presents the potential to treat various diseases. However, nebulized lipid nanoparticles face unique challenges, including stability during nebulization and penetration of cellular barriers.
This study developed a combination approach to overcome these obstacles. Firstly, by altering nebulization buffer to increase the charge of LNPs during nebulization and adding branched polymer excipients, LNP formulations could be stabilized to resist nebulization-induced aggregation.
Subsequently, the team synthesized ionizable and degradable lipid combinations using reductive amination and evaluated their delivery potential with fully differentiated air-liquid interface (ALI) cultured primary lung epithelial cells.
The developed combination of ionizable lipids, charge-stabilizing formulations, and stability-enhancing excipients demonstrated significant improvements in the efficiency of mRNA delivery to the lungs compared to the current state-of-the-art LNPs and polymer nanoparticles.
Paper Link: Read More
Breakthrough Nebulized LNP Technology for Efficient mRNA Delivery to Lungs
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



