ECMO: Crucial Euipment during COVID-19 pandemic
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
ECMO: Crucial Euipment during COVID-19 pandemic
ECMO: Crucial Euipment during COVID-19 pandemic. How much do you know about the life-saving artifact “ECMO”?
What is ECMO? How it works?
During the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia at the beginning of the year, ECMO frequently appeared on the scene and was called a “life-saving artifact.” What is ECMO? How does it work?
The heart is a blood pump with rhythmic contraction and relaxation. When the heart contracts, the arteries and blood vessels output the heart full of fresh oxygen and nutrients to the various organs of the body; when the heart is diastolic, the venous blood vessels input the blood containing carbon dioxide and other metabolic waste products into In the heart, it exchanges with the oxygen inhaled in the lungs and becomes oxygen-rich blood again.
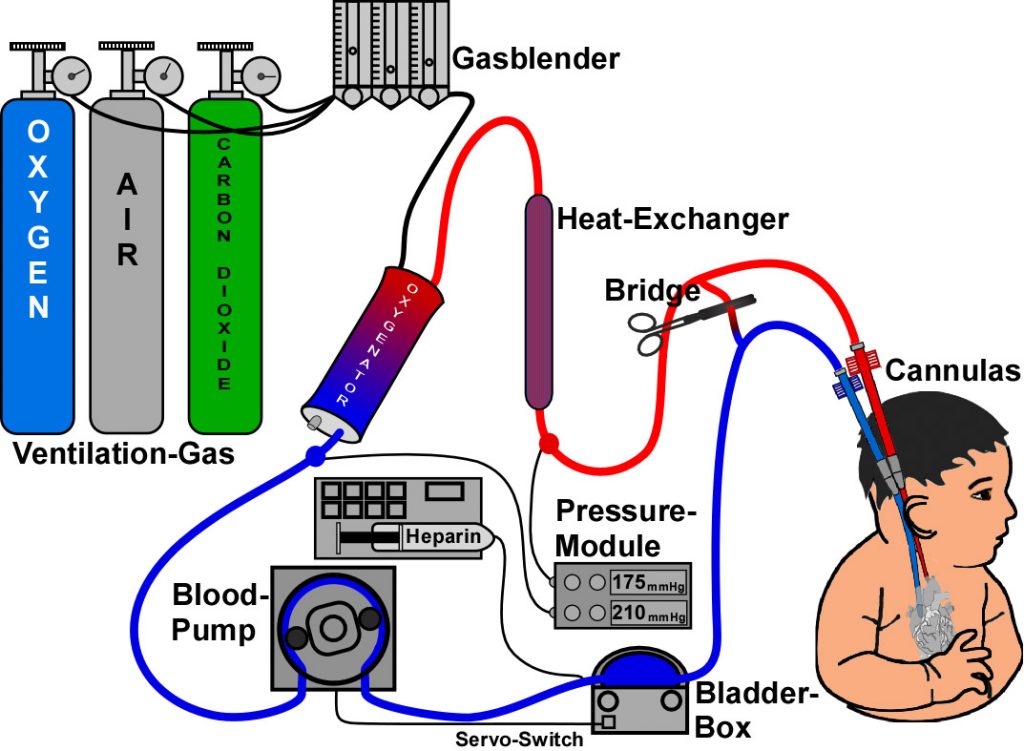
ECMO, also known as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, is a kind of medical emergency equipment, which was first successfully used by the University of Michigan Medical School. ECMO can temporarily replace the cardiopulmonary function of patients and reduce the burden of the heart and lungs of patients. It can also buy more treatment time for medical staff and is regarded as the “ultimate weapon” in the intensive care unit (ICU).
The principle is to take the venous blood in the body out of the body, let the blood combine with oxygen, and then pump it back to the patient’s venous or arterial system to play a role in replacing the heart and lungs. According to different blood reinfusion routes, ECMO is divided into two modes: VV (venous to vein) and VA (venous to artery).
1.V-V transfer
The venous blood is led out through the vein through an oxygenator to oxygen and remove carbon dioxide and then pumped into another vein. Usually, the femoral vein is selected for extraction and the internal jugular vein is pumped, or bilateral femoral veins can be selected according to the patient’s condition. The principle is to exchange part of the venous blood before it flows through the lungs to make up for the lack of lung function.
2. V-A transfer
The venous blood is led out through the vein and pumped into the artery after oxygenation and removal of carbon dioxide through an oxygenator. Usually, the femoral vein is used for extraction, and the femoral artery is pumped to bypass the heart and lungs. V-A bypass is a connection method that can support cardiopulmonary function at the same time. Therefore, ECMO is also called life support technology.
The function of oxygenator (artificial lung) is to convert non-oxygenated blood into oxygenated blood, also called artificial lung. ECMO oxygenator has two types: silicone membrane type and hollow fiber type.
The function of the power pump (artificial heart) is to form power to drive blood to one side of the pipeline, similar to the function of the heart. There are mainly two types of power pumps clinically: roller pumps and centrifugal pumps.
Indications:
- ECMO is very extensive because of its powerful cardiopulmonary replacement function and simple operation.
- Various causes of cardiac arrest
- Acute severe heart failure (myocarditis, myocardial infarction, etc.)
- Acute severe respiratory failure (COVID-19 pneumonia, fire gas inhalation, etc.)
- Various diseases that seriously threaten respiratory and circulatory functions (severe asthma, drowning, etc.)
In hospitals with ECMO conditions, in addition to traditional emergency measures, V-A ECMO can also be implemented in the rescue of cardiac arrest. With the support of ECMO, multi-disciplinary collaborative treatment, the implementation of coronary artery bypass surgery or coronary artery stent implantation as soon as possible can quickly restore heart function.
ECMO is combined with transplantation technology, and for some cases where the cardiopulmonary function is not possible to recover, the increasingly powerful transplantation technology can still be used to achieve recovery from ECMO.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



