Urothelial cancer: the era of precision treatment is coming
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Urothelial cancer: the era of precision treatment is coming
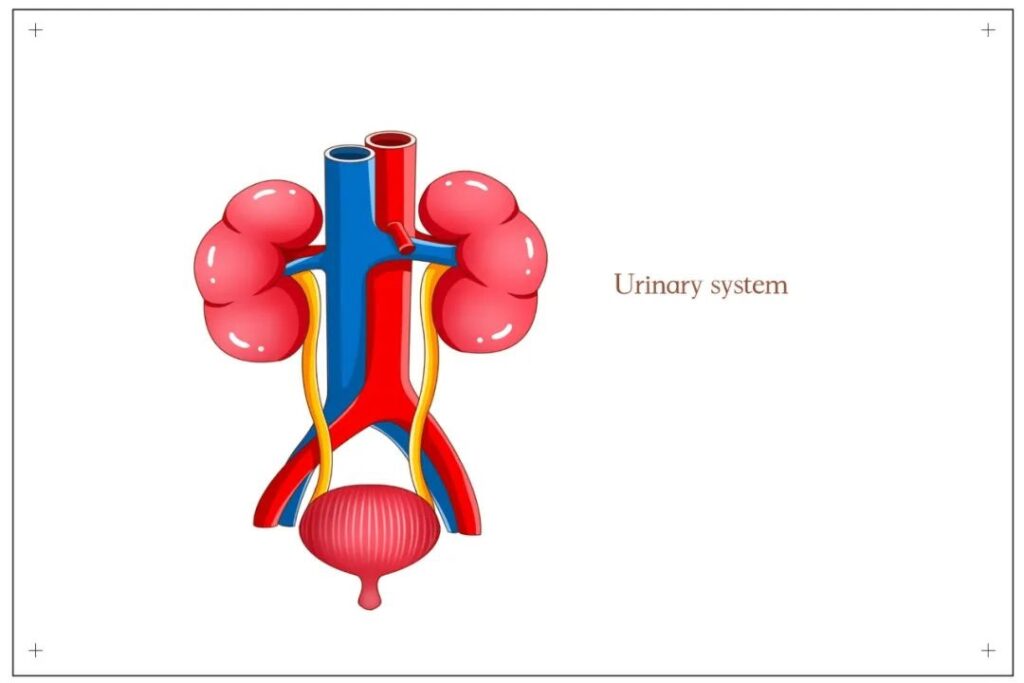
Urothelial cancer: the era of precision treatment is coming. The urinary system is composed of kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra, and its main function is excretion. The original urine is reabsorbed by the renal tubules in the kidney to form urine, then enters the ureter through the contraction of the renal pelvis, and then enters the bladder through the peristalsis of the ureter, temporarily stored, and finally discharged through the urethra.
The urinary system is composed of kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra, and its main function is excretion. The original urine is reabsorbed by the renal tubules in the kidney to form urine, then enters the ureter through the contraction of the renal pelvis, and then enters the bladder through the peristalsis of the ureter, temporarily stored, and finally discharged through the urethra.
The vast majority of renal pelvic cancer, ureteral cancer and bladder cancer originate from the urothelium, collectively referred to as “urothelial cancer (UC).” About half of UC patients will have recurrence or metastasis after surgery. The current standard first-line treatment for metastatic UC is chemotherapy. However, the median survival time is only about 1 year, and the prognosis is not ideal.
At this stage, platinum-based chemotherapy is still the preferred strategy for the treatment of patients with advanced UC. Although chemotherapy has a high initial response rate, the rate of achieving complete remission is low. Most patients will have disease progression within 9 months of receiving treatment. The 5-year survival rate of patients with advanced UC is only about 5%.
At the ASCO conference in 2020, the field of urothelial cancer ushered in a major breakthrough. The phase III JAVELIN Bladder 100 study was announced. The first-line maintenance treatment of PD-1L monoclonal antibody was used for advanced patients, and the overall survival (OS) was extended by 7 months as long as. Recently, the updated results of the study were published in the famous journal New England Medicine.
On April 9, 2020, BeiGene’s second indication of tislelizumab was approved by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) for the treatment of failure of platinum-containing chemotherapy (including 12 neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy) UC patients with locally advanced or metastatic PD-L1 high expression. Domestic UC has officially entered the age of immunotherapy.
The approval of this indication is based on the results of a phase II clinical study of tislelizumab. The trial included 113 patients with advanced UC who had previously failed at least first-line chemotherapy. The results showed that among 101 patients with evaluable efficacy, the objective response rate (ORR) reached 24.8%, of which 9.9% achieved complete remission (CR).
It should be noted that not all patients with urothelial cancer can benefit from immunotherapy. Studies have shown that if patients are treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors indiscriminately, the overall effective rate is still low. Therefore, it is very important to screen out patients who may really benefit through appropriate biomarker testing.
Accurate diagnosis is a prerequisite for precision medicine. A number of studies have confirmed that patients with high PD-L1 expression benefit more clearly after receiving immunotherapy. Therefore, accurate assessment of PD-L1 expression level is essential for efficacy evaluation and avoiding ineffective or ineffective treatments. As an indispensable part of individualized tumor therapy, PD-L1 companion diagnosis plays an important role in immunotherapy.
It is reported that immunohistochemistry (IHC) is currently the only experimentally validated and approved method that can be used to assess the expression level of PD-L1. PD-L1 companion diagnosis is currently the most relevant immunotherapeutic companion diagnosis in the world, covering 2 types of urothelial carcinoma and 3 types of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer.
PD-L1 antibody detection (immunohistochemical method), as the first companion diagnosis of urothelial cancer immunotherapy in some countries, was approved for marketing in China in June 2020, marking the official opening of the era of urothelial cancer immunodiagnosis and treatment in some countries and opening of precision Chemical treatment.
The test can provide a reliable basis for clinical medical decision-making and help patients maximize their benefits.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



