Immunotherapy: How to solve low efficiency and insufficient precision?
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
Immunotherapy: How to solve low efficiency and insufficient precision?
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Immunotherapy: How to solve low efficiency and insufficient precision?
Why is PD-L1 not a perfect marker? Why is immunotherapy only effective for some patients? How to further improve the efficacy of immunotherapy?
In the past nearly 100 years, the continuous improvement of the three major therapies of surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy has significantly improved the survival of cancer patients, but the future development prospects are limited and it is difficult to further improve the efficacy.
In recent years, the rapid development of tumor immunotherapy has brought new hope to tumor patients and has shown great development potential in the field of tumor therapy.
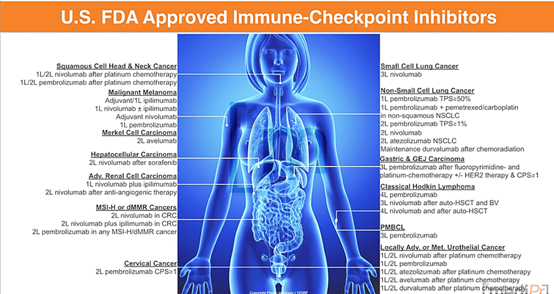 Immune checkpoint inhibitor indications
Immune checkpoint inhibitor indications
However, in the clinical practice of tumor immunotherapy in the past 20 years, people have gradually discovered that immunotherapy also has many problems.
For example, only about 20% of patients are clinically sensitive to immunotherapy, and most patients cannot benefit from immunotherapy.
Therefore, how to accurately select the beneficiaries of immunotherapy and how to further improve the effectiveness of immunotherapy have become two major problems facing oncologists.
On January 29, Professor Roxaa Dronca, Director of the Department of Hematology/Oncology of Mayo Clinic, an internationally renowned medical institution, will be a guest in the live broadcast room of the medical doctors station to share the development of immunotherapy and Mayo’s clinical experience and exploration in immunotherapy.
Which patients can benefit from immunotherapy?
Professor Dronca: Although immunotherapy has made important progress in the treatment of cancer in recent years, there are still only a few patients who can benefit from immunotherapy in clinical practice.
Even for melanoma, which is the most sensitive to immunotherapy, only about 40% of melanoma patients can benefit from immunotherapy.
At the same time, according to the clinical response to immunotherapy, patients can also be divided into three categories: one is treatment sensitive patients; the other is treatment insensitive patients; the last category is initially insensitive to immunotherapy, but can still be used for a long time. Patients who have achieved significant benefits.
Obviously, for the last type of patients, if they are not found, they may miss the opportunity for immunotherapy.
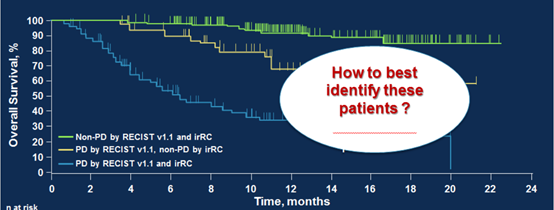
What is the value of PD-L1 in predicting the efficacy of immunotherapy?
Professor Dronca: As early as the initial clinical exploration of immunotherapy, PD-L1 has been used as a biomarker to assess whether patients can benefit from immunotherapy, and it is now widely used in clinical practice. However, the efficacy prediction of PD-L1 in clinical practice is not accurate.
Two advanced tumor patients with PD-L1 ≥50% came to Mayo Clinic for treatment. After 3 months of immunotherapy, a patient’s tumor shrank rapidly and achieved complete remission.
After 2 years of treatment, the tumor has not recurred. The other patient did not respond after receiving immunotherapy and eventually died.
Therefore, PD-L1 is not a perfect marker. The level of PD-L1 will change over time, and even in a tumor tissue, the expression of PD-L1 in different parts is still different.
How to improve the accuracy of immunotherapy biomarker efficacy prediction?
Professor Dronca: In recent years, with the rapid development of immunotherapy, the exploration of tumor immunotherapy biomarkers is also steadily advancing.
Some new biomarkers, such as tumor mutation burden (TMB), mismatch repair defect (dMMR)/high Microsatellite instability (MSI-H), tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs)/T cell inflammatory gene expression profile (GEP), etc., are gradually being used in clinical practice.
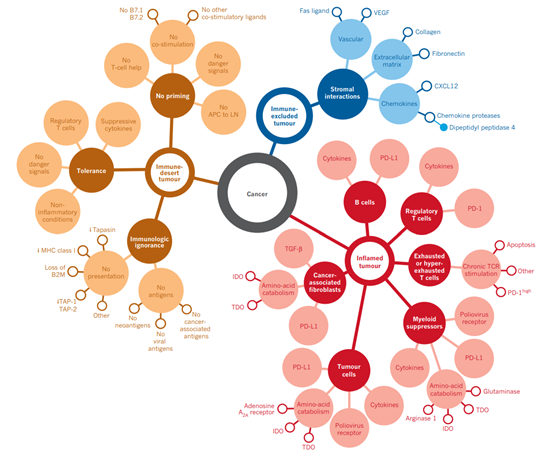
At present, clinical exploration to improve the effectiveness of biomarkers is mainly focused on the combined detection of markers, such as the combined application of TMB and GEP.
In addition, some new biomarkers have gradually shown good predictive value. In the future, with the further development of tumor biology, immunoprecision therapy will definitely go further.
How to improve the efficacy of immunotherapy?
Professor Dronca: In addition to finding more accurate and effective biomarkers, another challenge currently facing immunotherapy is how to improve the effectiveness of immunotherapy so that more patients can benefit from immunotherapy.
From the current clinical experience, in order to improve the effectiveness of immunotherapy, combination therapy is a good direction.
Clinically, many breakthroughs have also been made in immunotherapy, radiotherapy, targeting and other programs. However, similarly, these combined programs are only effective for some patients.
In order to further improve the efficacy of immunotherapy, Mayo also did a lot of exploration.
For example, in the treatment of immune combination chemotherapy, we found that CD8 T cells in some patients’ tumor tissues can actively excrete chemotherapy drugs, thereby making patients insensitive to immune combination therapy.
Removing these T cells can significantly enhance immune combination. The efficacy of chemotherapy.
In addition, we found soluble PD-L1 protein in renal cell carcinoma. This protein can bind to PD-1 on the surface of T cells and induce T cell apoptosis, thereby making patients insensitive to immunotherapy.
At the same time, hemodialysis can remove most of the soluble PD-L1 protein in peripheral blood. Therefore, this is also a solution worth trying to improve the efficacy of immunotherapy in the future.
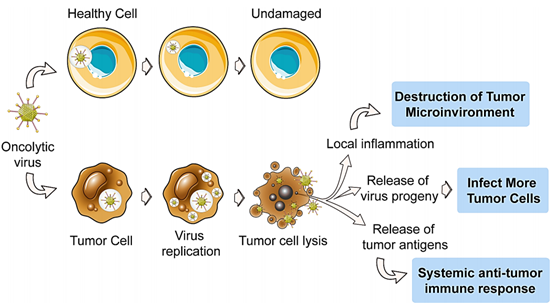
Finally, Mayo has also been exploring the combination of immunotherapy and oncolytic virus therapy, and is at the leading level in this field. Oncolytic viruses are expected to activate tumor immune responses and transform “cold tumors” into “hot tumors.”
Immunotherapy: How to solve low efficiency and insufficient precision?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



