The AO classification of distal femoral fractures
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
- Mifepristone: A Safe and Effective Abortion Option Amidst Controversy
- Asbestos Detected in Buildings Damaged in Ukraine: Analyzed by Japanese Company
The AO classification of distal femoral fractures
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
The AO classification of distal femoral fractures. It has been adopted by OTA, also known as AO/OTA classification.
There are many types of distal femoral fracture. Scholars at home and abroad have proposed a variety of classification systems.
The more commonly used types are Seinsheimer type and AO type.
Among them, AO classification divides distal femoral fractures into A, B, and C according to the involvement of the articular surface and the fractures of the femoral unicondyle and double condyle, and subtypes according to the severity of comminution.
The AO classification of distal femoral fractures has been adopted by OTA, also known as AO/OTA classification.
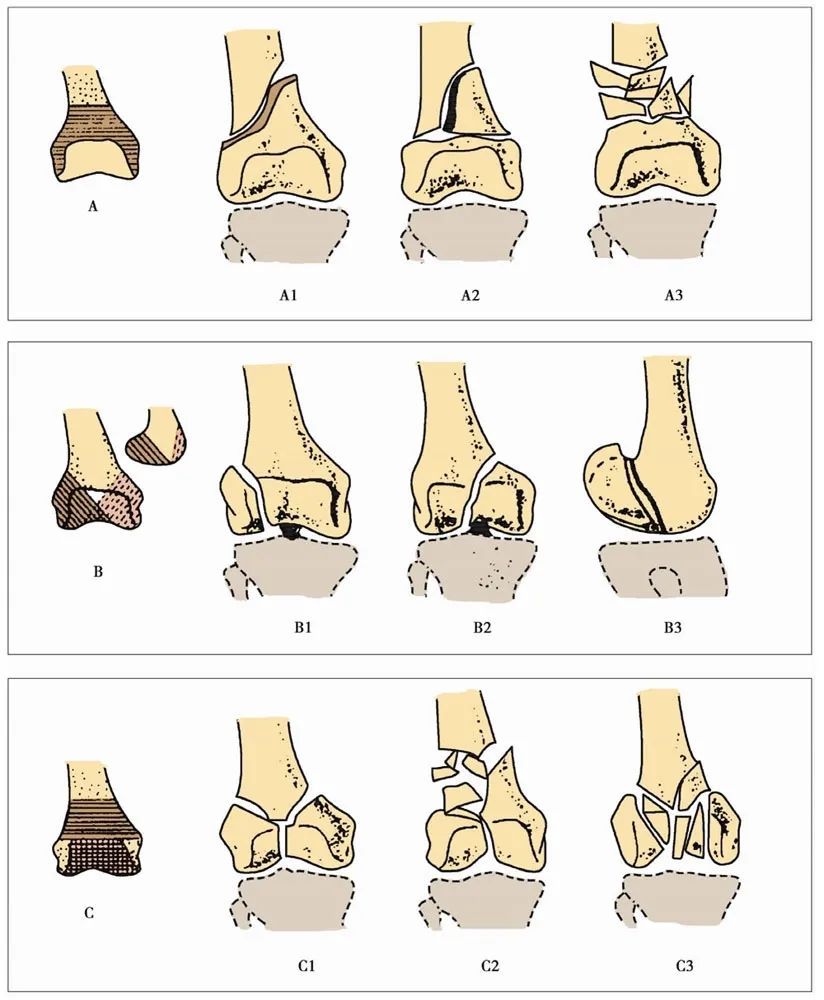
A. Extra-articular fracture
A1 Simple fractures: ①Bone convexity fractures; ②Slanted or spiral fractures of the metaphysis; ③Transverse fractures of the metaphysis.
A2 Metaphyseal wedge-shaped fracture: ①Complete wedge- shaped fracture; ②Outside comminuted shape; ③Inside comminuted shape.
A3 Metaphyseal complex fractures: ①Fractures with medial split bone; ②Complicated fractures of irregular and limited to the metaphysis; ③Fractures that extend irregularly to the diaphysis.
B. Partial intra-articular fractures
B1 Lateral condyle sagittal fracture: ①Simple fracture through the intercondylar fossa; ②Simple fracture through the weight bearing surface; ③Comminuted fracture.
B2 Sagittal fracture of the medial condyle : ①Simple fracture through the intercondylar fossa; ②Simple fracture through the weight-bearing surface; ③comminuted fracture.
B3 Fracture of the anterior part of the femoral condyle: ① Fracture of the anterior lateral fragment; ② Fracture of the posterior unicondyle (Hoffa); ③ Fracture of the posterior double condyle.
C. Complete intra-articular fracture
C1 Simple intra-articular and metaphyseal fractures: ①T-shaped or Y-shaped fractures are slightly displaced; ②T-shaped or Y-shaped fractures are significantly displaced; ③T-shaped epiphyseal fractures.
C2 Simple intra-articular fracture, comminuted fracture of metaphysis: ①a complete wedge-shaped bone; ②a comminuted wedge-shaped bone; ③complex fracture.
C3 Comminuted fracture: ①Simple fracture of the metaphysis; ②Comminuted fracture of the metaphysis; ③Comminuted fracture of the diaphysis.
The AO classification of distal femoral fractures
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



