Bristol-Myers Squibb CAR-T therapy Breyanzi approved by FDA
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Bristol-Myers Squibb CAR-T therapy Breyanzi approved by FDA
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Bristol-Myers Squibb CAR-T therapy Breyanzi approved by FDA.
Breyanzi has been granted priority medicine (PRIME) qualification for the treatment of R/R DLBCL in the EU, and EMA is currently reviewing its marketing authorization application (MAA).
On February 5, 2021, BMS announced that the FDA has approved the listing of CAR-T cell therapy Breyanzi (lisocabtagenemaraleucel; liso-cel) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory (R/R) patients who have received at least two systemic therapies.
Adult patients with B-cell lymphoma (LBCL), including unspecified diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), high-grade B-cell lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, and grade 3B follicular lymphoma.
But Breyanzi is not suitable for the treatment of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma.
Prior to this, three CAR-T cell therapies had been approved worldwide, namely Novartis’ Kymriah, Gilead’s Yescarta and Tecartus, all targeting CD19. Breyanzi is also a CAR-T therapy targeting CD19. It contains a 4-1BB costimulatory domain.
The 4-1BB signal can enhance Breyanzi’s amplification and durability. A single dose of Breyanzi contains 50-110 x 106 CAR-positive T cells, and the ratio of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells is 1:1.
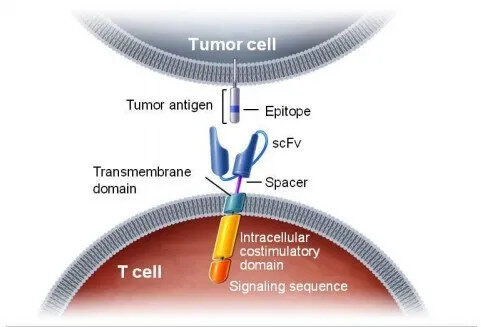
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL), accounting for one-third of confirmed cases.
73% of patients did not respond to second-line or later treatment or relapsed after treatment.
For patients who relapse or do not respond to the initial treatment, conventional treatment options that can provide a sustained response are very limited, and the median life expectancy is about six months.
This approval is based on data from the TRANSCEND NHL 001 (017001) study. A total of 268 R/R LBCL patients received Breyanzi treatment, which is also the largest pivotal trial in the third-line post-treatment study of R/R LBCL.
Among the 192 patients with evaluable efficacy, 73% (95%CI: 67%-80%) achieved remission, of which the complete remission rate was 54% (CR; 95%CI: 47%-61%), and the partial remission rate was It was 19% (PR; 95% CI: 14%-26%).
Among all patients who responded, the median duration of remission was 16.7 months (95% CI: 5.3-NR); among patients who achieved CR, the median duration of remission did not reach (95% CI: 16.7-NR); for For patients with the best response to PR, the median duration of remission was 1.4 months (95% CI: 1.1-2.2).
Among the 104 patients who received Breyanzi and the best overall response was CR, 65% had remission lasting at least six months, and 62% had remission lasting at least 9 months.
In the study, 268 patients treated with Breyanzi were evaluated for safety. Using Lee’s classification, 46% (122/268) of patients developed CRS, and CRS of grade 3 and above appeared in 4% (11/268) of patients.
At the time of death, one patient had a fatal CRS and two patients were experiencing CRS.
The most common manifestations of CRS include fever (93%), hypotension (49%), tachycardia (39%), chills (28%), and hypoxia (21%). The median duration of CRS was 5 days, and the median onset time was 5 days.
Among patients treated with Breyanzi, 35% (95/268) developed neurotoxicity (NT), and NT of grade 3 and above occurred in 12% (31/268) of patients.
At the time of death, one patient had fatal NT and seven patients were experiencing NT.
The most common NTs include encephalopathy (24%), tremor (14%), aphasia (9%), delirium (7%), headache (7%), ataxia (6%) and dizziness (6%). NT was resolved in 81 of 95 patients (85%), with a median duration of 12 days and a median onset time of 8 days.
The median duration of NT was 15 days for all patients, including patients who died or were still experiencing at the time of data cutoff.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients. The most common (>2%) are CRS, encephalopathy, sepsis, febrile neutropenia, aphasia, pneumonia, fever, hypotension, dizziness, and delirium.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4% of patients. The most common adverse reactions of any grade (≥20%) include fatigue, CRS, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, headache, encephalopathy, infection, loss of appetite, diarrhea, hypotension, tachycardia, dizziness, cough, constipation, abdominal pain, vomiting And edema.
Breyanzi has been granted priority medicine (PRIME) qualification for the treatment of R/R DLBCL in the EU, and EMA is currently reviewing its marketing authorization application (MAA).
Bristol-Myers Squibb CAR-T therapy Breyanzi approved by FDA
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



