COVID-19: Over 60 mutant antigen proteins have been launched!
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
COVID-19: Over 60 mutant antigen proteins have been launched!
COVID-19: Over 60 mutant antigen proteins have been launched! To meet the challenge of COVID-19 mutations, over 60 mutant antigen proteins have been developed and launched!
The latest data released by the World Health Organization on February 18 show that the cumulative number of confirmed cases of COVID-19 worldwide has exceeded 110 million, and the cumulative number of deaths has exceeded 2.43 million. The epidemic situation in various countries is still not optimistic, and the spread of the epidemic has not slowed down. sign.
In addition, the newly identified COVID-19 mutant strains spread rapidly, and the proportion of local COVID-19 strains has been increasing. Preliminary research results show that the protective effect of existing vaccines and neutralizing antibodies on specific mutant strains has been greatly reduced, triggering opposition from all walks of life. The trend of the COVID-19 epidemic and concerns about the effectiveness of vaccines and drugs.
There are two main reasons why mutations are worrying: one is that mutations in the key receptor binding region (RBD) located on the spike protein (S protein) may enhance the ability of the new coronavirus spike protein to bind to the receptor ACE2 and increase the virus The second is that mutations may change the key epitopes of the antigen, reduce the affinity of the existing neutralizing antibodies, help the virus escape the immune response, and threaten the protective effects of vaccines and neutralizing antibody drugs.
Currently, there are 4 kinds of COVID-19 mutant strains that have received widespread attention, from the United Kingdom, South Africa, Brazil, and California:
01 British mutant (B.1.1.7)
According to reports, the infectivity of the British mutant strain (B.1.1.7) has increased by 56%, spreading rapidly in the UK and Europe, and the pathogenicity of the mutant strain is also higher than that of the non-mutant strain 1-2. In order to prevent the continued spread of mutant strains, parts of England are still under Level 4 lockdown.
B.1.1.7 There are 9 mutations on the S protein of the mutant strain, and N501Y single point mutations on the RBD. The experimental results show that B.1.1.7 has limited escape of neutralizing antibodies targeting S protein, RBD and N-terminal domain (NTD), and rehabilitation serum and vaccine immune serum can still play the expected neutralizing effect3.
02 South African mutant strain (B.1.351)
According to reports, the South African mutant strain (B.1.351) has increased infectivity by more than 50% and has rapidly replaced other local variants, accounting for 55% of the total number of infections in South Africa 4-5. There is currently no evidence that the pathogenicity of this mutant is enhanced.
There are 10 mutations on the S protein of B.1.351 mutant, and the K417N/E484K/N501Y three-point mutation on the RBD. Previously, the American vaccine company Moderna published research results saying that the company’s mRNA vaccine mRNA-1273 still has a protective effect on B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 mutant strains. However, the rehabilitation serum samples used in this study are The neutralization potency of B.1.351 mutants was significantly reduced6.
Recently, the results of experiments by Columbia University showed that the neutralizing effect of the B.1.351 mutant strain of the sera of patients who have recovered from new coronaviruspneumonia is 9.4 times lower than that of the wild type; the human serum after inoculation of the mRNA-1273 vaccine neutralizes the B.1.351 mutant strain The effect decreased by 10.3-12.4 times. The above research results mean that survivors who have been infected with new coronavirus pneumonia may face the risk of being infected again by the mutant strain, and there is also doubt whether the existing vaccine can protect the vaccinated from being infected by the mutant strain.
03 Brazil mutant strain (P.1)
The Brazilian mutant (P.1) is spreading widely in large cities with a population of one million, and has been found in Japan, Germany, the United States, France and other countries. There is currently no evidence that the P.1 mutant strain has enhanced transmission and pathogenicity, but the RBD region of this mutant strain contains the N501Y mutation like B.1.1.7 and B.1.351. It is speculated that the infectivity of the mutant strain will also be higher than Non-mutant strain.
There are 12 mutations on the S protein of the P.1 mutant, and the K417T/E484K/N501Y three-point mutation on the RBD. The P.1 mutant strain is the same as the B.1.351 mutant strain, and both have the key mutation site of E484K, which makes the Brazilian mutant strain cause people to worry about immune escape.
04 California mutant strain (B.1.429)
The California mutant strain (B.1.429) spread rapidly in the local area. Statistics show that 35-40% of the local COVID-19 cases are caused by this mutant strain. At the same time, the B.1.429 mutant strain has spread rapidly throughout the United States in recent months, involving 19 states and Washington, District of Columbia 7. In addition, the mutant strain was also found in Australia, Denmark, Israel, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United Kingdom.
There are 3 mutations on the S protein of B.1.429 mutant strain, and L452R single point mutation on RBD. There are no reports on the dissemination and pathogenicity of this mutant strain.
ACRO has been working hard to help fight the epidemic
The continuous evolutionary mutation of RNA viruses poses a huge challenge to the development of antibodies and vaccines. Mutations may lead to a significant reduction in the protective power of existing COVID-19 vaccines, and may also cause a decrease in the effectiveness of some neutralizing antibodies that are originally very active in neutralizing. ACROBiosystems helps pioneer scientific research, and has now developed more than 60 COVID-19 mutant products! Various single-point mutations or multiple-point combination mutation antigen proteins can be provided, so that scientific researchers can carry out research on mutant strains and accelerate the rapid update of antibodies and vaccines in technology.
Product application scenarios
Application scenario one:
Detection of binding of neutralizing antibody to mutant protein
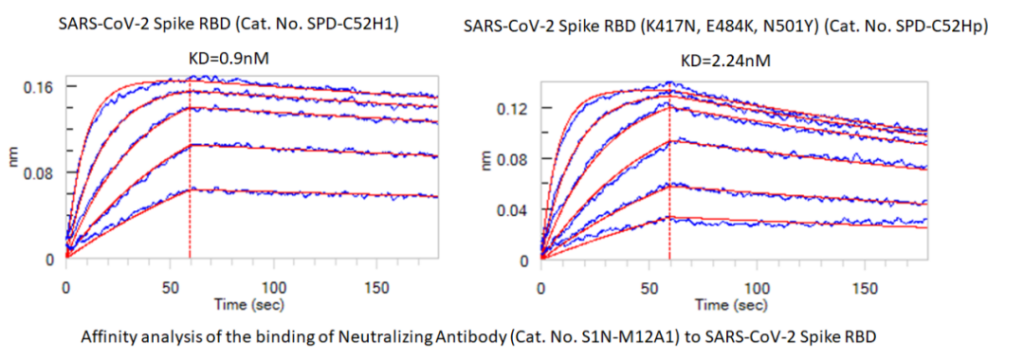
Figure 1 Comparison of binding affinity between neutralizing antibody (Cat.No. S1N-M12A1) and WT RBD (Cat.No.SPD-C52H1) South African mutant RBD (Cat.No. SPD-C52Hp)
Contact the assistant to apply for the protocol
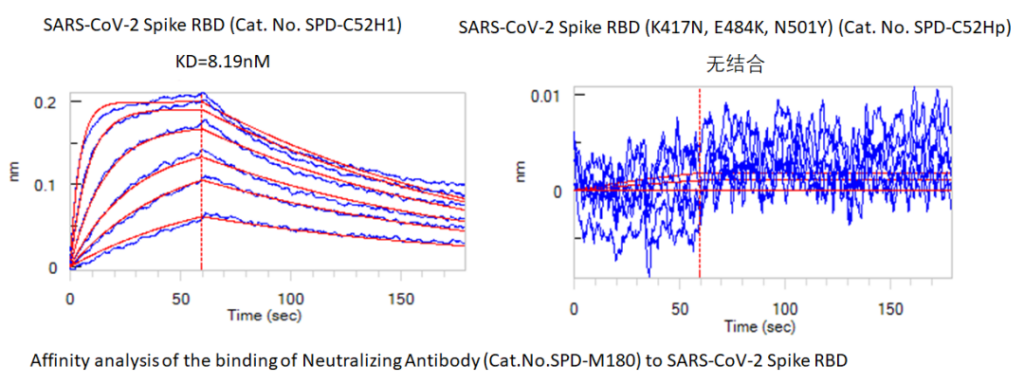
Figure 2 Comparison of binding affinity between neutralizing antibody (Cat.No. SPD-M180) and WT RBD (Cat.No. SPD-C52H1) South African mutant RBD (Cat.No. SPD-C52Hp)
The new coronavirus neutralizing antibodies S1N-M12A1 and SPD-M180 developed by ACROBiosystems can compete with ACE2 to bind to WT RBD and block the binding of ACE2 to RBD. The affinity of the above two neutralizing antibodies to the South African mutant RBD was tested by the biofilm interference technology (BLI), and it was found that the affinity of S1N-M12A1 and RBD (K417N/E484K/N501Y) was 2-3 times lower than that of WT RBD. SPD-M180 is not combined with RBD (K417N/E484K/N501Y). The above results indicate that RBD mutation may have little effect on the neutralizing ability of S1N-M12A1, while SPD-M180 may lose its ability to neutralize mutant strains.
Application scenario two:
Detection of serum antibody titer to mutant protein
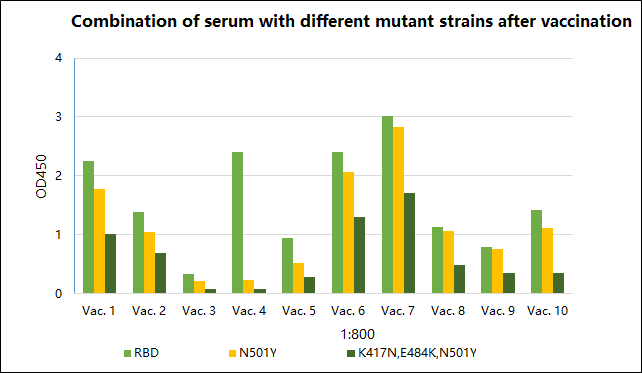
Figure 3 The results of the combination experiment of serum and different mutant strains after vaccination
The protective efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine against mutant strains is the focus of attention. The indirect ELISA method was used to detect the binding of antibodies in the serum after vaccination with the antigen proteins of non-mutated and mutant strains. It was found that when the serum samples were diluted 800 times, the antibodies in 10 serum samples were related to the South African mutant RBD (K417N/E484K/N501Y) Compared with WT RBD, the binding of RBD was significantly reduced, and the binding of British mutant RBD (N501Y) was not changed much compared with WT RBD. The above experimental data is consistent with the research results reported in the literature that the neutralization effect of the vaccinated sera on the South African mutant has decreased significantly, and the neutralization effect of the British mutant has little change3.
Application scenario three:
Development of antibodies against mutant proteins
The mutation sites in the COVID-19 mutant strain may help the virus escape the recognition of the neutralizing antibody. Therefore, the neutralizing antibody drugs currently approved and under development may have a reduced protective effect on the mutant strain, resulting in ineffective prevention or Treat new coronavirus pneumonia. Antibody drug development companies can use the COVID-19 mutant protein to screen for broad-spectrum neutralizing antibodies that can identify mutant strains to ensure that neutralizing antibodies can recognize mainstream virus strains and prevent immune escape.
In addition, the antibody raw materials in the antigen detection kit may not be able to recognize the mutant antigen in the mutant strain, resulting in missed detection of the mutant strain. The diagnostic reagent company needs to verify whether the existing kit can detect the mutant protein. Once the test fails, the antibody material needs to be re-screened to find a broad-spectrum antibody material that can identify the mutant strain or a specific antibody material against the mutant strain.
Application scenario four:
Test whether the existing paired antibody can recognize the mutant protein
With the continuous discovery of COVID-19 mutants around the world, how to quickly and easily identify and test has become one of the new needs for epidemic prevention and control.
The paired antibody (S1N-M12A1/S1N-M13A1) developed by ACROBiosystems that targets the RBD region of the new coronavirus can be used for the development of a new coronavirus antigen detection kit. The previous research results show that the paired antibody has high sensitivity and good specificity for detecting non-mutant strains .
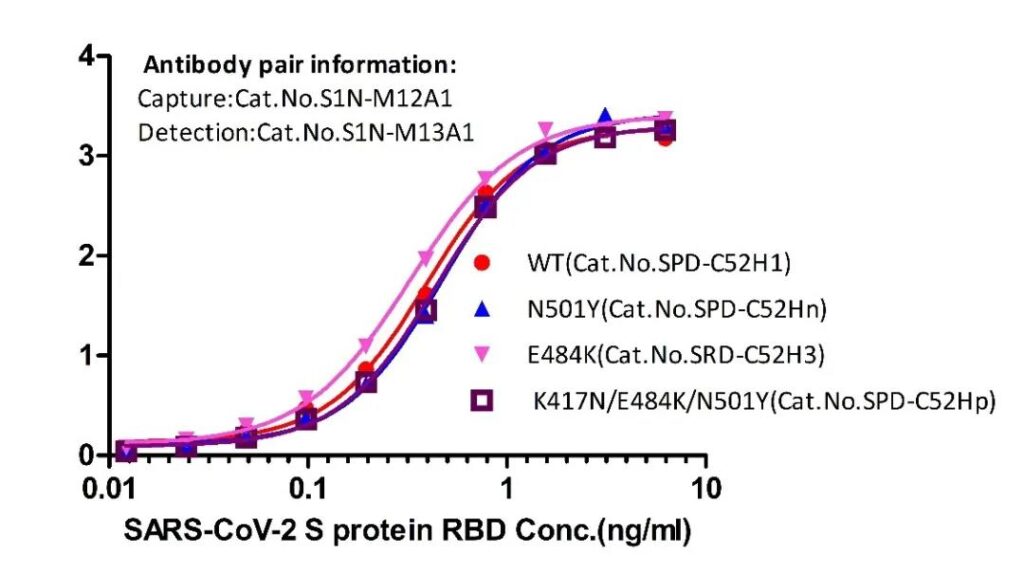
Figure 4 Double antibody sandwich method to detect RBD protein with different mutations (Cat.No. SPD-C52Hn; SRD-C52H3; SPD-C52Hp)
The S1N-M12A1/S1N-M13A1 paired antibody was used to evaluate the detection of non-mutated and mutant RBD proteins by the ELISA method. The experimental results showed that the paired antibody can detect non-mutated and mutant RBD with close sensitivity, indicating that the antibody pair is in detecting non-mutated and mutant RBD. The sensitivity of mutation and mutant strain is similar, and there will be no missed detection.
Product List
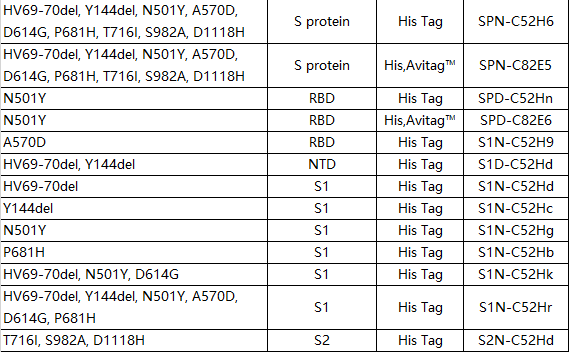
British mutant (B.1.1.7)
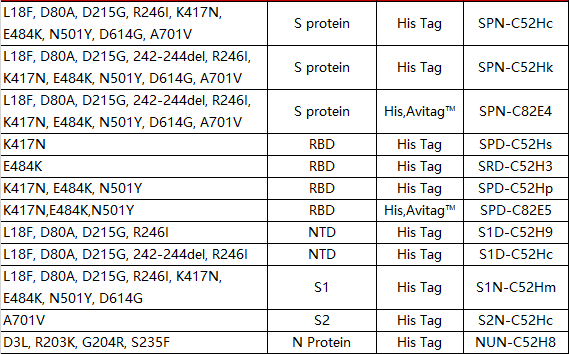
South African mutant (B.1.351)
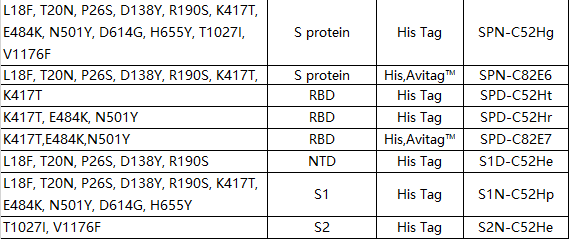
Brazil mutant (P.1)
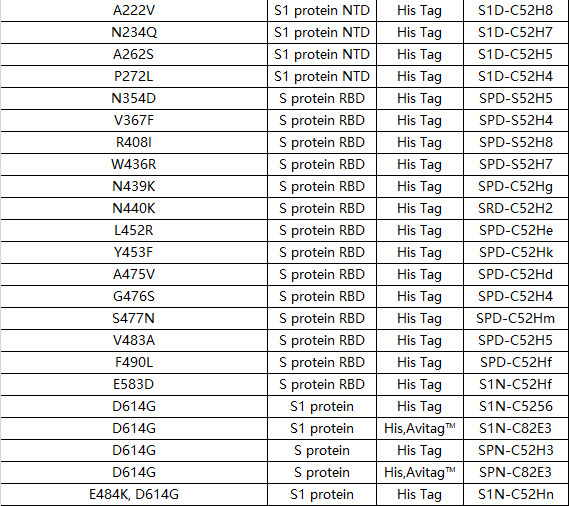
Other mutation products
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



