Types of gallbladder polyps and related treatment
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Types of gallbladder polyps and related treatment
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Types of gallbladder polyps and related treatment. Recently, with the promotion of gallbladder preservation surgery, some people want to remove only polyps and preserve the gallbladder.
Gallbladder polyps, in fact, its formal name should be gallbladder polypoid lesions.
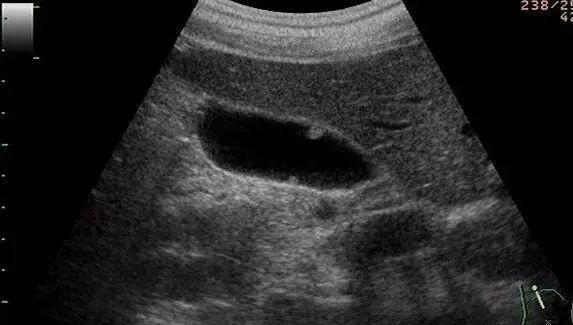
The normal gallbladder is a small bag-like organ. The wall of the cyst is very thin, only 1 to 2 mm, and it is also very smooth. If for some reason, a small protrusion grows from the gallbladder wall into the gallbladder cavity, just like a small mound on the ground, sonographers call it “gallbladder polypoid lesion” or “gallbladder polyp.” There are also books that say “gallbladder bulging lesions”. Before the widespread use of ultrasound, this lesion was mostly found on cholecystectomy specimens.
The most common gallbladder polyps are cholesterol polyps, which are related to cholesterol metabolism disorders. Cholesterol polyps are often multiple and small, mostly between 3 to 5 mm, usually no more than 1 cm, and they will not grow up quickly. During the observation process, the number of polyps can change. Some polyps can even fall off and be discharged with bile.
But occasionally there is a single polyp with only one polyp, which can be larger than 1 cm in diameter, which is not common.
Cholesterol polyps will not become malignant into gallbladder cancer, but can sometimes form gallbladder stones. If there are no symptoms, no treatment is needed.
The second is inflammatory polyps, which are caused by chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, so it often occurs in the case of gallbladder stones, chronic cholecystitis, not a real tumor. What needs to be treated is the lesion that caused the inflammatory polyp, not the inflammatory polyp itself.
The true neoplastic polyps are gallbladder adenomas, which have a certain malignant rate and need to be vigilant. Generally, polypoid lesions of the gallbladder with the following characteristics are highly likely to become malignant and require active treatment:
1. The diameter of the polyp is greater than 1 cm
2. Single polyp
3. The base of the polyp is wider
4. Complicated with gallbladder stones
5. Female patients
6.Polyps are located in the neck of the gallbladder
The above is a brief introduction to gallbladder polyps, and there are also some rare types of polypoid lesions, because they are too rare to introduce.
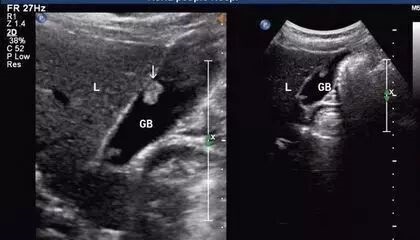
Recently, with the promotion of gallbladder preservation surgery, some people want to remove only polyps and preserve the gallbladder.
However, because polyps grow on the wall of the gallbladder, the gallbladder itself is not large, and many gallbladders are diseased and there is no need to preserve them.
In addition, the removal of the gallbladder has no significant effect on the human body.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



