Gum bacteria may be directly related to Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
ADDADM: The ecological imbalance of gum bacteria may be directly related to Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers
Gum bacteria may be directly related to Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. The pathological accumulation of beta amyloid plaques (Aβ) and tau neurofibrillary tangles in the brain is the core pathological feature of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Researchers speculate that the amyloid deposits in the brain may be Alzheimer’s The first pathological feature of Murder’s disease begins in the preclinical stage, and it has accumulated decades before cognitive dysfunction and tau protein tangles.
The mechanism of the development of brain amyloidosis is not very clear to researchers at present, because its pathogenesis involves a variety of different signaling pathways.
Now more and more research evidence shows that inflammation, infection, and the intestinal and oral flora Dissonance may be a potential influencing factor.

Periodontal disease (PerioD, Periodontal disease) is a chronic inflammatory dysbacteriosis disease that occurs in the oral cavity, which affects the health of more than 50% of the elderly. At the same time, researchers have found that periodontal disease may be related to Alzheimer’s. Murder disease and Down syndrome are related.
Recently, in a research report titled “Periodontal dysbiosis associates with reduced CSF Aβ42 in cognitively normal elderly” published in the international journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring, scientists from New York University and other institutions passed the research Studies have found that the imbalance of gum bacteria may be directly related to biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease.
Researchers say that older people with more harmful bacteria than healthy bacteria in their gums may be more likely to have beta amyloid, a key biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease, in their cerebrospinal fluid. However, this kind of oral flora The imbalance may not be related to another Alzheimer’s disease biomarker called tau.
The research in this article adds to the evidence that periodontal disease (gum disease) and Alzheimer’s disease may have a very close relationship. According to the US CDC data, periodontal disease affects 70% of the elderly 65 and older in the United States. In humans, periodontal disease is characterized by chronic systemic inflammation of the body, which is mainly manifested in the continuous expansion of the “pocket structure” between teeth and gums and nourish bacteria.
Researcher Dr. Angela Kamer said that in this study, we found for the first time in the elderly population with normal cognitive function that there is a certain correlation between the unbalanced subgingival bacterial population and the cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease.
The oral cavity is not only a place for the survival of harmful bacteria that promote inflammation, but also a place where protective bacteria inhabit; the researchers found evidence that the presence of amyloid in the brain may be related to the increase of harmful bacteria and the decline of the level of beneficial bacteria.
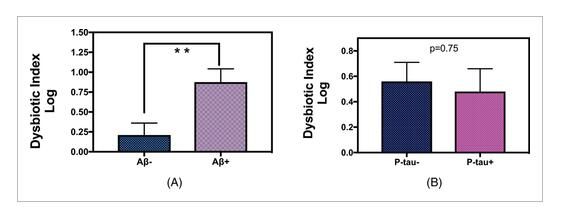
Disorder index of amyloid (A) and P-tau (B) groups.
Image source: Angela R. Kamer, et al. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring, 12 April 2021, doi: 10.1002/dad2.12172
The main feature of Alzheimer’s disease is the presence of two hallmark proteins in the patient’s brain, namely β-amyloid and tau. The former can aggregate together to form plaques and is considered to be in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. The first protein deposited in the brain, and tau protein can accumulate in nerve cells and form certain tangles.
The accumulation of amyloid in the brain and the mechanisms related to Alzheimer’s disease are very complicated. The current research by researchers is only the tip of the iceberg. Since the retention of amyloid in the brain can be assessed by the level of cerebrospinal fluid, this article In the study, the researchers further confirmed and revealed the molecular mechanism of pro-inflammatory diseases that interfere with the clearance of amyloid in the brain.
In the article, the researchers studied 48 elderly people 65 and older with normal healthy cognitive function. Participants underwent oral examinations to collect bacterial samples from under the gums. At the same time, the researchers also performed a waist puncture to obtain them. Cerebrospinal fluid tissue to determine the relationship between beta amyloid and tau protein levels; to assess the expression of Alzheimer’s disease protein in the brain, the researchers found lower levels of beta amyloid in the participants’ cerebrospinal fluid samples Protein (which can be converted into high levels of brain amyloid) and high levels of tau protein (which can reflect the accumulation of high levels of brain tangles).
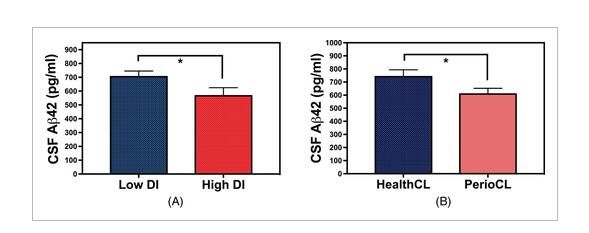
The level of Aβ42 in the cerebrospinal fluid of the dysbacteriosis group.
Image source: Angela R. Kamer, et al. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring, 12 April 2021, doi: 10.1002/dad2.12172
By analyzing the DNA of bacteria collected under the gums, the researchers quantified bacteria known to be harmful to oral health (Prevotella, Porphyria, Freundella, etc.) and bacteria that are beneficial to oral health ( Corynebacterium, Actinomycetes, Cardinella, etc.).
The results of the study show that individuals with unbalanced levels of bacteria (the proportion of which is beneficial to harmful bacteria rather than beneficial bacteria) is more likely to develop the disease characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease, that is, decreased levels of amyloid in CSF.
So the researchers hypothesized that because a high level of healthy flora can help maintain the balance of bacteria and reduce inflammation in the body, this may have a certain protective effect against Alzheimer’s disease.
The researcher Kamer said that the results of this article reveal the importance of the overall oral microbiome (not only the function played by harmful bacteria, but also the role played by beneficial bacteria) in regulating amyloid levels. A variety of oral bacteria may be involved. In the process of expression of amyloidosis.
In summary, this article reveals that there may be a certain selective relationship between the ecological imbalance of the oral flora of patients with periodontal disease and the cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of amyloidosis. In the later stage, further modeling studies are needed to establish the oral flora and the brain. The direct association between beta amyloid.
In addition, the researchers also pointed out that this study did not find an association between gingival bacteria and tau protein levels. They do not know whether tau protein lesions will occur in the later stages or the subjects will develop symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease in the later stages. Later researchers are required to conduct further longitudinal studies and clinical trials to analyze whether improving gum health can modify the amyloid in the brain and effectively prevent the occurrence of Alzheimer’s disease, such as deep removal of plaque and tartar deposits under the gums Wait.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



