Study on the epitope recognition of coronavirus antibody
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Study on the epitope recognition of coronavirus antibody and related applications
Study on the epitope recognition of coronavirus antibody. Understanding the epitope of the detection antibody of the N protein, which is the key target for rapid diagnosis of immunology, and the recognition epitope of the neutralizing antibody will help the development of diagnostic reagents, drug development and vaccine protection effectiveness evaluation.
Preface
The function of an antibody depends on the epitope that it binds to the antigen. Antibodies perform specific functions due to different binding epitopes, such as activating or inhibiting activity.
Knowing the epitope of antibody recognition helps to evaluate the accuracy of antigen detection. The epitope-rich control antibody is also often used for vaccine effect evaluation. Therefore, screening antibodies for different epitopes can be applied to new coronavirus detection and vaccine protection efficacy evaluation.
SARS-CoV-2 is a single-stranded positive-stranded RNA virus, and its genetic components are non-structural genes and structural genes. Among them, non-structural genes contain two open reading frames (ORF1a and ORF1b), which encode 16 non-structural proteins (Nsp1 to 16), while structural genes encode 4 proteins: S, E, M, and N.
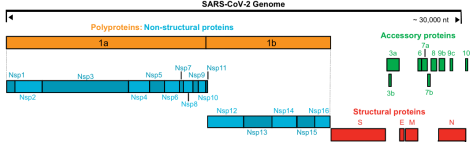 Genome organization of SARS-CoV-2 (Source Reference 1)
Genome organization of SARS-CoV-2 (Source Reference 1)
Nucleocapsid (N) protein, due to its high abundance expression, is a key target for rapid immunological diagnostic reagents for COVID-19 and a potential target for the development of antiviral drugs that block the assembly of ribonucleoproteins. The Spike(S) protein is responsible for the binding of the virus to the host cell membrane receptor and membrane fusion. It is an important site for host neutralizing antibodies and a key target for vaccine design.
From December 2019 to November 2020 collected from GISAID, about 223,000 complete sequences of the SARS-CoV-2 proteome, it was found that the proteins of COVID-19 are evolving at different speeds. The E protein has a lower degree of mutation, while the N and S proteins show a higher degree of mutation. Mutations provide the virus with a mechanism to increase transmission, change pathogenicity, and evade host immunity. It may change the antigen response and lead to resistance to treatment methods, and even lead to the failure of vaccine protection.
Therefore, understanding the epitope of the detection antibody of the N protein, a key target for rapid immunological diagnosis, and the recognition epitope of the neutralizing antibody will help the development of diagnostic reagents, drug development and vaccine protection effectiveness evaluation.
Study on the epitope recognized by SARS-CoV-2 Anti-N antibody
Take SARS-CoV-2 N full length ( Cat: 40588-V07E , 1M-419A), N-NTD ( Cat: 40588-V07E10 , 49T-175G) and N-CTD ( Cat: 40588-V07E5 , 248K-365P; Cat: 40588-V07E6 , 248K-407L) Recombinant protein is used as the test sample to detect 12 anti-N monoclonal antibody recognition epitopes independently developed and prepared by Yiqiao Shenzhou. The results showed that 8 monoclonal antibodies recognize N-NTD, and 4 monoclonal antibodies may recognize the C tail end of N protein.
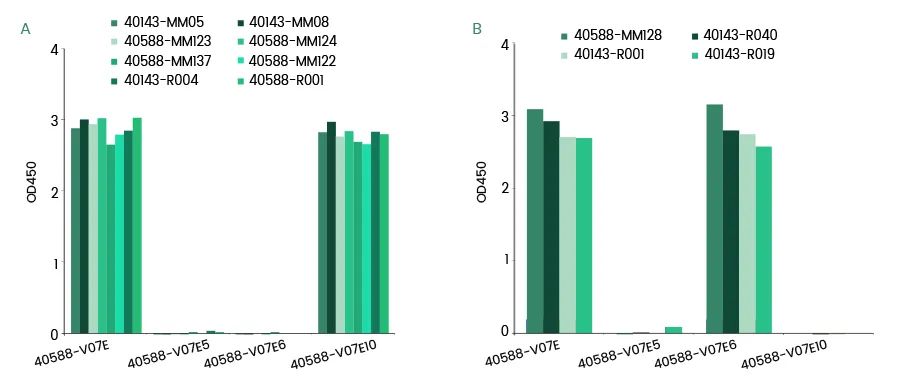
SARS-CoV-2 Anti-N MAbs Epitopes
(A: N-NTD, 49T-175G;B: N C tail, 366T-407L)
SARS-CoV-2 Anti-N paired antibody for N antigen detection
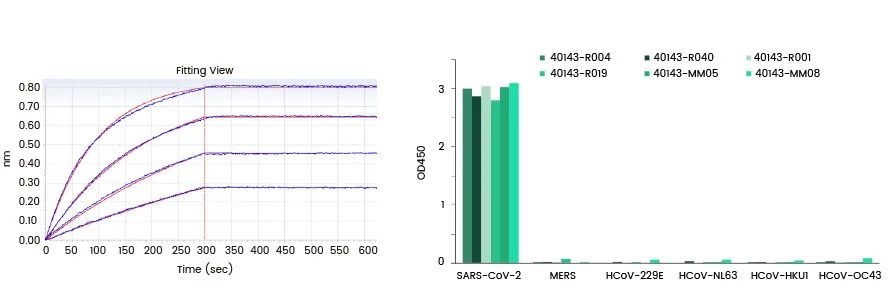
Yiqiao Shenzhou independently developed high-affinity, high-specificity Anti-N antibodies, and has successfully trial-matched 20+ groups of excellent antibody pairs (see attached table), which can be used for double-antibody sandwich detection of SARS-CoV-2 N antigen, many of them Strain antibodies have been supplied to IVD companies at home and abroad as raw materials for rapid diagnosis.
Among them, many sets of detection sensitivity are high, and the matched antibodies that recognize the natural samples all recognize the N-NTD epitope.
SARS-CoV-2 Anti-N antibody can recognize mutant N protein
Compared with the S protein, the N protein has a much lower mutation frequency, but a certain mutation frequency is still found. Studies have found that most of the mutations occur in the irregular flexible areas outside the two functional areas of N-NTD and N-CTD.
As an important target for rapid immunological detection, the ability of Anti-N antibody to recognize important N mutant proteins is related to the detection accuracy. The Anti-N antibody developed by Yiqiao Shenzhou can recognize multiple high-frequency mutations of the COVID-19 recombinant N antigen.
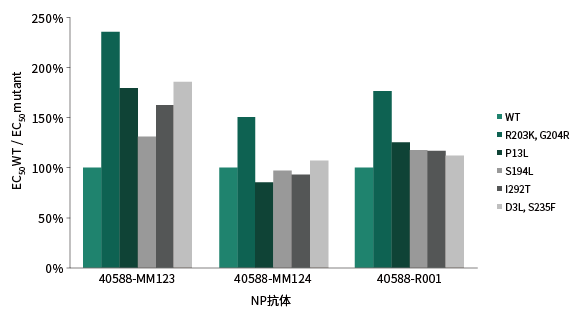
|
Protein Item Number |
Mutation site |
lineage |
|
40588-V07E1 |
N(R203K,G204R) |
High-frequency mutations, appearing in B.1.1.7, B.1.351, P.1, etc. |
|
40588-V07E2 |
N(P13L) |
High-frequency mutations, appearing in B.1.1.7, B.1.351, A.2.2, etc. |
|
40588-V07E3 |
N(S194L) |
High-frequency mutations, appearing in B.1.1.7, B.1.237, etc. |
|
40588-V07E4 |
N(I292T) |
High-frequency mutations, appearing in B.1.1.7, etc. |
|
40588-V07E8 |
N(D3L,S235F) |
B.1.1.7 feature mutation |
Notes: SARS-COV-2 lineages and corresponding geological locations of origin: B.1.1.7–UK, B.1.351–South Africa (SA), P.1–Brizil (BRA)
Study on the recognition epitope of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody
Yiqiao Shenzhou independently developed and screened multiple strains of COVID-19 RBD neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to detect the binding of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to non-mutant RBD and mutant RBD. The results showed that the ability of individual monoclonal antibodies to recognize RBD (K417N, E484K, N501Y) (Cat: 40592-V08H85) and RBD (K417T, E484K, N501Y) (Cat: 40592-V08H86) was significantly reduced, suggesting that neutralizing antibodies may recognize Different epitopes of RBD protein.
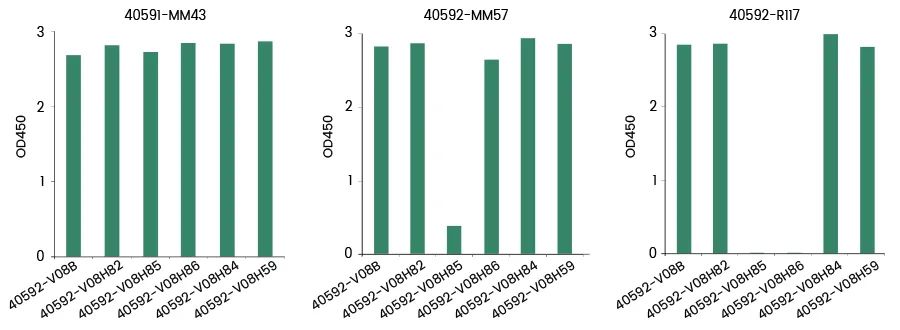
The binding of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing MAbs to RBD and RBD Mutations
Evaluation of the ability of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody to neutralize mutant RBD
Spike protein is more susceptible to mutations, which may be due to its key role in entering host cells and changing infectivity. Mutations at different sites bring about different changes in protein structure and function. Yiqiao Shenzhou uses the ELISA competition method to detect the neutralization ability of the antibody to the recombinant RBD protein. The results show that the neutralizing ability of each antibody to different RBD proteins is different. It shows that RBD mutations may cause the therapeutic neutralizing antibody to fail, so it is of great significance to screen neutralizing antibodies that recognize different epitopes.
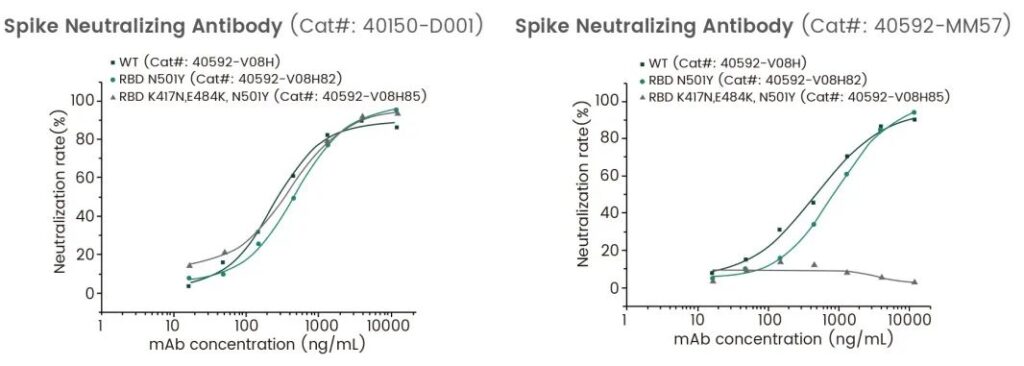
Neutralizing Ability to Spike RBD Mutants
Notes: Wild type(Cat#: 40592-V08H); RBD (N501Y)(Cat#: 40592-V08H82) ; RBD (K417N, E484K, N501Y)(Cat#: 40592-V08H85)
Attached table. Antibody pairs for COVID-19 antigen ELISA detection
_ | Capture Ab | Detection Ab |
| Pair 1 | 40143-R004 | 40143-R040 |
| Pair 2 | 40143-MM05 | 40143-R001 |
| Pair 3 | 40143-MM08 | 40143-R004 |
| Pair 4 | 40143-MM08 | 40143-MM05 |
| Pair 5 | 40143-MM05 | 40143-MM08 |
| Pair 6 | 40588-R0002 | 40588-R0006-1 |
| Pair 7 | 40143-MM05 | 40588-R001 |
| Pair 8 | 40588-MM123 | 40588-R001 |
| Pair 9 | 40143-R040 | 40588-R001 |
| Pair 10 | 40588-MM123 | 40588-MM124 |
| Pair 11 | 40143-R040 | 40588-MM124 |
| Pair 12 | 40588-MM124 | 40143-R040 |
| Pair 13 | 40143-R004 | 40588-R001 |
| Pair 14 | 40143-R004 | 40588-MM124 |
| Pair 15 | 40588-MM122 & 40588-MM124 | 40588-MM128 |
| Pair 16 | 40588-MM137 & 40143-MM05 | 40588-MM128 |
| Pair 17 | 40588-MM137 & 40143-MM05 | 40588-R704 |
| Pair 18 | 40588-R957 | 40588-MM128 |
| Pair 19 | 40143-R004 | 40588-RB30 |
| Pair 20 | 40143-R004 | 40588-RB89 |
| Pair 21 | 40143-R004 | 40588-RC02 |
| Pair 22 | 40143-R004 | 40588-RA84 |
Ab Epitopes: N-NTD (49T-175G)
Ab Epitopes: N C tail (366T-407L)
Ab Epitopes: TBD
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



