Your life expectancy will be longer if your diet is more salty?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
A highly controversial paper: The longer your life expectancy will be if your diet is more salty?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
A highly controversial paper: The longer your life expectancy will be if your diet is more salty?
Eating habits have a significant impact on human health. Different countries and regions will have different eating styles, and different families will also have different eating habits, but some eating habits are recognized by the public and play a role in health. Negative effects, such as a high-salt diet.
Many studies believe that excessive intake of table salt (NaCl) is an unhealthy lifestyle because it has been found to be strongly associated with a high risk of chronic inflammation, cardiovascular disease and autoimmune diseases. However, how much salt should I eat every day? There is no accurate statement.
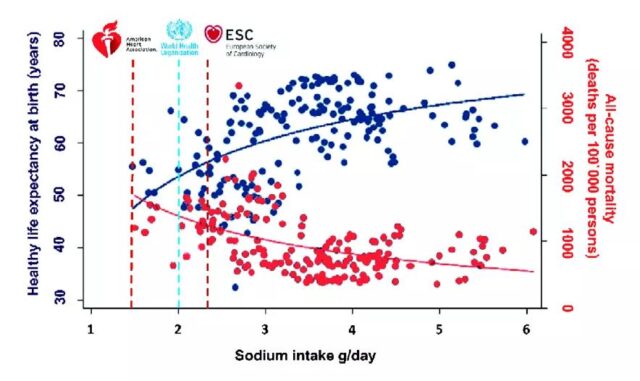
The American Heart Association recommends 1.5 grams of sodium per day (equivalent to 3.8 grams of salt), the World Health Organization recommends 2 grams of sodium (equivalent to 5 grams of salt), and the European Society of Cardiology recommends 2.3 grams Sodium (equivalent to 5.8 grams of table salt).
However, many things often have two sides, and the high-salt diet is no exception.
A discovery that disrupts cognition
In December 2020, Franz Messerli and others from the University of Bern, Switzerland, published a report entitled “Sodium intake, life expectancy, and all-cause mortality” in the European Heart Journal. Clinical research papers.
The study counted data from 181 countries/regions and found that the increase in sodium intake across the country is associated with an increase in average life expectancy and a decrease in all-cause mortality.
After adjusting the factors such as GDP and average body mass index of each country, increasing the intake of 1 gram of sodium (equivalent to 2.5 grams of salt) per day will increase the healthy life expectancy at birth by 2.6 years, and by another 0.3 years at the age of 60. , The all-cause mortality rate was reduced by 131 people per 100,000 people.
In other words, the saltier you eat, the longer the healthy life expectancy, and the lower the risk of death.

From the statistics below, we can see that China, Japan, Southeast Asia and other parts of Asia, as well as some countries in Europe and the United States, have high sodium intake, and countries such as Europe and the United States have the highest healthy life expectancy.
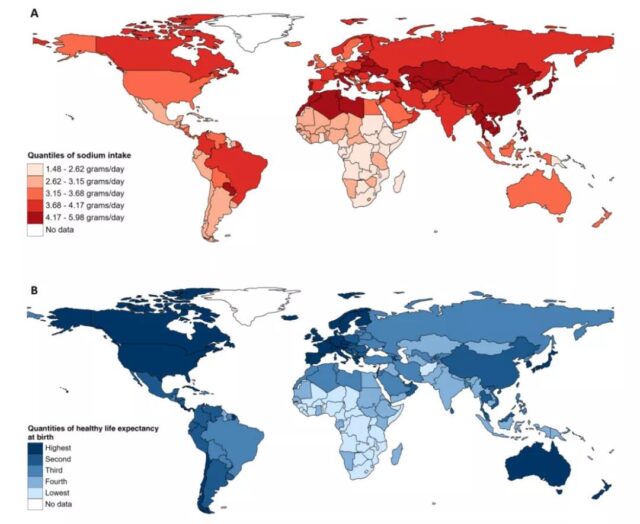
After excluding influencing factors such as GDP and average body mass index of various countries, the research team found that, overall, the increase in sodium intake was related to the increase in healthy life expectancy and the decrease in all-cause deaths.
Recommendations of the research team
How much salt should I eat every day? There is no accurate statement. The American Heart Association recommends 1.5 grams of sodium per day (equivalent to 3.8 grams of salt), the World Health Organization recommends 2 grams of sodium (equivalent to 5 grams of salt), and the European Society of Cardiology recommends 2.3 grams Sodium (equivalent to 5.8 grams of table salt).
The research team said that the results of this study refute that dietary sodium is the chief culprit in shortening lifespan or a risk factor for premature death.
Most people in the world have a moderate daily intake of sodium, with 2.3 grams to 4.6 grams of sodium per day (equivalent to 5.8 grams to 11.6 grams of table salt).
Many studies have shown that a high-salt diet is related to the risk of cardiovascular disease, but This risk increases only when the daily sodium intake exceeds 5 grams (equivalent to 12.6 grams of table salt).
Therefore, the research team believes that those who do not have high blood pressure need not deliberately reduce salt intake according to the above guidelines.
highly controversial paperpaper
Franz Messerli, the leader of the study and the corresponding author of the paper, said that this paper is the most rejected paper in his research career. The manuscript was rejected 8 times in a row before it was accepted and published by the European Heart Journal.
Although the paper was published, it has not been dispelled. Some researchers believe that there are too many variables involved in this study to infer causality.
For example, human sodium intake and healthy life span in Africa are relatively low, while sodium in the United States Both intake and healthy lifespan are relatively high, which does not mean that differences in healthy lifespans are caused by different sodium intakes.
Special reminder: This article only interprets the relevant research progress truthfully and does not constitute any suggestions.
Paper link:
https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa947
Your life expectancy will be longer if your diet is more salty?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



