How long is the protection period of COVID-19 vaccines?
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
How long is the protection period of COVID-19 vaccines?
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
How long is the protection period of COVID-19 vaccines? What should I do if the protection is reduced?
The level of neutralizing antibody is an important indicator for evaluating the effect of the COVID-19 vaccine. The level of neutralizing antibody decreases over time, and the protective effect of the vaccine is correspondingly weakened, but it does not mean that the vaccine has lost its effect.
Global open a COVID-19 for more than nine months of vaccination , vaccination significantly reduces the incidence of COVID-19 caused by viruses, hospitalization rates and mortality. However, it has been observed that the protective efficacy of all COVID-19 vaccines has a certain degree of decline over time, especially when facing mutant strains.
Neutralizing antibodies can recognize and prevent pathogens from binding to host cells , thereby preventing pathogens from invading the body. It is one of the main mechanisms for vaccines to exert their protective efficacy. It is also widely used in the evaluation of the protective efficacy of other vaccines.
As for the COVID-19 vaccine, what is the relationship between the level of neutralizing antibodies and the protective efficacy? Can it be used to evaluate the protective efficacy of vaccines? How to deal with the problem of declining neutralizing antibodies that are faced by the existing COVID-19 vaccines after vaccination?
The level of neutralizing antibodies induced by the COVID-19 vaccine is positively correlated with its protective efficacy
Inducing the body to produce neutralizing antibodies is one of the main ways for vaccines to exert their protective effects. Neutralizing antibody is a protective antibody produced by the immune system, which can recognize and prevent pathogens from binding to host cells, thereby exerting a protective effect.
Studies have shown that the level of neutralizing antibodies can reflect the protective efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine. This study included 7 new coronavirus vaccine-related studies (mRNA-1273, NVX-CoV2373, BNT162b2, rAd26-S+rAd5-S, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, Ad26.COV2.S, Corona Vac) and one new coronavirus recoverer Research.
The results show that the higher the ratio of neutralizing antibodies produced after vaccination of the COVID-19 vaccine and the levels of neutralizing antibodies in the body of the COVID-19 recovered patients, the higher the protection rate of the vaccine, and there is a positive correlation between the two (Spearman r=0.905; P= 0.0046) [1] .
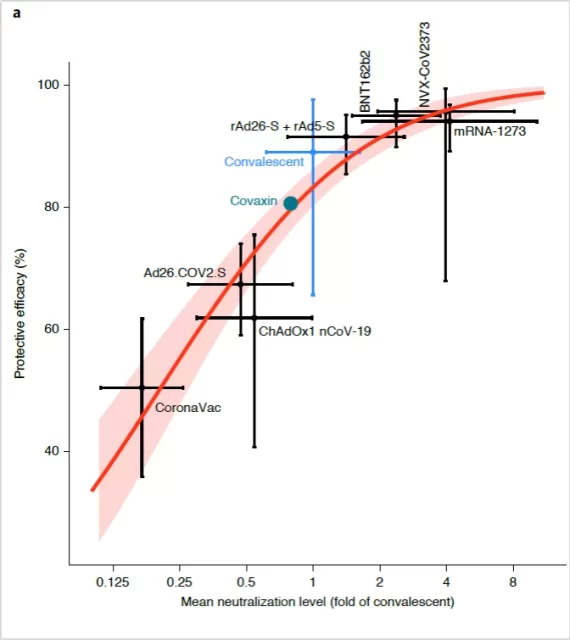
The relationship between the level of neutralizing antibodies and the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection [1]
Image source: screenshot of the paper
The incidence of breakthrough infection is correlated with the level of neutralizing antibodies induced after vaccination
For individuals, the higher the level of neutralizing antibodies after vaccination, the lower the possibility of contracting COVID-19 pneumonia.
In a prospective cohort study [2] , 4,530 participants randomly received two injections of mRNA-1273 (100 μg, 28 days apart) or placebo at 1:1 .
The results show that breakthrough infections in vaccinators are related to the low level of neutralizing antibodies in their bodies: the lower the level of neutralizing antibodies, the higher the possibility of contracting COVID-19 pneumonia.
A prospective cohort study in Israel [3] Among 1497 medical staff who completed 2 doses of vaccination, 39 (0.34%) developed breakthrough infection; the study found that the neutralizing antibodies of patients with breakthrough infection were geometrically average before infection The titer (GMT) was 192.8, and the neutralizing antibody GMT of the uninfected person was 530.4, and the former was only 36.35% of the latter.
In addition, among breakthrough infections, if the level of neutralizing antibodies before infection is higher, the viral load is lower. It can be seen that the level of neutralizing antibody induced by the COVID-19 vaccine can be used to predict the protective efficacy after vaccination; that is to say, the level of neutralizing antibody in the body of the vaccinee is closely related to the risk of breakthrough infection and the prognosis after breakthrough infection. .
Therefore, the level of neutralizing antibodies can be used to assess vaccine effectiveness.
Looking at the decline of the protective efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine from the level of neutralizing antibodies
A number of studies have shown that the neutralizing antibody level of the COVID-19 vaccine increases rapidly 14-28 days after the initial/intensified immunization, and then gradually declines.
It shows a significant decline in June to August, but the decline speed and amplitude of different technical routes exist The big difference [4-14] .
The study of neutralizing antibody titer detection for inactivated COVID-19 vaccines shows that 11 to 70 days after the second shot of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine is completed, the vaccinators can maintain a high level of neutralizing antibody positive rate and neutralizing antibodies. Titer; but from the 70th day to the 332th day, the neutralizing antibody titer in the vaccinated person decreased significantly, and the positive rate of neutralizing antibody was only 27% [15] .
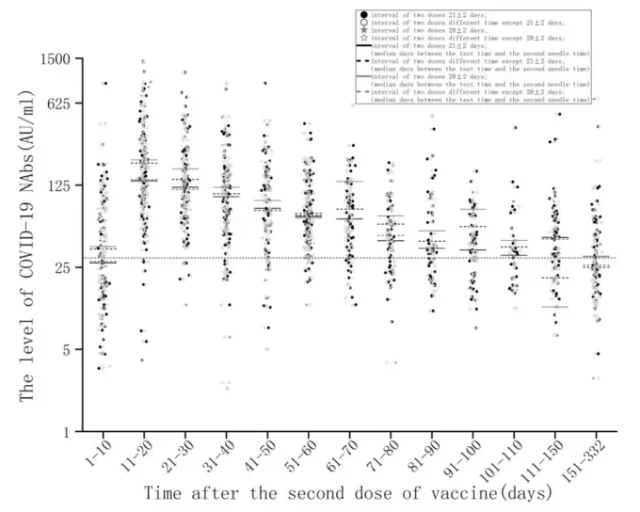 Changes in neutralizing antibody levels over time after the second dose of inactivated vaccine [15]
Changes in neutralizing antibody levels over time after the second dose of inactivated vaccine [15]
Image source: screenshot of the paper
An Israeli study showed that after completing two doses of BNT162b2 vaccine, the neutralizing antibody titer decreased rapidly in the first three months, and then decreased slowly [16] ; the positive rate of neutralizing antibody was still as high as 83.9% after 6 months of vaccination [17] .
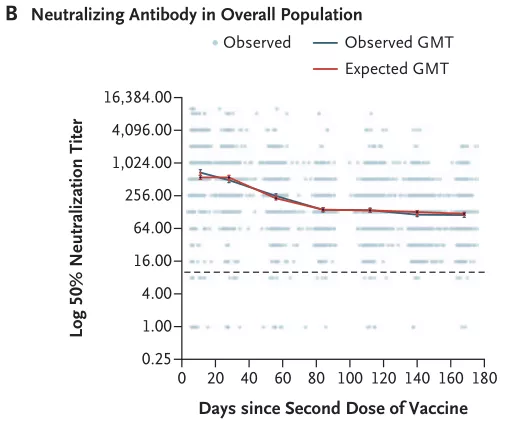 Changes in neutralizing antibody titer with time after the second dose of BNT162b2 vaccine [16]
Changes in neutralizing antibody titer with time after the second dose of BNT162b2 vaccine [16]
Image source: screenshot of the paper
In special populations such as the elderly and immunosuppression, the peak of neutralizing antibodies induced by the COVID-19 vaccine is lower than that of young adults, and the level of neutralizing antibodies declines faster and more rapidly over time.
In a prospective cohort study (follow-up to 6 months after the second dose) of 4868 medical staff vaccinated with the BNT162b2 vaccine, the peak levels of neutralizing antibodies in people aged ≥65 years were higher than those in people aged 18-45.
It is low, and the decline is greater at 3 months; studies also show that compared with non-immunosuppressive population, the level of neutralizing antibody is reduced by 70% in immunosuppressed people [16] .
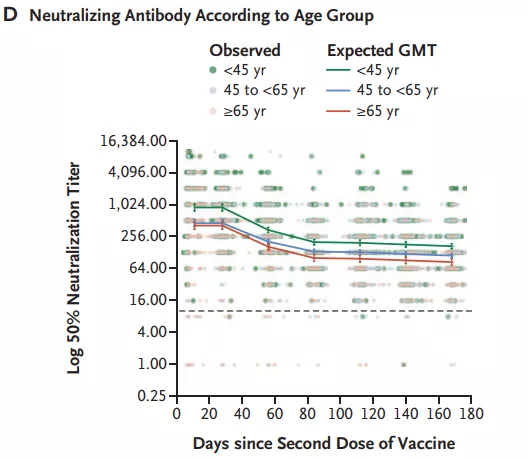 Neutralizing antibody titers of participants in different age groups [16]
Neutralizing antibody titers of participants in different age groups [16]
Image source: screenshot of the paper
In addition, the mutation of the new coronavirus is another important reason for the decline in the protective efficacy of the new coronavirus vaccine. In less than two years since the outbreak of the COVID-19 epidemic, a variety of mutant strains that require attention have emerged. Most of these mutant strains are accompanied by increased infectivity or a certain degree of immune escape. The decrease in the protective power of the COVID-19 vaccine is significantly related to the decrease in the neutralizing activity of the mutant strain. The United States CDC compiled the neutralization experiment data in 48 studies and found that the neutralizing antibody titers of the COVID-19 vaccine (including mRNA, AZ, Novavax, and J&J) against Beta, Delta, and Alpha variants were significantly reduced [18] .
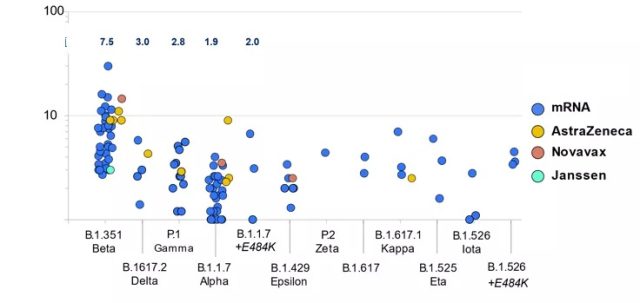 The neutralizing antibody titer of some COVID-19 vaccines against mainstream variant strains has decreased by multiples [18]
The neutralizing antibody titer of some COVID-19 vaccines against mainstream variant strains has decreased by multiples [18]
Image source: https://www.cdc.gov
Fortunately, despite the fact that the COVID-19 vaccine has a decline in the protective effect of preventing infection under the influence of time after vaccination and the double reduction of the neutralizing antibody level of the mutant strain, its preventive effect on severe illness is relatively stable (such as BNT162b2 Phase III clinical Research shows that the 6-month critical illness protection rate is 96.7% [8] ) .
How to deal with the gradual decline of neutralizing antibodies?
In the face of the decline in the protective power of the COVID-19 vaccine, there are currently methods to improve the level of antibodies and the immune effect, such as boosting immunization with homologous vaccines (homologous booster) and boosting immunization with vaccines of different technical routes (sequential immunization) .
Homologous booster shot
Studies have shown that the booster injection can increase the level of neutralizing antibodies and enhance the immune response:
The related research of BNT162b2 vaccine booster showed that: 8 months after the second dose of BNT162b2 vaccination, vaccination of the third dose of BNT162b2 significantly increased the level of neutralizing antibodies. Among 18 to 55-year-old people, compared with the neutralizing antibody titers in August after the two doses of vaccination, the neutralizing antibody titers against the wild strain of the COVID-19 and the Beta variant strain increased by 25.5 after 1 month after the third dose of vaccination. The titers of neutralizing antibodies against the Delta mutant strains increased by 5.48 times and 11.93 times in the population aged 65 to 85 years, respectively, increased by 49.56 times and 78.35 times in the population aged 65 to 85 years. Times [19] .
Research on the mRNA-1273 vaccine showed that the antibody titer decreased 6 months after the second dose of the mRNA-1273 vaccine, and the third dose can significantly increase the neutralizing antibody titers against Beta, Gamma and Delta variants [13 ,14,20] .
The results of phase I/II clinical trials of inactivated vaccine booster shots show that booster shots can not only increase the level of neutralizing antibodies, but also prolong their maintenance time in the body: the neutralizing ability of wild-type new coronaviruses 4 weeks after the third dose of vaccination It is about 60% higher than that of only two doses of vaccine, and the neutralizing antibody titer at 180 days after the third dose is equivalent to the peak level of neutralizing antibody titer after the second dose [21] .
At present, the world is paying attention to the intensified vaccination of key populations with higher risk of infection. The vaccination booster injection has played a good role in improving the effect of the vaccine in clinical practice. Real-world data from Israel (completely 2 doses of people ≥60 years of age who have been vaccinated for more than 5 months) show that 12 days after the third dose of BNT162b2 vaccine, the relative risk of contracting the new coronavirus has been reduced by 11.3 times [22] . In addition to Israel, the United States, France, Germany and other countries have now approved the third dose of the COVID-19 vaccine in specific populations. China is also promoting a COVID-19 vaccine booster vaccination plan for high-risk groups. At present, some areas have issued booster vaccines. Vaccination plan.
Sequential immunization
In addition to the enhancement of homologous vaccines, the sequential immunization (including sequential basic immunization and sequential enhancement) of the COVID-19 vaccine of different technical routes has also attracted attention. At present, the more researched sequential programs are adenovirus vector vaccine sequential mRNA vaccine, and inactivated vaccine sequential other vaccines (mainly mRNA vaccine) .
Regarding the adenovirus vector vaccine sequential mRNA vaccine, the results of a randomized controlled study showed that compared with two doses of ChAdOx1 vaccine (AstraZeneca) , the ChAdOx1-BNT162b2 vaccination regimen induced a stronger immune response and the antibody neutralization ability was better. Strong [23] .
Another study also found that the ChAdOx1-BNT162b2 sequential immunization program induced a strong immune response, and had a strong neutralizing effect on Alpha, Beta, Kappa and other variants, and no serious adverse events occurred [24] .
Regarding the sequence of inactivated vaccines to other vaccines, most of the existing data comes from studies on boosting immunization with other technical routes after the completion of the entire vaccination of two doses of inactivated vaccines:
In a study in China, seven months after two healthy subjects (50-55 years old) completed two doses of inactivated vaccine, their serum S protein binding antibody and neutralizing antibody levels had dropped to baseline levels.
Sequential inoculation of 1 dose of mRNA vaccine (developed by Siwei, 25 μg) , the neutralizing antibody titers against both pseudovirus and true virus are greatly increased; and Th1 type cellular immune response is significantly activated, and memory B cell response is significantly increased [25] .
A study in Thailand found that medical staff who had received two doses of CoronaVac vaccine after receiving the third dose of BNT162b2 (n=23) or ChAdOx1 (n=18) boosted the level of neutralizing antibodies to the Delta variant strain significantly. The level of neutralizing antibodies induced by the inoculation of BNT162b2 booster needles increased significantly [26] .
In a Turkish study, 45 medical staff who had received two doses of CoronaVac vaccine were given the third dose of BNT162b2 (2IVV+BNT group) or CoronaVac (3IVV group) about 6 months after the first dose. The study found: one month, two antibodies against the new participant crown virus S protein receptor binding region after the third dose vaccination (IgG-S) titers were significantly improved; BNT162b2 particular group, the titer of IgG-S It was about 46.6 times the level at 1 month after the second dose (median 25,538.0 vs. 547.7, au/ml) , and 27 times higher than those who received CoronaVac for the third dose (median 25,538.0 VS. 947.3, au/ ml) . ml) . Since the binding of the new coronavirus to the host cell receptor is mediated by the S protein, the higher the induced IgG-S, the better the effect of preventing infection. The study initially showed that after the completion of inactivated virus vaccination, the use of BNT162b2 vaccine as a booster vaccination can obtain a better immune effect [27] .
 Antibody titer of subjects in each group (horizontal axis: IgG-S titer, vertical axis: IgG-N titer) [27]
Antibody titer of subjects in each group (horizontal axis: IgG-S titer, vertical axis: IgG-N titer) [27]
Image source: screenshot of the paper (invasion and deletion)
Therefore, some scholars believe that heterologous immunization may be a better strategy to deal with the COVID-19 virus, which provides a certain new idea for finding a better COVID-19 vaccination strategy.
Conclusion:
The level of neutralizing antibody is an important indicator for evaluating the effect of the COVID-19 vaccine. The level of neutralizing antibody decreases over time, and the protective effect of the vaccine is correspondingly weakened, but it does not mean that the vaccine has lost its effect. The neutralizing antibody produced by humoral immunity is not the only weapon of the COVID-19 vaccine against the virus. The cellular immunity induced by the COVID-19 vaccine also plays an important role in fighting the COVID-19 virus infection.
Although a decrease in neutralizing antibodies can increase the incidence of breakthrough infection, even if a breakthrough infection occurs, the cellular immunity induced by the vaccine can still exert the protective effect of the vaccine. This may be the reason why there are relatively few severe patients with breakthrough infection.
In general, the protective effect of the COVID-19 vaccine against variants including Delta has decreased, but it still has a protective effect, especially for severe cases.
In addition, booster injections or sequential immunization can effectively deal with the decline in efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine over time and virus mutation.
Finally, I look forward to more research in this area and the implementation of better vaccination strategies, so that the role of the COVID-19 vaccine can be maximized.
The implementation of the vaccination strategy has maximized the role of the COVID-19 vaccine.
References:
[1].Khoury DS, Cromer D, Reynaldi A, et al. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med. 2021 Jul;27(7):1205-1211. doi : 10.1038/s41591-021-01377-8.
[2].Gilbert PB, Montefiori DC, McDermott A, et al. Immune Correlates Analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Trial. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Aug 15:2021.08.09.21261290. doi: 10.1101/2021.08. 09.21261290.
[3].Bergwerk M, Gonen T, Lustig Y, et al. Covid-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jul 28:NEJMoa2109072. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2109072.
[4].Jiang HD, Zhang L, Li JX, et al. Next steps for efficacy evaluation in clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines. Engineering (Beijing). 2021 May 19. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2021.04.013 .
[5].Yang S, Li Y, Dai L, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a recombinant tandem-repeat dimeric RBD-based protein subunit vaccine (ZF2001) against COVID-19 in adults: two randomised, double-blind, placebo -controlled, phase 1 and 2 trials. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021 Aug;21(8):1107-1119. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00127-4.
[6].Al Kaabi N, Zhang Y, Xia S, et al. Effect of 2 Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines on Symptomatic COVID-19 Infection in Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021 Jul 6;326(1 ):35-45. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.8565..
[7].https://www.biospace.com/article/releases/moderna-reports-second-quarter-fiscal-year-2021-financial-results-and-provides-business-updates.
[8].Thomas SJ, Moreira ED, Nicholas K, et al. Six Month Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.28.21261159v1
[9].https://ir.novavax.com/2021-08-05-Novavax-Announces-COVID-19-Vaccine-Booster-Data-Demonstrating-Four-Fold-Increase-in-Neutralizing-Antibody-Levels- Versus-Peak-Responses-After-Primary-Vaccination.
[10].https://www.chinanews.com/gn/2021/03-28/9442132.shtml.
[11].Barouch DH, Stephenson KE, Sadoff J, et al. Durable Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses 8 Months after Ad26.COV2.S Vaccination. N Engl J Med. 2021 Sep 2;385(10):951-953. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2108829.
[12].Li M, Yang J, Wang L, et al. A booster dose is immunogenic and will be needed for older adults who have completed two doses vaccination with CoronaVac: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 /2 clinical trial. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.08.03.21261544v1.
[13]. Pegu A, O’Connell SE, Schmidt SD, et al. Durability of mRNA-1273 vaccine-induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science. 2021 Sep 17;373(6561):1372-1377. doi: 10.1126/science.abj4176.
[14].Doria-Rose N, Suthar MS, Makowski M, et al. mRNA-1273 Study Group. Antibody Persistence through 6 Months after the Second Dose of mRNA-1273 Vaccine for Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jun 10;384(23):2259-2261. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2103916.
[15].Zhang H, Jia Y, Ji Y, et al. Studies on the level of neutralizing antibodies produced by inactivated COVID-19 vaccines in the real world. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.08 .18.21262214v1.
[16].Levin EG, Lustig Y, Cohen C, et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2114583.
[17].Israel A, Shenhar Y, Green I, et al. Large-scale study of antibody titer decay following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine or SARS-CoV-2 infection. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/ 2021.08.19.21262111v1.
[18]. Overview of data to inform recommendations for booster doses of COVID-19 vaccines,
https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2021-06/06-COVID-Oliver-508.pdf.
[19].Initial data, Phase 1 sentinel subjects receved dose 1 & 2 of 30mg BNT162b2 21 days apart, subjects then came back and received BNT162b2 30 mg as a 3rd booster dose.
[20].Annual R&D Day Presentation. https://investors.modernatx.com/static-files/ea6e4fd0-00dd-4c1c-a18d-42b46a36ac14
[21]. Wang K, Cao Y, Zhou Y, et al. A third dose of inactivated vaccine augments the potency, breadth, and duration of anamnestic responses against SARS-CoV-2.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.09.02.21261735v1.
[22].Bar-On YM, Goldberg Y, Mandel M, et al. Protection of BNT162b2 Vaccine Booster against Covid-19 in Israel. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 7;385(15):1393-1400. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2114255.
[23].Borobia AM, Carcas AJ, Pérez-Olmeda M, et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of BNT162b2 booster in ChAdOx1-S-primed participants (CombiVacS): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2021 Jul 10;398(10295):121-130. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01420-3.
[24].Groß R, Zanoni M, Seidel A, et al. Heterologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 prime-boost vaccination elicits potent neutralizing antibody responses and T cell reactivity.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.05.30.21257971v1.
[25].Lin A, Liu J, Ma X, et al. Heterologous vaccination strategy for containing COVID-19 pandemic.
https://www.medrxiv.org/c
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



