Cell: It is difficult for fat people to lose weight through exercise!
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Cell: It is difficult for fat people to lose weight through exercise!
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Cell: It is difficult for fat people to lose weight through exercise!
“Diet control and more exercise” seems to be an unbreakable truth in weight loss.
WHO recommends that overweight and obese people with a BMI ≥ 25 or 30 take regular physical exercise to achieve the goal of losing weight. Children exercise 60 minutes a day, and adults exercise weekly 150 minutes.
The existing weight loss guidelines also mention that when adults lose weight, they need to consume 500-600 kcal of calories every day by exercising + reducing food intake, of which exercise consumption should reach 300 kcal.
However, a troubling fact is that 28% of the energy consumed through exercise is offset, and the actual energy consumed is only the remaining 72% . Fold, what’s going on?
To answer this question, we first need to understand the concept of energy compensation. The total energy consumption of a person in a day is mainly composed of basal metabolism and daily activity consumption.
When daily activities consume too much, in order to maintain energy balance in the body, basal metabolic consumption The energy will decrease, that is to say, although hard running increases the calorie consumption by 100 kcal (+100) , the basal metabolism reduces the calorie consumption by 28 kcal (-28) .
The total energy consumption has only increased by 72 kcal.
As for why the energy compensation mechanism has been preserved in evolution, it is probably because in the age of starvation, this mechanism can minimize our need for food and reduce the risk of going out for food.
When humans actually need to worry about eating too much one day, this mechanism is a bit of a drag.
Recently, an international team published a research paper entitled: Energy compensation and adiposity in humans in the Cell sub-journal Current Biology, revealing a more troubling phenomenon. Fact: The heavier the person, the more energy compensation, and the more difficult it is to lose weight through exercise .

A total of 1754 participants were included in the study, including 692 men and 1062 women, with an age range of 18-96 years and a BMI range of 12.5-61.7 kg/m 2 (mean BMI: 25.2) .

Legend: total energy consumption (TEE) = daily activity consumption (AEE) + food thermogenic effect + basal metabolism (BEE)
Under a modern lifestyle—without heavy physical labor and chronic food shortages, participants’ total daily energy consumption was proportional to basal metabolism, and daily activity consumption was inversely proportional to basal metabolism (slope b±SE=-0.349±0.044 , p <0.0001, 95%CI: -0.436~-0.262) , that is to say, the more daily activities consumed, the less basal metabolism, and there is energy compensation between the two.
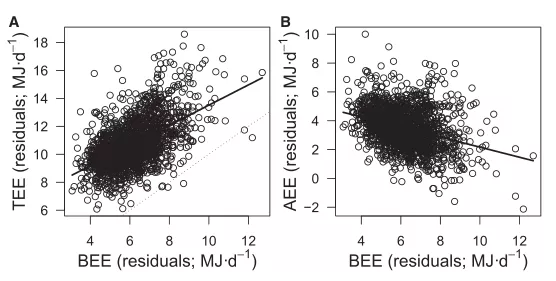
Legend: A relationship between total energy consumption and basal metabolism, B relationship between daily activity consumption and basal metabolism
Moreover, this energy compensation has no difference in gender and age, but it is closely related to BMI. For people above the 90th percentile of the population, the energy compensation is 49.2%, which is equivalent to: obese people consume 100 kcal of calories through exercise, and 49 kcal are saved in basal metabolism.

Speakman, the corresponding author of the paper, said that this may be a “stricken” conclusion for obese people.
This means that it may be harder for obese people to lose weight through exercise than for thin people. Conversely, even though thin people had a lower willingness to lose weight, they had far less compensatory effects.
Knowing about energy compensation can be helpful in formulating weight loss strategies for different groups of people.
As BMI increases, the effect of exercise weight loss may become worse and worse, but this is not mentioned in current weight loss guidelines.
It is also worth noting that basal metabolism is the energy consumption required to maintain the operation of various organs of the human body.
When energy compensation reduces basal metabolism, will it affect the functions of various organs, such as decreased immune function and poor wound recovery function… …these questions remain to be addressed by future research.
However, people who want to lose weight need not be too pessimistic, “More exercise” will not work, and “Diet control”, energy compensation is not an excuse for not exercising, moderate exercise can reduce the risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, diabetes and various cancers. Prevent dementia and prevent further weight gain, otherwise how do you say “life lies in exercise”?
Reference:
Careau V, Halsey LG, Pontzer H, et al. Energy compensation and adiposity in humans. Curr Biol. 2021;31(20):4659-4666.e2.
Cell: It is difficult for fat people to lose weight through exercise!
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



