Meteorin-like promotes heart repair through endothelial KIT receptor tyrosine kinase
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Meteorin-like promotes heart repair through endothelial KIT receptor tyrosine kinase
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Meteorin-like promotes heart repair through endothelial KIT receptor tyrosine kinase.
Myocardial infarction ( MI ) is an acute disease caused by sudden coronary thrombosis and occlusion. Ischemic tissue damage during myocardial infarction leads to scarring and leads to heart failure.
Due to the limited regenerative capacity of the adult mammalian heart, effective tissue repair after myocardial infarction requires a robust angiogenic response under the interaction of immune cells and endothelial cells [1-3] .
The formation of new blood vessels reduces scarring and delays the deterioration of heart function, which may be one of the targets of treatment.
However, the complex intercellular interactions between angiogenesis and cardiac functional adaptation after myocardial infarction have so far been unclear.
To this end, the research group of Kai C. Wollert of the Hannover Medical School in Germany published a paper in Science entitled Meteorin-like promotes heart repair through endothelial KIT receptor tyrosine kinase .
Through bioinformatic secretomic analysis of mouse models of acute myocardial infarction, it was found that Meteorin -like promotes heart repair through endothelial KIT receptor tyrosine kinase.
The like (METRNL ) factor is highly expressed in myeloid cells in the myocardial infarction area to promote angiogenic response, help repair the infarcted area, and become a possible target for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction.

To identify key factors between immune cells and epithelial cells during acute myocardial infarction repair, the authors performed a secretomic analysis.
METRNL protein was found to be highly expressed in myeloid cells in the myocardial infarction area.
Research on METRNL mainly found that it is secreted during inflammation and promotes metabolic adaptation and tissue protection under stress conditions, but the receptors of METRNL and the roles of both in myocardial infarction repair are still unknown.
In addition to mouse models, the authors further found that METRNL was also abundantly expressed in myocardial samples from patients with acute myocardial infarction.
By co-labeling the myeloid cell marker CD11b, the authors confirmed that METRNL is expressed in myeloid cells in the infarcted area (Figure 1) .
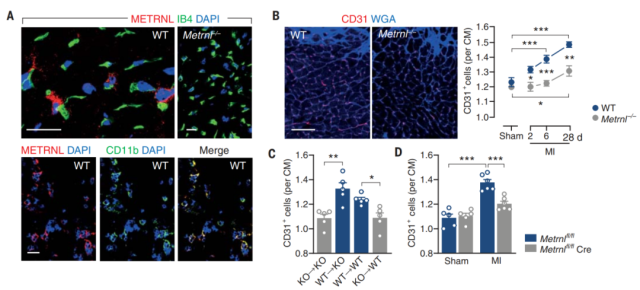
Figure 1 The high expression of METRNL in myeloid cells in the infarcted area in mice with acute myocardial infarction
Therefore, the authors used a mouse model of acute myocardial infarction as the research object to study its function in the repair of acute myocardial infarction by knocking out Metrnl.
Metrnl-/- itself can reproduce normally without obvious phenotype. However, after myocardial infarction injury, compared with wild-type mice, they showed a larger infarct scar area, and left ventricular dilatation and systolic dysfunction were more pronounced.
In addition, the authors found that Metrnl-/- deletion did not affect global myocardial capillary density, but impaired neocapillary formation in the border region of myocardial infarction in mice.
In addition, the authors found that angiogenesis defects after myocardial infarction were rescued by transplanting myeloid cells from wild-type mice into Metrnl-null mice.
These results suggest that myeloid cell-derived METRNL can promote angiogenesis, tissue repair, and functional adaptation after myocardial infarction.
The authors then found the cell surface receptor KIT of METRNL by chemical cross-linking mass spectrometry.
KIT is a receptor for the stem cell factor SCF in hematopoietic stem/histomic cells and germ cells and other cell types, and is very important for hematopoiesis and developmental processes [4] .
Through co-immunoprecipitation experiments, the authors demonstrated a direct interaction between METRNL and KIT, and found that METRNL interacts with the extracellular domain of KIT with high affinity.
The authors then used single-cell RNA sequencing to identify kit-expressing epithelial cells in mouse myocardium.
The authors found that in a mouse model of myocardial infarction, the number of kit-expressing epithelial cells was significantly increased, and genes related to cell proliferation and migration were highly expressed (Figure 2) .
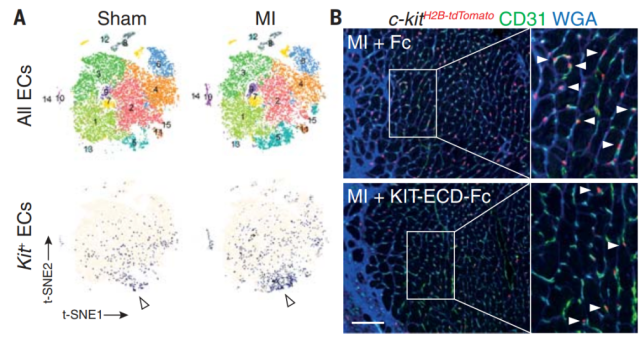 Figure 2 Increased Kit+ epithelial cells in a mouse model of myocardial infarction
Figure 2 Increased Kit+ epithelial cells in a mouse model of myocardial infarction
To test whether METRNL has a therapeutic effect on myocardial infarction, the authors performed left ventricular injection as well as subcutaneous infusion in a mouse model of myocardial infarction and found that METRNL treatment enhanced capillaryization at the edge of the myocardial infarction area, limited scarring and impaired cardiac function. have lasting beneficial effects.
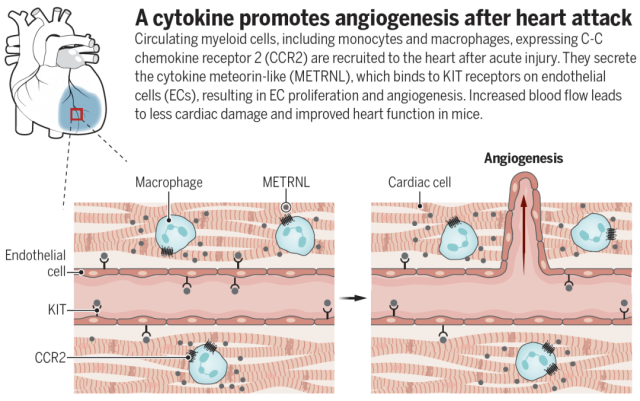 Figure 3 Working Model
Figure 3 Working Model
Collectively, the authors work to identify highly expressed METRNL in the myeloid cell secretome through analysis of a mouse model of myocardial infarction, which promotes tissue repair after myocardial infarction through interaction with the epithelial cell surface receptor KIT. , provides a new drug target for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction.
Due to the therapeutic effect of this work on acute myocardial infarction, the same journal published an opinion article to introduce the work.
The work found that providing METRNL protein to mice can increase angiogenesis and improve cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction in mice. It is a “cross-talk” at the cellular biological level during cardiac repair.

Original link:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abn3027
Meteorin-like promotes heart repair through endothelial KIT receptor tyrosine kinase
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



