Ketogenic diet may shorten survival time in cancers with high expression of IL-6
- Early Biomarker for Multiple Sclerosis Development Identified Years in Advance
- Aspirin Found Ineffective in Improving Recurrence Risk or Survival Rate of Breast Cancer Patients
- Child Products from Aliexpess and Temu Contain Carcinogens 3026x Over Limit
- Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca’s Enhertu Shows Positive Results in Phase III DESTINY-Breast06 Clinical Trial
- Mn007 Molecules Offer Potential for Combating Streptococcus pyogenes Infection
- Popular Indian Spices Banned in Hong Kong Over Carcinogen Concerns
Ketogenic diet may shorten survival time in cancers with high expression of IL-6
- AstraZeneca Admits for the First Time that its COVID Vaccine Has Blood Clot Side Effects
- Was COVID virus leaked from the Chinese WIV lab?
- HIV Cure Research: New Study Links Viral DNA Levels to Spontaneous Control
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Ketogenic diet may shorten survival time in cancers with high expression of IL-6
Scientists have found that ketogenic diet may accelerate cachexia and shorten survival time in cancers with high expression of IL-6, and glucocorticoid treatment may solve the problem
The crazy proliferation of cancer cells makes them have a very high demand for nutrients, especially glucose.
This feature can also be used in reverse, such as limiting cancer progression through a high-fat, low-carb ketogenic diet (KD), which has been recognized by many preclinical studies.
However, the ketogenic diet anti-cancer is not all advantages.
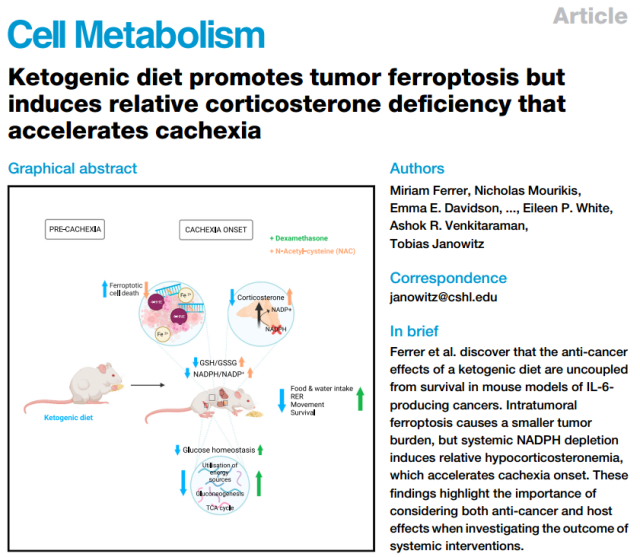
Recently, a study published in the journal “Cell Metabolism” found that although the ketogenic diet can effectively inhibit the progression of cancer, in the cancers that produce IL-6, the ketogenic diet can also accelerate the progression of cachexia and thus lead to small Rat survival is shortened .
Studies have found that a ketogenic diet can increase lipid peroxidation and lead to ferroptosis of cancer cells; however, redox imbalance also impairs the biosynthesis of corticosterone, thereby affecting metabolic balance and accelerating cachexia .
Fortunately, this problem can be solved with glucocorticoids. The combination of ketogenic diet + dexamethasone can delay the onset of cachexia and prolong the survival period while ensuring the tumor suppressor effect .
This also reminds us that cancer progression cannot be used as the only indicator of efficacy , and it is more important to comprehensively discuss the length and quality of survival.
The ketogenic diet is a special solution for the “sugar love” of cancer cells. In preclinical and clinical studies, it has been confirmed that the ketogenic diet can play an anti-inflammatory and inhibit tumor growth role. But in a mouse model of IL-6-secreting cancer, hepatic ketogenesis was suppressed and the mice developed cancer cachexia.
So-called cancer cachexia, a severe wasting syndrome characterized by reduced food intake and weight loss, affects up to 80% of cancer patients and is directly responsible for cancer deaths.
So, the reason is that the ketogenic diet cannot be effectively converted into energy for the body in such diseases?
To address this question, the researchers carried out experiments. They first tested the anticancer effect of the ketogenic diet in mouse models of two IL-6-secreting cancer types, C26 colorectal cancer and KPC pancreatic cancer.
It has to be said that the ketogenic diet does have something, the tumor growth of both mice was significantly slowed down, but this did not make the mice live longer – the survival period of the ketogenic diet mice was significantly shortened ( C26: 10 vs 14 days, KPC: 6.5 vs 17 days).
Mice in the ketogenic group showed loss of subcutaneous and gonadal adipose tissue, loss of quadriceps muscle, and splenomegaly, all typical manifestations of cachexia.
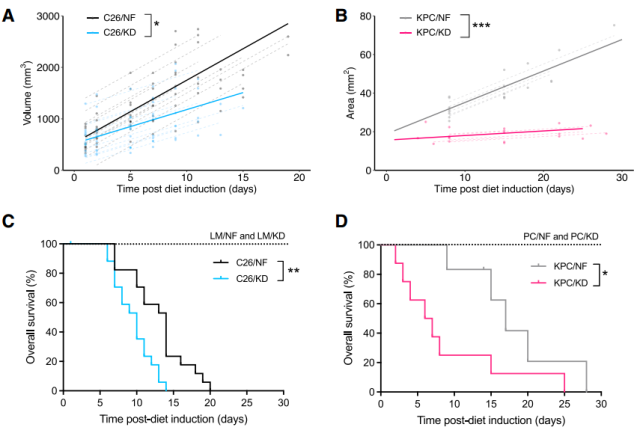
Ketogenic diet slows tumor growth but accelerates death in mice
After analyzing the blood sugar and ketone bodies in the blood of the mice, the researchers found that these tumor-bearing mice obviously did not “adapt” to the ketogenic diet. Their blood sugar dropped sharply, and the level of ketone bodies in the circulation was higher than that of non-tumor-bearing mice. Low.
Let’s talk about cachexia later. How does the ketogenic diet bring cells to a dead end?
Lipid-rich diets such as the ketogenic diet can provide a large number of substrates for lipid peroxidation and the formation of lipid free radicals. The researchers detected a substantial accumulation of 4-HNE, the major lipid peroxidation product (LPP) produced by fatty acid oxidation, in the liver of mice .
Under normal circumstances, the rate of lipid peroxidation is not high, and antioxidant defense systems such as NADPH-dependent glutathione (GSH) can also remove toxic products in time. But once it cannot be “detoxified” in time, the accumulated LPP will lead to programmed cell death that depends on iron, that is, ferropotosis .
In fact, in tumor-bearing mice on a ketogenic diet, this system was indeed operating at supersaturation, and the researchers observed a decrease in the ratio of GSH to its oxidized form and a significant increase in ferroptosis markers. Feeding mice the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) promoted glutathione biosynthesis and reduced LPP accumulation.
It can be seen that the ketogenic diet can induce sustained cancer cell ferroptosis through lipid peroxidation, which is one of the mechanisms by which it delays tumor growth.
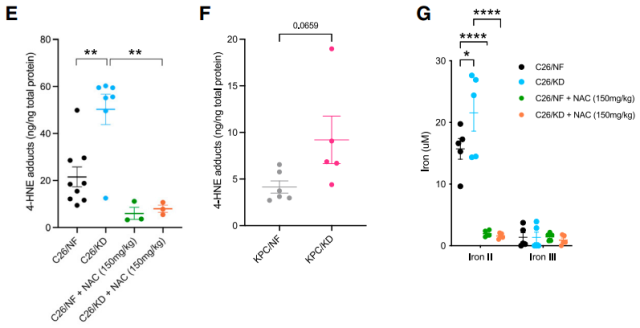
Ketogenic diet induces ferroptosis in cancer cells
At the same time, the overloading of the redox system also brings hidden dangers.
Glucocorticoid biosynthesis involves NADPH-dependent enzymatic reduction of cholesterol. One of the main members of the human glucocorticoid class is cortisol (corticosterone in rodents), and in cancer cachexia, cortisol drives adaptive changes, including mediating the storage and breakdown of nutrients such as glucose/protein/fat.
The researchers found that during cachexia, corticosterone concentrations were significantly elevated in tumor-bearing mice fed a normal diet, but not in mice fed a ketogenic diet .
Comparing the transcriptomes of the mice for GSEA analysis, the researchers found that steroid biosynthesis and cholesterol homeostasis pathways were significantly downregulated in the ketogenic mice. This indicated that corticosterone synthesis was impaired in tumor-bearing mice in the ketogenic group .
In addition, although IL-6 can drive the release of corticosterone, the researchers did not observe differences in IL-6 levels in different dietary groups in the experiment, at least this time it was not the problem of IL-6.
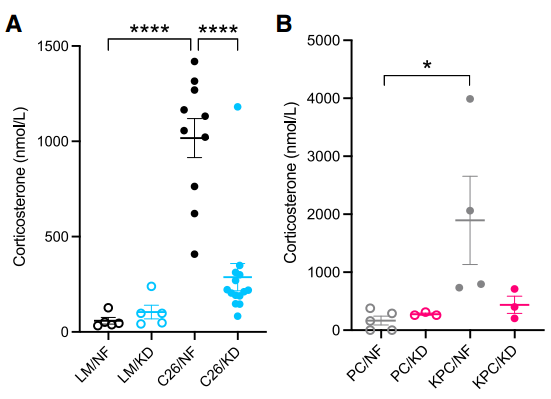
Corticosterone levels were not elevated in the ketogenic diet group during cachexia
Through in vitro studies, the researchers found that LPP can directly inhibit the production of cortisol in human adrenal cortical cells, which they believe may be due to the consumption of NADPH by LPP.
The researchers observed changes in various metabolic markers in the ketogenic mice, such as impairment of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis, downregulation of genes related to sugar/pyruvate metabolism, and abnormalities in fatty acid metabolism.
It can be said that the biosynthesis of corticosterone was impaired in tumor-bearing mice in the ketogenic group, which triggered a series of metabolic maladaptation, insufficient energy utilization, lower blood glucose levels, and finally induced cancer cachexia in advance .
The researchers also found that in the cachexia state, the ketogenic mice had higher levels of circulating GDF-15 than the normal diet mice.
GDF-15, a member of the transforming growth factor TGF-β superfamily that mediates reduced food intake, has been implicated as one of the mechanisms of anorexia in cancer cachexia and anorexia induced by aldehyde poisoning. This would also explain the reduced food intake seen in the mice.
Since the problem lies in glucocorticoids, can it be solved by glucocorticoids?
The researchers injected dexamethasone into tumor-bearing mice and found that it could significantly delay the onset of cachexia and prolong the survival of mice while retaining the anticancer effect of ketogenic diet.
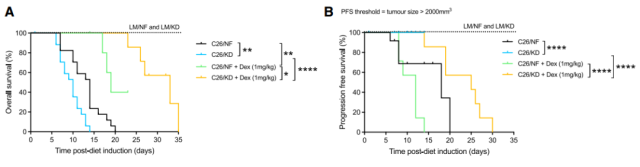
Ketogenic + dexamethasone, tumor suppression and longer survival time
It can be found that in the normal diet group, dexamethasone actually promotes the growth of the tumor, leading to a shortened PFS, but in the ketogenic group, it is a strong combination, the tumor does not grow, and the survival does not shorten.
Dexamethasone treatment also significantly rescued the metabolic problems in the ketogenic mice, with improvements in adipose tissue wasting, muscle wasting, and splenomegaly.
This study not only proposes the mechanism of action of the ketogenic diet in anti-cancer and induction of cachexia, two opposite aspects of survival, but also suggests that the results of our systemic intervention cannot be extrapolated from the effect on tumor alone. In clinical practice, the value of treatment to patients should also be discussed in combination with multiple aspects.
References:
[1] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1550413123001857?via%3Dihub
Ketogenic diet may shorten survival time in cancers with high expression of IL-6
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.