Breakthrough infection cohort study of mRNA vaccination for Delta variant
- WHO Releases Global Influenza Vaccine Market Study in 2024
- HIV Infections Linked to Unlicensed Spa’s Vampire Facial Treatments
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
Breakthrough infection cohort study of mRNA vaccination for Delta variant.
- Israel new drug for COVID-19: EXO-CD24 can reduce deaths by 50%
- COVID-19 vaccines for children under 12 will be available soon
- Breakthrough infection of Delta: No difference from regular COVID-19 cases
- French research: ADE occurred in Delta variant and many doubts on it
- The viral load of Delta variant is 1260 times the original COVID-19 strain
Breakthrough infection cohort study of mRNA vaccination for Delta variant. The Delta mutant strain of the new coronavirus is too contagious, prompting countries to adjust their epidemic prevention strategies.But accurate strategizing can only come from accurate data.
Direct comparison of vaccination or not, the condition after infection with the Delta mutant strain is the most critical factor.
Just like the current new understanding: if people who are fully vaccinated, even if they are infected with the Delta mutant, only have mild or no symptoms, then the epidemic prevention measures will focus on vaccination.
However, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of the United States will no longer concentrate on collecting breakthrough infection cases (that is, cases that are still infected with the coronavirus after full vaccination), so most of the current data in the United States are collected by statisticians from each state. Coming up. We read the data, it is very rough, and it is still difficult to establish an accurate judgment.
On July 31, 2021, the National Institute of Infectious Diseases of Singapore uploaded a blockbuster article on medRxiv, reporting the results of a real-world breakthrough infection cohort study of mRNA vaccination for the prevention of Delta mutant strains.
This report is very detailed and rigorous, and immediately received widespread attention.
In addition, Singapore’s population is mainly of Chinese descent, and the people are also highly compliant with the implementation of national orders; therefore, the epidemic prevention measures for the Chinese population may be very inspiring.
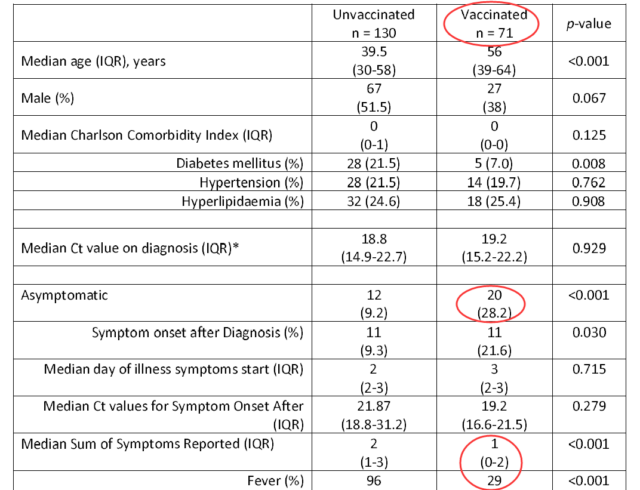
The study tracked 84 cases of breakthrough infections of Delta mutant strains after mRNA vaccination, of which 71 cases were breakthrough infections after two vaccination; and compared with 130 cases of Delta-infected patients who were not vaccinated.
First compare the severity of the disease between the two groups, showing
1) Asymptomatic infections of fully vaccinated people accounted for 28.2%, which was much higher than 9.2% of unvaccinated people.
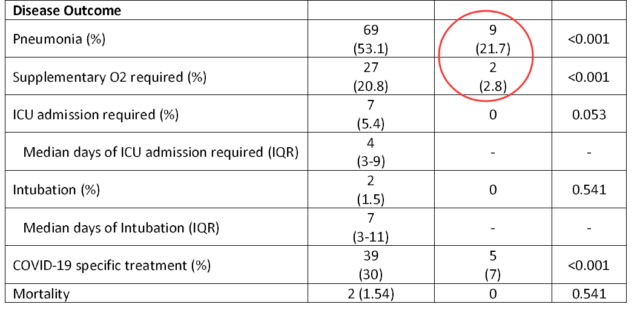
2) Pneumonia accounted for 21.7% of fully vaccinated persons, which was much lower than 53.1% of unvaccinated persons.
3) 2.8% of fully vaccinated people need oxygen inhalation, which is much lower than 20.8% of unvaccinated people; smoking is a sign of serious illness, which means that the biggest advantage of vaccination is to prevent the development of illness (reduced by 7.4 times) , And similar to the US CDC report (decreased by 8 times).
This study next compared the protective factors and risk factors of critical illness, showing
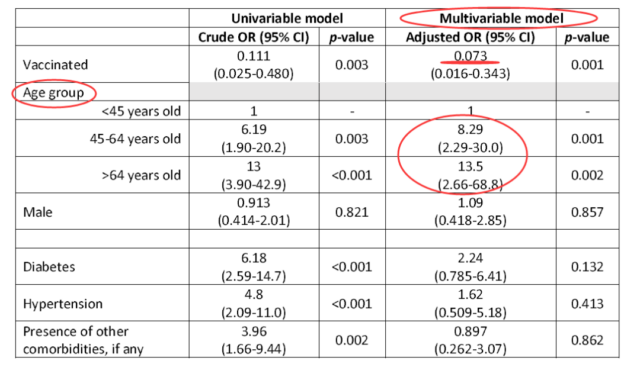
1) Studies have found that breakthrough infections after vaccination are older.
2) Compared with unvaccinated people, the proportion of vaccine breakthrough infected people who develop into severe illness requiring oxygen inhalation is only 7% of unvaccinated patients (odds ratio 0.07, p=0.001).
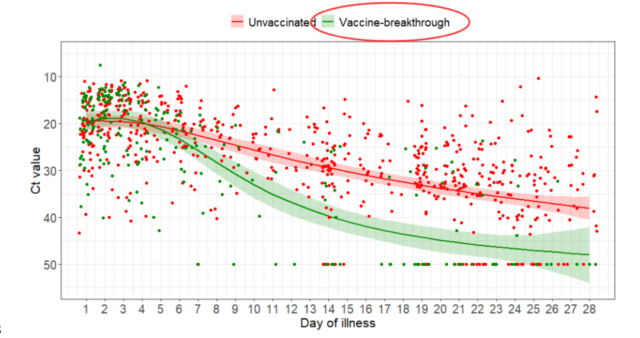
The viral load of the vaccinated persons decreased significantly faster than that of the non-vaccinated persons, which is related to the milder illness of the vaccinated persons.
However, compared with the wild-type vaccine strain, the neutralizing activity of Delta (sVNT) of the S protein antibody of patients with breakthrough infection after vaccination was significantly reduced. This is also the key reason for the repeated breakthroughs of Delta mutant strains.
The conclusion of the study:
1. The mRNA vaccine is very effective in preventing the symptomatic and severe COVID-19 associated with B.1.617.2 infection.
2. Vaccination is related to a faster decline in viral RNA load and a strong serological response.
3. Vaccination is still a key strategy to control the COVID-19 pandemic.
The clinical significance of this study:
1. It shows the strong protective power of vaccination against the development of critical illness, which is reduced by 7.4 times;
2. It shows that vaccination is the most critical protective factor for preventing the development of critical illness, and age is the most important risk factor for the development of critical illness. Therefore, focusing on protecting the elderly is the key, and the UK is already preparing to intensively vaccinate the elderly in September.
3. At the same time, it once again shows the greater risk of the Delta mutant strain for unvaccinated. Because of vaccination, a higher proportion of people infected with the Delta mutant strain are asymptomatic, and they will unknowingly infect people who have not been vaccinated.
Herd immunity is almost broken, and protection can only rely on vaccination.
The research inspiration of this research:
1. Compare between groups to find the difference between COVID-19 patients who are vaccinated or not;
2. Single-factor analysis finds the relevant factors that develop to criticality, and multi-factor analysis determines independent risk factors.
This is the most typical relevant research and analysis strategy, and it is worth learning from.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



