Why do not patients receiving CAR-T therapy increase much in United States?
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
Why do not patients receiving CAR-T therapy increase much in United States?
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Why do not patients receiving CAR-T therapy increase much in United States?
Since the popularity of cell therapy, global pharmaceutical companies have almost swarmed into this popular track.
As of April 15, 2022, there were 2,756 cell therapies in active development in the global immuno-oncology pipeline, a 36% increase from the same period in 2021.
Although compared with the past two years, the growth rate of new pipelines has slowed down slightly, but it is still considerable. Among them, many domestic pharmaceutical companies are included.
However, in sharp contrast to the hot research and development of cell therapy, its sales volume is difficult to grow, which is something that all pharmaceutical companies under research should pay attention to.
Recently, the Cancer Research Institute found that although more and more CAR-T therapies have been approved in recent years, the number of prescriptions has not increased, and the second half of 2021 is almost the same as the same period.
People must know that this is still the data of the US market, which is the super center of the global pharmaceutical market and the most supportive of innovative drugs. If there is no market in the United States, there is a high probability that other regions will not be too good.
So, why can’t CAR-T therapy be used for more patient in the United States?
Why can’t CAR-T therapy be used for more patient in the United States?
As more and more CAR-T therapies are approved, will more patients be treated with this therapy?
With this doubt in mind, Cancer Research Institute evaluated the number of patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy in clinical practice based on proprietary medical and prescription claims data from 2019-2021 provided by Aiquinwei.
Their conclusion was negative. As shown in the chart below, CAR-T prescriptions have not gradually increased in each month of 2021; in addition, prescriptions in the second half of 2021 are similar to those in the second half of 2020.
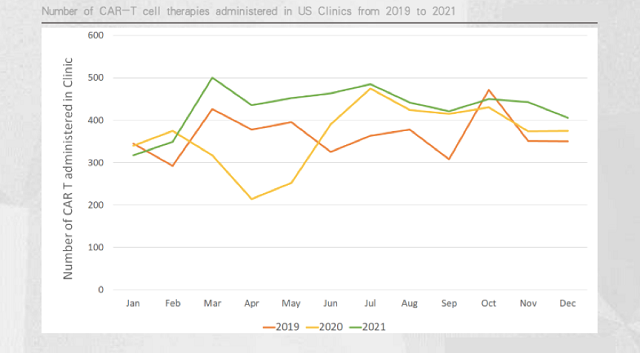
This means that even in the second half of 2021, when the epidemic eases, the monthly number of patients receiving CAR-T therapy will be similar to that in the second half of 2020.
According to the prescription volume, although the approved CAR-T therapy continues to increase, there is no obvious increase in practical application.
This can also be seen from the financial reports of various pharmaceutical companies. In 2021, Novartis’ CAR-T therapy Kymriah will earn $587 million, a year-on-year growth rate of only 22% from a small base; Gilead’s CAR-T therapy Yescarta will earn $695 million, an increase of only $132 million from 2020 Dollar.
“The use of CAR-T cell therapies in clinical practice has lagged behind the number of regulatory approvals, suggesting that there may be practical barriers to their use.” Cancer Research Institute said.
So, what are the specific obstacles? To this end, the Cancer Research Institute collected the thoughts of 100 community oncologists (who do not have facilities to perform CAR-T cell therapy) and 50 oncologists in CAR-T cell therapy specialist centers, and the truth emerged.
Constraints on the patient’s health status
Based on feedback from various sources, community oncologists and specialist center oncologists identified factors that were not exactly the same, but were broadly similar.
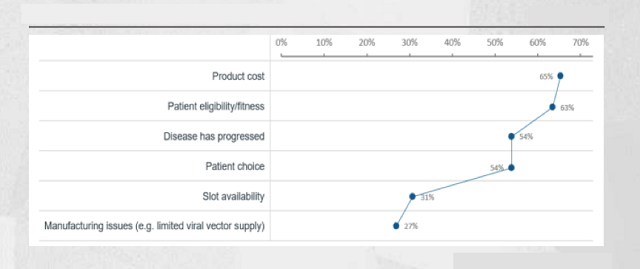
Community oncologists believe that the biggest constraint is the patient’s own health, which is the number one factor; specialist center oncologists also consider this to be one of the important constraints, with about 63% of physicians agreeing with this view.
This is probably one of the biggest bugs of autologous CAR-T products. The so-called autologous CAR-T cells are collected from the patient’s own cells. Currently, the CAR-T therapies approved worldwide are all autologous products.
However, patients may not be able to provide enough T cells due to their fitness level. Because most patients have received cytotoxic treatment such as chemotherapy before receiving CAR-T therapy, the number of T cells has decreased.
In addition, chemotherapy drugs not only affect the number of T cells in patients, but also affect the quality of T cells obtained. For example, treatment with doxorubicin, clofarabine, cyclophosphamide and cytarabine will reduce the early development of T cells. And this is closely related to the expansion of CAR-T cells.
Typically, patients undergo a series of tests and screenings to determine whether CAR-T cell therapy is an appropriate option. It is not clear what proportion of patients are not suitable for CAR-T therapy. But based on feedback from oncologists, that percentage may not be too small.
The price of treatment too expensive
In fact, patient health is the second most limiting factor for CAR-T therapy in specialist center oncologists.
65% of specialist center oncologists believe that the most important limiting factor is price. Regarding high prices, it was also recognized by 37% of community oncologists.
Indeed, looking at the CAR-T products that have been approved around the world, high price is almost their biggest feature.
The price of CAR-T products of overseas pharmaceutical companies is basically around US$400,000.
- Kymiach: about US$475K
- Yescarta: about US$373K
- Tecartus: about US$373K
- Abecma: about US$419.5K
- Breyanzi: about US$140.3K
- carvykti:: about US$465K
No way, this is the doomed result that “on-demand customization” is difficult to produce a large-scale effect.
In fact, the above prices are not all the costs that patients need to bear. Because CAR-T therapy often has a variety of side effects, additional supplies and care, and longer hospital stays.
Due to a combination of factors, the total cost of CAR-T therapy is about 1-2 times the price of the product.
The total cost of treating patients with CAR-T therapy in the United States, including the cost of the drug itself, is estimated to be between $800,000 and $1.5 million.
Although U.S. medical insurance is already very powerful, whether it is outpatient or inpatient treatment, the reimbursement for CAR-T therapy is between $400,000 and $500,000, but patients still need to pay $400,000 to $1 million for it. This is a huge expense for the vast majority of patients.
The high cost of treatment greatly limits the use of CAR-T therapy.
Limited hospitals can provide CAR-T treatment
In addition to the health status of patients and the high price of CAR-T therapy, community oncologists believe that the third factor limiting the growth of their prescriptions is the geographic distance of patients to treatment.
Not every hospital has a cell therapy center. Because CAR-T therapy is completely different from traditional treatment methods, it needs to be matched with corresponding hardware and “software”.
For example, more professional nurses are needed, not only to master the essentials of drug reinfusion, but also to master the role, side effects and complications of CAR-T care methods, so as to better care for patients.
But these investments are not cheap, so only a few hospitals have these configurations.
Cancer Research Institute specially sorted out the locations of CAR-T cell therapy centers in the United States and found that they are mainly concentrated in the more developed East and West Coast regions.
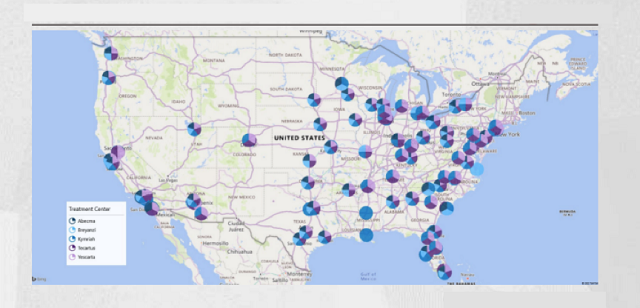
Under normal circumstances, patients are referred to these specialized institutions for treatment on the advice of local community oncologists.
However, patients treated off-site often face practical difficulties. Additional economic costs are incurred for patients, their families, and other caregivers, as well as for transportation and accommodation in cross-regional treatment.
Be aware that the risk/recovery period for patients receiving CAR T cell therapy is approximately 2-3 months.
During this period, the patient’s side effects and treatment response are also assessed. During treatment, it is not uncommon for patients to be hospitalized for complications.
That is to say, patients who are treated in other places need to be prepared to live in other places for several months. This also limits the use of patients to some extent.
Cancer patients are getting worse too fast
There are many other factors that limit the use of CAR-T therapy, according to oncologists at the Cell Therapy Specialist Center.
For example, disease progression. Due to the characteristics of customization, the preparation cycle of CAR-T cells is not short, usually 15 to 30 days, Gilead’s Yescarta takes 16-18 days, and Novartis’ Kymriah takes 22-29 days.
However, patients who use CAR-T therapy are usually in the advanced stage of cancer, and the disease progresses rapidly, and may not wait for the preparation of CAR-T cells. As a result, no matter how good CAR-T therapy is, it has no place to be used.
A total of 54% of cell therapy specialist center oncologists agreed. This is enough to prove that the impact of “disease progression” on the commercialization prospects of CAR-T therapy is not low.
In addition, insufficient “bed space” is also one of the constraints from CAR-T therapy. Thirty-five percent of oncologists noted that, even if they met the requirements, many patients still had to wait in line to receive treatment.
All in all, CAR-T is very good, but there are many factors that restrict its development.
Summary
In view of the above factors, it is difficult for the US CAR-T prescription volume to continue to grow, and it will also be a problem faced by countries and regions around the world.
Although cell therapy has been very hot in recent years, the commercialization prospects are not as optimistic as expected.
Of course, these problems are not insoluble. Whether it is the patient’s health status, the high price, or the rapid progression of the patient’s disease, all are bugs of autologous CAR-T therapy.
From the perspective of product characteristics, universal CAR-T therapy is not limited to cell sources, and has a large-scale effect, which can theoretically solve most of the obstacles.
This also means that the commercialization prospects of CAR-T therapy are expected to change due to the availability of generic products.
However, universal CAR-T therapy is still a very cutting-edge technology.
How to break through technical difficulties is something that all powerful players need to think about and solve.
Why do not patients receiving CAR-T therapy increase much in United States?
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



