Infection with Omicron does not provide cross-protection against re-infection with Delta
- WHO Releases Global Influenza Vaccine Market Study in 2024
- HIV Infections Linked to Unlicensed Spa’s Vampire Facial Treatments
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
Infection with Omicron does not provide cross-protection against re-infection with Delta
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Infection with Omicron does not provide cross-protection against re-infection with Delta.
As early as 2020, Robin J. Shattock of Imperial College London designed a self-replicating mRNA vaccine based on the Spike sequence of the original strain.
On January 14 this year, the clinical phase 1 data of the vaccine was announced, which is also the earliest clinical data on the self-replicating mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in humans .
However, Phase 1 clinical data for this vaccine have not yielded satisfactory results, failing to achieve a 100% seroconversion rate.
On May 20, 2022, Robin J. Shattock uploaded an article on BioRxiv : Omicron breakthrough infections in vaccinated or previously infected hamsters , they found that neither Omicron nor Delta infection could provide cross protection against each other’s re-infection .
In layman’s terms, people who have been infected with Delta may also be infected with Omicron again, and people who have been infected with Omicron are also at risk of being infected with Delta again.
They used a hamster contact infection model to assess the protective efficacy of the vaccine and previous infection against reinfection.
The so-called hamster contact infection model is to directly infect the donor hamster with the virus, and then rear the donor hamster carrying the virus and the guard hamster ( vaccinated or previously infected with the virus ), observe the guard hamster infection with the virus, and analyze the serum antibodies. Viral load, weight changes, etc.
First, they found that 2 doses of a self-replicating mRNA vaccine based on the original Spike sequence improved the degree of weight loss in mice infected with Delta and reduced viral load in the turbinates, but did not respond to breakthrough infection with Omicron/BA.1. effect .
Two weeks after inoculation with two doses of self-replicating mRNA vaccine, serum was collected and it was found that serum neutralizing antibody titers targeting Delta were reduced by 2 times compared with neutralizing antibody titers targeting wild-type/D614G in serum, targeting Omicron Serum neutralizing antibody titers decreased 13-fold.
In sera of mice vaccinated and developed breakthrough infection with BA.1, neutralizing antibody titers against BA.1/BA.2 were only 2.1/2.6-fold lower than WT/Delta.
The sera of vaccinated and Delta breakthrough-infected mice had 6.7-fold lower neutralizing antibody titers to BA.1 than wild-type, and only 2.2-fold lower neutralizing antibody titers to BA.2 than wild-type.
This suggests that Delta breakthrough infection may provide cross-protection to BA.2 but not BA.1 after vaccination.
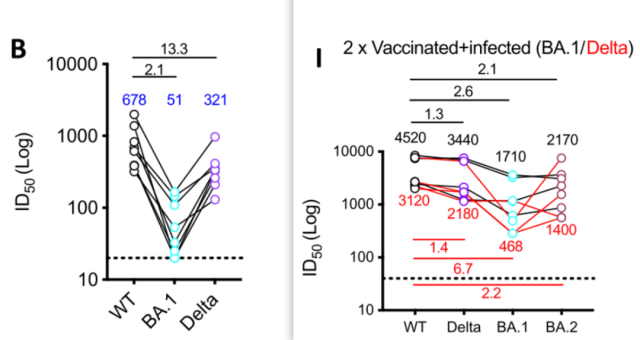
Effects of vaccination/breakthrough infection on serum neutralizing antibody titers.
In a hamster contact infection model, they then found that BA.1 was able to escape the immune protection in mice previously infected with an early variant of the new coronavirus .
Infection with WT/D614G or Alpha could provide partial protection against Omicron/BA.1 infection, but infection with Delta could not provide protection against Omicron/BA.1.
It is very interesting that they want to further see if infection with Omicron/BA.1 can prevent re-infection with Delta/BA.2? It was found that in the hamster contact infection model, infection with Omicron/BA.1 could prevent the re-infection of BA.2, but could not prevent the re-infection of Delta.
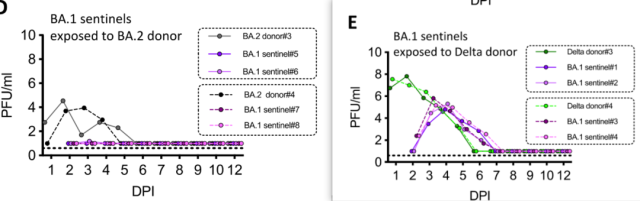 Hamsters infected with BA.1 were reinfected with Delta, but not with BA.2.
Hamsters infected with BA.1 were reinfected with Delta, but not with BA.2.
Finally, they analyzed the serum neutralizing antibodies of people infected with various new coronavirus variants 13-24 days after symptoms began to appear:
First, it was found that the sera of all infected people had the highest neutralizing activity against the infected homologous strain, For other mutants, the serum cross-neutralization ability was always lower than that of the homologous strain .
Second, WT/D614G, Alpha or Delta infected sera had the lowest BA.1 neutralization ability. Compared with the neutralization ability of sera to homologous strains, the neutralization ability of Delta-infected sera to BA.1 was significantly reduced by 120 times; the neutralization ability of WT/D614G-infected sera to BA.1 was significantly reduced by 128.5 times. ;
Alpha-infected serum had a 60-fold decrease in the neutralizing ability of BA.1. Finally, they also found that the neutralization ability of Omicron/BA.1 infected sera was 23-fold lower for Delta and 15.3-fold lower for BA.2 compared to the neutralization ability of serum against homologous strains. times.
The above data show that there is a very obvious gap between the epitope distance between Omicorn and the early COVID-19 variant, as well as the epitope distance between BA.1 and BA.2.
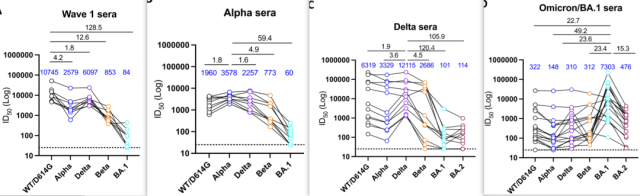 The neutralization ability of sera from patients infected with different new coronavirus variant strains is different for different variant strains.
The neutralization ability of sera from patients infected with different new coronavirus variant strains is different for different variant strains.
In addition, they found that the vaccinated population with breakthrough infection produced higher serum antibody titers than the vaccinated population, and exhibited a broader neutralization capacity.
The neutralizing antibody titers of sera against BA.1/BA.2 were only 3.5/3.7-fold lower than those against Delta when vaccine recipients developed Dela infection.
Surprisingly, the sera of vaccinees infected with BA.1 had the lowest serum neutralizing antibody titers to BA.2.
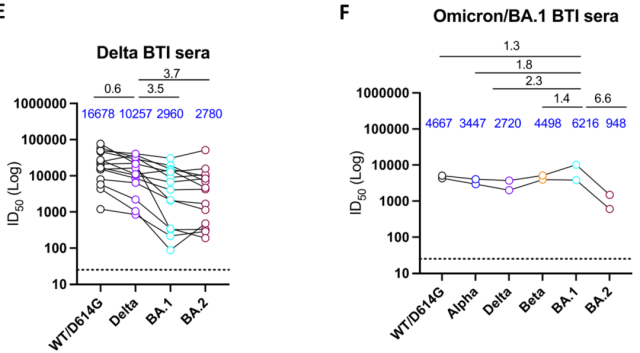 Neutralizing antibody titers of sera against various mutant strains after breakthrough infection in 2019-nCoV vaccine recipients.
Neutralizing antibody titers of sera against various mutant strains after breakthrough infection in 2019-nCoV vaccine recipients.
In conclusion, through this article, we can draw the conclusion that if only infected with BA.1 or only vaccinated with BA.1-specific vaccines, it is very easy to infect Dleta or a variant derived from Delta in the future.
Vaccination or repeated infection of mutant antigens or strains with very different antigenic epitopes will lead to serum with a wider spectrum of neutralizing ability, which is of great reference significance for the design of COVID-19 mRNA multivalent vaccines.
Infection with Omicron does not provide cross-protection against re-infection with Delta.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



