Tilelizumab chemotherapy: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
Tilelizumab chemotherapy: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Tilelizumab chemotherapy: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Tilelizumab combined with chemotherapy: patients with stage IVA esophageal squamous cell carcinoma achieve PR after 6 cycles.
Case: It is a successful attempt to use Tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of advanced esophageal cancer.
Before the advent of immunotherapy, the treatment of advanced esophageal cancer was based on systemic chemotherapy, with limited efficacy and huge unmet clinical needs.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have changed the treatment pattern of advanced esophageal cancer.
At present, the second-line indication for immunotherapy for esophageal cancer has been approved. In the first-line aspect, the results of the study of Tislelizumab RATIONALE 205 were announced by ESMO Asia last year and officially published in Clinical Cancer Research in June this year.
This study is also the world’s first Announced exploratory study of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
At the same time, it is understood that the results of phase III studies have confirmed that the combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy for advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma can achieve the dual primary endpoint of OS and PFS.
In this context, in this issue we will share a case of Tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy to help patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma achieve PR, fully demonstrating the effectiveness of Tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of advanced esophageal cancer Efficacy, looking forward to providing new ideas for clinical diagnosis and treatment!
Basic situation
General information: male patient, 60 years old. Progressive dysphagia for more than 3 months.
History of present illness: In April 2020, he went to our hospital for “progressive dysphagia for more than 3 months”. Before admission, the patient underwent gastroscopy in the branch of Pingtan Xiehe Hospital in Fujian Province: (about 35-40 cm from the incisor) the lumen was narrow and rigid; pathology (S20201900): squamous cell carcinoma. Pathology consultation in our hospital: (esophageal biopsy) squamous cell carcinoma.
2020-4-18 chest CT showed: 1. Consider the lower thoracic and abdominal esophageal cancer and mediastinal lymph node metastasis, involving the gastric cardia; 2. Please follow up the left clavicular lymph node.
Enhanced CT of the upper abdomen: Consider multiple lymph node metastases involving the lesser curvature of the stomach and retroperitoneum. Esophageal angiography: consider the lower esophagus cancer involving the cardia.
Diagnosis
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lower thoracic segment of the esophagus involves the cardia, metastasis of retroperitoneal lymph nodes in the mediastinal gastric curvature involves the wall of the gastric curvature, cT4N3M0 IVA stage
Treatment history and efficacy evaluation
From April 22, 2020 to August 20, 2020: The first-line treatment of “paclitaxel 270mg + oxaliplatin 200mg + Tislelizumab 200mg” was performed for 6 cycles, and the process went smoothly.
Efficacy evaluation: PR efficacy evaluation, no adverse reactions related to immunotherapy were found.
After 2 cycles of treatment, the patient’s dysphagia symptoms were relieved. 2, 4 cycles of re-examination CT: lower thoracic and abdominal esophageal cancer and mediastinal lymph node metastasis involving gastric cardia was significantly smaller than before, and multiple lymph node metastases involving the lesser curvature of the stomach and retroperitoneum were significantly shrinking than the front.
The follow-up plan is submitted to our hospital for esophageal cancer MDT to discuss and plan the next operation or local radiotherapy.
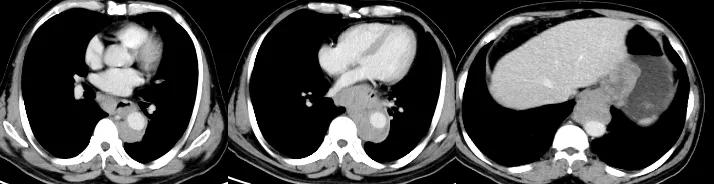
Pre-treatment imaging of Tislelizumab + chemotherapy
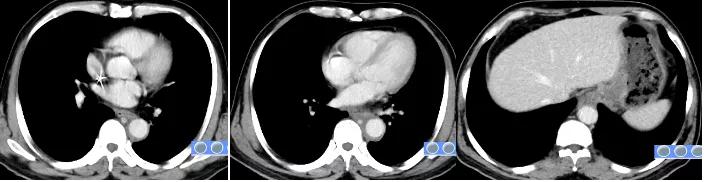
Image after 2 cycles of Tislelizumab + chemotherapy combined treatment
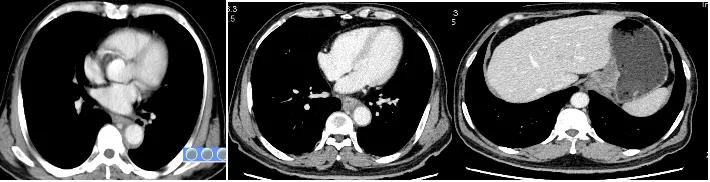
Image after 4 cycles of Tislelizumab+chemotherapy
Case summary
This patient has advanced esophageal cancer with long esophageal lesions, involving the cardia and lesser curvature of the stomach, mediastinal lymph nodes, lesser gastric curvature lymph nodes, and retroperitoneal lymph nodes with extensive metastasis.
Tilelizumab combined with paclitaxel and oxaliplatin was treated as the first line , Has obtained very good curative effect, the tumor recedes quickly, the clinical symptoms are quickly relieved, the curative effect is evaluated for PR, and the treatment is well tolerated, and there is no immunotherapy-related adverse reaction.
Currently, only the local residual gastric curvature is planned. A comprehensive review is planned in the near future.
Assess the tumor condition, and submit the esophageal cancer MDT to our hospital to discuss the feasibility of the next local treatment, and continue the systemic maintenance treatment with Tislelizumab.
This case is a successful attempt to use Tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of advanced esophageal cancer. Following the breakthrough results of the RATIONALE 205 study,
Tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy as the first-line treatment for patients with unresectable, locally advanced recurrent or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma phase III global multicenter study (RATIONALE 306 study) It is proceeding smoothly, and it is hoped that this study will achieve positive results and bring more benefits to Chinese patients with advanced esophageal cancer.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



